PSF - ESO
... Each program has its own method - sometimes several methods – of performing this, but the basic idea is to produce an initial list of approximate centroid positions for all stars that can be distinguished in the two dimensional data array. The star finder must have at least some ability to tell the ...
... Each program has its own method - sometimes several methods – of performing this, but the basic idea is to produce an initial list of approximate centroid positions for all stars that can be distinguished in the two dimensional data array. The star finder must have at least some ability to tell the ...
The Effect of Stacking Multiple Sub
... extra number to stack is dependent not only on the proportions of the noise sources but also on the ratio of TL to TS: there are gains to be had from making the sub exposure period as long as conveniently possible, usually limited by tracking errors or saturation of brighter parts of the image. To h ...
... extra number to stack is dependent not only on the proportions of the noise sources but also on the ratio of TL to TS: there are gains to be had from making the sub exposure period as long as conveniently possible, usually limited by tracking errors or saturation of brighter parts of the image. To h ...
Death by Black Hole Study Guide-Answers - crespiphysics
... Venus has phases; Jupiter has 4 large moons that orbit it 4. Describe how Harlow Shapely used the distribution of globular clusters to determine we were not at the center of the Milky Way (or universe). He observed they were not evenly distributed in the sky 5. In 1923, how did Edwin Hubble determin ...
... Venus has phases; Jupiter has 4 large moons that orbit it 4. Describe how Harlow Shapely used the distribution of globular clusters to determine we were not at the center of the Milky Way (or universe). He observed they were not evenly distributed in the sky 5. In 1923, how did Edwin Hubble determin ...
bildsten
... Highlights so Far • Acoustic waves seen in nearly all evolved stars with amplitudes of 3-200 parts per million. • Measured frequency spacing and maximum observed frequency give R, M and D for >10,000 stars across the galaxy. Great test for GAIA and new galactic science enabled. • Useful diagnostics ...
... Highlights so Far • Acoustic waves seen in nearly all evolved stars with amplitudes of 3-200 parts per million. • Measured frequency spacing and maximum observed frequency give R, M and D for >10,000 stars across the galaxy. Great test for GAIA and new galactic science enabled. • Useful diagnostics ...
PPT
... There must be some very large distance such that light from a galaxy at that distance hasn’t reached us during the age of the universe. The expansion velocity of galaxies at that distance, relative to us, must be a) zero b) infinite c) less than the speed of light d) the speed of light or greater Pa ...
... There must be some very large distance such that light from a galaxy at that distance hasn’t reached us during the age of the universe. The expansion velocity of galaxies at that distance, relative to us, must be a) zero b) infinite c) less than the speed of light d) the speed of light or greater Pa ...
February 13
... Radiative zone – inner 71 percent of the Sun’s Interior were all atoms are ionized. Takes a photon 170,000 years to reach the convective zone. Each time a photon is absorbed ...
... Radiative zone – inner 71 percent of the Sun’s Interior were all atoms are ionized. Takes a photon 170,000 years to reach the convective zone. Each time a photon is absorbed ...
Lect15-3-23-11-stars..
... space essentially all of the heat generated from gravitational potential energy release, its surface temperature warms only slightly. However, as the collapse proceeds, the surface area of the cloud is diminished,, so that its luminosityy is diminished accordingly. This stage lasts only a few millio ...
... space essentially all of the heat generated from gravitational potential energy release, its surface temperature warms only slightly. However, as the collapse proceeds, the surface area of the cloud is diminished,, so that its luminosityy is diminished accordingly. This stage lasts only a few millio ...
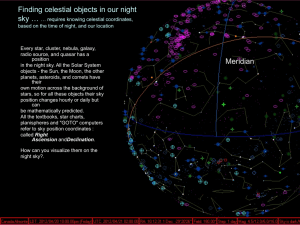
Local Horizon View
... of sky is facing north, stars rise in the east (on your right) and set in the west (on your left). Everything on your Meridian has therefore reached its HIGHEST point in the sky tonight, and is therefore at its best for viewing since it is as far as it can be away from the (murky) horizons. Observer ...
... of sky is facing north, stars rise in the east (on your right) and set in the west (on your left). Everything on your Meridian has therefore reached its HIGHEST point in the sky tonight, and is therefore at its best for viewing since it is as far as it can be away from the (murky) horizons. Observer ...
Word - El Camino College
... The image is in near-infrared, just outside the human range of vision. This is a good place to hunt for young planets, because for millions of years after they are formed, planets are hot and glow in the infrared, while stars like the Sun are faint in the IR. Well, relatively faint; they still pour ...
... The image is in near-infrared, just outside the human range of vision. This is a good place to hunt for young planets, because for millions of years after they are formed, planets are hot and glow in the infrared, while stars like the Sun are faint in the IR. Well, relatively faint; they still pour ...
