Cell_Transport_Notes_2013
... •Salt water fish pump salt out of their specialized gills so they do not dehydrate. •Animal cells are bathed in blood. Kidneys keep the blood isotonic by remove excess salt and water. ...
... •Salt water fish pump salt out of their specialized gills so they do not dehydrate. •Animal cells are bathed in blood. Kidneys keep the blood isotonic by remove excess salt and water. ...
A. diffuser
... 9. Why is it able to pass through the plastic bag? A. It is a sneaky molecule B. It is a large molecule that can push through the pores C. It is a small enough molecule to move freely through pores 10. All of the following are kinds of passive transport EXCEPT A. diffusion B. facilitated diffusion ...
... 9. Why is it able to pass through the plastic bag? A. It is a sneaky molecule B. It is a large molecule that can push through the pores C. It is a small enough molecule to move freely through pores 10. All of the following are kinds of passive transport EXCEPT A. diffusion B. facilitated diffusion ...
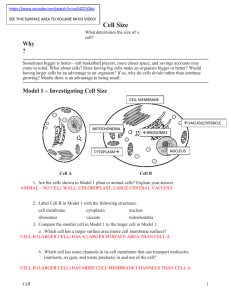
Model 1 – Investigating Cell Size
... SHEET-LIKE SHAPE WITH LARGE SURFACE AREA *skin cells (epithelium—think of those thin, thin cheek cells that occur in layers…) e. Importing large quantities of material for transfer to other cells. ANY OF THE SMALL, SYMMETRICAL SHAPES FOR MAXIMUM SURFACE AREA TO VOLUME RATIO 18. Among unicellular euk ...
... SHEET-LIKE SHAPE WITH LARGE SURFACE AREA *skin cells (epithelium—think of those thin, thin cheek cells that occur in layers…) e. Importing large quantities of material for transfer to other cells. ANY OF THE SMALL, SYMMETRICAL SHAPES FOR MAXIMUM SURFACE AREA TO VOLUME RATIO 18. Among unicellular euk ...
Cellular Transport Powerpoint
... -The diffusion of water is given its own name, osmosis, because water is such an important substance for all living organism. ...
... -The diffusion of water is given its own name, osmosis, because water is such an important substance for all living organism. ...
WALL PROJECTIONS IN THE SPOROPHYTE AND
... acetone series and embedded in Epon 812 (6) . Sections cut on a Porter-Blum MT-2 microtome were stained with uranyl magnesium acetate (2) for 10 min and lead citrate (10) for 5 min and were examined with an RCA EMU-3H electron microscope . Material for light microscopy was fixed in FAA (forinalin, a ...
... acetone series and embedded in Epon 812 (6) . Sections cut on a Porter-Blum MT-2 microtome were stained with uranyl magnesium acetate (2) for 10 min and lead citrate (10) for 5 min and were examined with an RCA EMU-3H electron microscope . Material for light microscopy was fixed in FAA (forinalin, a ...
Cell Membrane Transport
... Cell Membrane - Function - Endocytosis In this process the membrane itself wraps around the particle and pinches off a vesicle inside the cell. ...
... Cell Membrane - Function - Endocytosis In this process the membrane itself wraps around the particle and pinches off a vesicle inside the cell. ...
Microbial Cell Surfaces and Secretion Systems
... and proteins involved in cell-wall synthesis, including two chitin synthases, one 1,3-β-d-glucan synthase, and three glucan elongases. ...
... and proteins involved in cell-wall synthesis, including two chitin synthases, one 1,3-β-d-glucan synthase, and three glucan elongases. ...
Unit I - Biological Classification
... ∗ Chromatophores are one to many and present in the peripheral cytoplasm. These are discoid and have few isolated lamellae with or without pyrenoids that lack starch. They have chlorophyll a and c, Lutein, Fucoxanthin and β-carotene. ∗ Reserve food is usually oil stored in the cytoplasm nearer to th ...
... ∗ Chromatophores are one to many and present in the peripheral cytoplasm. These are discoid and have few isolated lamellae with or without pyrenoids that lack starch. They have chlorophyll a and c, Lutein, Fucoxanthin and β-carotene. ∗ Reserve food is usually oil stored in the cytoplasm nearer to th ...
cytology_osmosis and..
... some to pass through the pores; this will happen more often on the side with more molecules. The dye diffuses from where it is more concentrated to where it is less concentrated (called diffusing down a concentration gradient). This leads to a dynamic equilibrium: The solute molecules continue to cr ...