Neither Star nor Trigram - 5 Yellow Focus of Attention
... If not you saw mutual understanding between Stars, this may not be to account of the Wuxing ‘controlling cycle’, but Stars not ‘at ease’ due to just lack of affinity, as one Star could innately come under forces of expansion, the other Star under forces of contraction. In fact, as we saw 5 Yellow to ...
... If not you saw mutual understanding between Stars, this may not be to account of the Wuxing ‘controlling cycle’, but Stars not ‘at ease’ due to just lack of affinity, as one Star could innately come under forces of expansion, the other Star under forces of contraction. In fact, as we saw 5 Yellow to ...
Astronomy Triemester Review Sheet 2015
... 2. Describe how a shadow changes position and shape as the Sun moves across the daytime sky. 3. Are celestial objects like stars and planets in the daytime sky? 4. What is the relationship between latitude and the angular height of the Sun? 5. Explain how angular height of the Sun in different parts ...
... 2. Describe how a shadow changes position and shape as the Sun moves across the daytime sky. 3. Are celestial objects like stars and planets in the daytime sky? 4. What is the relationship between latitude and the angular height of the Sun? 5. Explain how angular height of the Sun in different parts ...
Answer
... temperature? The dominant type of fusion has changed. The core of the star has collapsed under gravity as there is no longer an outward pressure from the radiation to create balanced forces. This collapse causes the temperature to suddenly increase. The outer layer of the star expands to a Red Giant ...
... temperature? The dominant type of fusion has changed. The core of the star has collapsed under gravity as there is no longer an outward pressure from the radiation to create balanced forces. This collapse causes the temperature to suddenly increase. The outer layer of the star expands to a Red Giant ...
Comet Catalina 2016 - Fraser Heights Chess Club
... Comets formed at the same time our solar system did, 4.6 billion years ago, perhaps even in among the planets. By examining them up close with satellites and landers, scientists hope to learn more about what our Solar System looked like in its earliest days. ...
... Comets formed at the same time our solar system did, 4.6 billion years ago, perhaps even in among the planets. By examining them up close with satellites and landers, scientists hope to learn more about what our Solar System looked like in its earliest days. ...
Chapter 16 Star Birth Where do stars form? Star
... Mass of a Star-Forming Cloud • A typical molecular cloud (T~ 30 K, n ~ 300 particles/cm3) must contain at least a few hundred solar masses for gravity to overcome pressure • Emission lines from molecules in a cloud can prevent a pressure buildup by converting thermal energy into infrared and radio p ...
... Mass of a Star-Forming Cloud • A typical molecular cloud (T~ 30 K, n ~ 300 particles/cm3) must contain at least a few hundred solar masses for gravity to overcome pressure • Emission lines from molecules in a cloud can prevent a pressure buildup by converting thermal energy into infrared and radio p ...
Chapter 16 Star Birth
... • Contraction must continue until the core becomes hot enough for nuclear fusion • Contraction stops when the energy released by core fusion balances energy radiated from the surface—the star is now a main-sequence star ...
... • Contraction must continue until the core becomes hot enough for nuclear fusion • Contraction stops when the energy released by core fusion balances energy radiated from the surface—the star is now a main-sequence star ...
Chapter 20: Stellar Evolution: The Death of Stars PowerPoint
... Low-Mass Stars End As White Dwarfs • UV radiation ionizes the expanding gas shell – This glows in what we see as a planetary nebula • Name given because they look somewhat like planets • No suggestion that they have, had, or will form planets ...
... Low-Mass Stars End As White Dwarfs • UV radiation ionizes the expanding gas shell – This glows in what we see as a planetary nebula • Name given because they look somewhat like planets • No suggestion that they have, had, or will form planets ...
talk.wyse - Johns Hopkins University
... Little evolution in dark matter profile in models of dwarf spheroidals Read et al 2006 A, B denote star-formation prescriptions; B includes feedback from supernovae `weak’ wind has average speed 222km/s Dark solid line is dark-matter only simulation 108 M ...
... Little evolution in dark matter profile in models of dwarf spheroidals Read et al 2006 A, B denote star-formation prescriptions; B includes feedback from supernovae `weak’ wind has average speed 222km/s Dark solid line is dark-matter only simulation 108 M ...
What is the minimum size of a star that will go supernova? A. Half
... A. Very polite motion from a star B. Angular change in position by a star as seen from Earth C. The correct motion of a star Answer: B. The angular change in position by a star as seen from Earth. Stars appear to have fixed positions on the sky. That’s one reason why the constellations are ...
... A. Very polite motion from a star B. Angular change in position by a star as seen from Earth C. The correct motion of a star Answer: B. The angular change in position by a star as seen from Earth. Stars appear to have fixed positions on the sky. That’s one reason why the constellations are ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.