... some to pass through the pores; this will happen more often on the side with more molecules. The dye diffuses from where it is more concentrated to where it is less concentrated (called diffusing down a concentration gradient). This leads to a dynamic equilibrium: The solute molecules continue to cr ...
3.1 Cell Theory Early studies led to the development of the cell theory.
... Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. • The Cell theory has three principles. – All organisms are made of cells. – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. – The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
... Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. • The Cell theory has three principles. – All organisms are made of cells. – All existing cells are produced by other living cells. – The cell is the most basic unit of life. ...
CellCycle_Mitosis
... All special cells originally come from stem cells that came from egg cells that came from our parent cells. Babies are made from cells from parents! ...
... All special cells originally come from stem cells that came from egg cells that came from our parent cells. Babies are made from cells from parents! ...
Cells & Their Environment
... • ✔I can – predict the direction of substance movement into and out of the cells in terms of diffusion • 1) Grab an index card. • 2) Write a description of your movement. Use the new terms you just learned such as – diffusion, high to low concentration, concentration gradient, and equilibrium • 3) S ...
... • ✔I can – predict the direction of substance movement into and out of the cells in terms of diffusion • 1) Grab an index card. • 2) Write a description of your movement. Use the new terms you just learned such as – diffusion, high to low concentration, concentration gradient, and equilibrium • 3) S ...
Cell Structure & Function Tissues
... • All cells are surrounded by a thin, outer membrane called the plasma membrane (PM). – This separates the cell from interstitial fluid which bathes the outside of the cell. • On the inside of the cell is a gel-like fluid called cytoplasm. This contains specialized structures called organelles and t ...
... • All cells are surrounded by a thin, outer membrane called the plasma membrane (PM). – This separates the cell from interstitial fluid which bathes the outside of the cell. • On the inside of the cell is a gel-like fluid called cytoplasm. This contains specialized structures called organelles and t ...
Chapter 4 Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... the center for the synthesis of ribosomal RNA, are present. DNA is combined with protein histones and nonhistones. The combination is called a nucleosome. When the cell is not reproducing, DNA and associated proteins are visible as a mass called chromatin. When reproducing, chromatin becomes visible ...
... the center for the synthesis of ribosomal RNA, are present. DNA is combined with protein histones and nonhistones. The combination is called a nucleosome. When the cell is not reproducing, DNA and associated proteins are visible as a mass called chromatin. When reproducing, chromatin becomes visible ...
2014073149hortplantcellsandfunctions
... •Is the smallest unit of all living organisms •Are the building blocks responsible for life ...
... •Is the smallest unit of all living organisms •Are the building blocks responsible for life ...
Slide 1
... Staining • Those that resist decolorization by 95% ethanol are arbitrarily termed Gram positive and those that do not are Gram negative • (the terms positive and negative have nothing to do with charges • of the cell but based on differences in the cell wall structure of • these two groups of bacter ...
... Staining • Those that resist decolorization by 95% ethanol are arbitrarily termed Gram positive and those that do not are Gram negative • (the terms positive and negative have nothing to do with charges • of the cell but based on differences in the cell wall structure of • these two groups of bacter ...
This is Jeopardy
... Using an ATP-driven membrane protein to “pump” molecules against a concentration gradient is an example of: Molecular Active Transport ...
... Using an ATP-driven membrane protein to “pump” molecules against a concentration gradient is an example of: Molecular Active Transport ...
cell structure and function
... and in many cells a cytoskeleton. Some bacterial cells produce internal, resistant, dormant forms called endospores. Endospores can survive under harsh conditions, making them a concern to food processors and health care professionals. • The liquid portion of the cytoplasm is called cytosol. It is m ...
... and in many cells a cytoskeleton. Some bacterial cells produce internal, resistant, dormant forms called endospores. Endospores can survive under harsh conditions, making them a concern to food processors and health care professionals. • The liquid portion of the cytoplasm is called cytosol. It is m ...
Cell wall
The cell wall is a tough, flexible and sometimes rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It surrounds the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection. In addition, the cell wall acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to act as a pressure vessel, preventing over-expansion when water enters the cell. Cell walls are found in plants, fungi and prokaryotic cells but not in mycoplasmas.The composition of the cell wall varies between species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin. In bacteria, peptidoglycan forms the cell wall. Archaean cell walls have various compositions, and may be formed of glycoprotein S-layers, pseudopeptidoglycan, or polysaccharides. Fungi possess cell walls made of the glucosamine polymer chitin, and algae typically possess walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides. Unusually, diatoms have a cell wall composed of biogenic silica. Often, other accessory molecules are found anchored to the cell wall.