The Essential Cosmic Perspective, 6e
... percent of this material into heavier elements, including all the elements of which we and Earth are made. Stars expel this material through winds and explosions, and the galaxy recycles it into new generations of stars. When a new star system forms, it therefore contains the ingredients needed to m ...
... percent of this material into heavier elements, including all the elements of which we and Earth are made. Stars expel this material through winds and explosions, and the galaxy recycles it into new generations of stars. When a new star system forms, it therefore contains the ingredients needed to m ...
ISP205L Spring 2006 Supplementary Instructions for SkyGazer Homework Assignments
... sky that are due to the various motions of the Earth. But the stars themselves, including our Sun, are moving through our Galaxy, all with slightly different motions from each other. This causes the positions of the stars as seen on the sky to gradually change with respect to each other. This is cal ...
... sky that are due to the various motions of the Earth. But the stars themselves, including our Sun, are moving through our Galaxy, all with slightly different motions from each other. This causes the positions of the stars as seen on the sky to gradually change with respect to each other. This is cal ...
Deriving the Isoradius Lines (optional, mathematical
... c) Draw in an arrow showing the direction of increasing radius on the diagram. (hint: this must be perpendicular to the isoradius lines.) d) Draw in an arrow showing the direction of increasing mass for main sequence stars on the diagram. (Note that his arrow only applies to main sequence stars, but ...
... c) Draw in an arrow showing the direction of increasing radius on the diagram. (hint: this must be perpendicular to the isoradius lines.) d) Draw in an arrow showing the direction of increasing mass for main sequence stars on the diagram. (Note that his arrow only applies to main sequence stars, but ...
Star formation and internal kinematics of irregular galaxies
... (a few times) the local scale height. In most cases this is a few hundred parsecs. This is the picture that I will proceed with in this thesis; that star formation is a local process, with the same basic physics occuring in independent cells with dimensions between tens of parsecs and a couple of ki ...
... (a few times) the local scale height. In most cases this is a few hundred parsecs. This is the picture that I will proceed with in this thesis; that star formation is a local process, with the same basic physics occuring in independent cells with dimensions between tens of parsecs and a couple of ki ...
11 Stellar Remnants - Journigan-wiki
... In searching for an explanation, astronomers began to take a new look at Fritz and Zwicky’s 30 year old ideas about neutron stars. It was Italian astronomer Franco Pacini that linked the super dense neutron star idea with the rapidly pulsating radio signals by proposing that the stars didn’t actuall ...
... In searching for an explanation, astronomers began to take a new look at Fritz and Zwicky’s 30 year old ideas about neutron stars. It was Italian astronomer Franco Pacini that linked the super dense neutron star idea with the rapidly pulsating radio signals by proposing that the stars didn’t actuall ...
Feb 2015 - Bays Mountain Park
... start of the month. Four weeks later it will come up a little after midnight. The best time to view is probably before dawn. Its +0.5 magnitude and 16″ diameter makes it very visible just above the three bright stars that make up the “head” of Scorpius. An added bonus is that the rings are tilted at ...
... start of the month. Four weeks later it will come up a little after midnight. The best time to view is probably before dawn. Its +0.5 magnitude and 16″ diameter makes it very visible just above the three bright stars that make up the “head” of Scorpius. An added bonus is that the rings are tilted at ...
Chapter 20
... Because a thick disk of cool gas and dust surrounds the premainsequence star, the gas squirts outward along the pre-main-sequence star’s axis of rotation at speeds of perhaps 1 million km /hr. HH–1 and HH–2 (see figure) are more irregular in shape than many other Herbig-Haro objects, perhaps because ...
... Because a thick disk of cool gas and dust surrounds the premainsequence star, the gas squirts outward along the pre-main-sequence star’s axis of rotation at speeds of perhaps 1 million km /hr. HH–1 and HH–2 (see figure) are more irregular in shape than many other Herbig-Haro objects, perhaps because ...
Final Review Sheet
... in the future. Its radius is gradually increasing, but it is getting denser in its center. V. Post Main Sequence Evolution of Stars Lighter than 8 Msun Hydrogen fuel exhausted in inner 10 - 15% of mass. Helium core contracts and grows hotter. Hydrogen continues to burn in an overlying shell that is ...
... in the future. Its radius is gradually increasing, but it is getting denser in its center. V. Post Main Sequence Evolution of Stars Lighter than 8 Msun Hydrogen fuel exhausted in inner 10 - 15% of mass. Helium core contracts and grows hotter. Hydrogen continues to burn in an overlying shell that is ...
Killer Skies
... known as the Crab Nebula. The Crab Nebula is called so for its many-legged shape. The ‘legs’ are filaments of gas that are moving away from the site of the explosion at about 1,400 km/s. Comparing the nebula’s radius, 1.35 pc, with its velocity of expansion reveals that the nebula began expanding ni ...
... known as the Crab Nebula. The Crab Nebula is called so for its many-legged shape. The ‘legs’ are filaments of gas that are moving away from the site of the explosion at about 1,400 km/s. Comparing the nebula’s radius, 1.35 pc, with its velocity of expansion reveals that the nebula began expanding ni ...
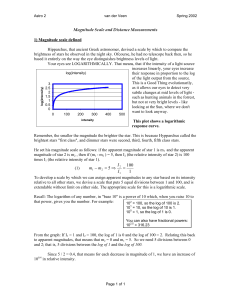
Magnitude Scale and Distance Measurements
... subtle changes at mid levels of light 1.5 such as hunting animals in the forrest, ...
... subtle changes at mid levels of light 1.5 such as hunting animals in the forrest, ...
PC3692: Physics of Stellar Structure (and Evolution)
... One striking feature is there is a sequence of stars running from the top left to the bottom right. This sequence is called main sequence. You also see a clump of to the right of the main sequence, these stars are called red clump stars, and the stars further to the right, red giants. You can also v ...
... One striking feature is there is a sequence of stars running from the top left to the bottom right. This sequence is called main sequence. You also see a clump of to the right of the main sequence, these stars are called red clump stars, and the stars further to the right, red giants. You can also v ...
Local group
... IR, x-ray sources and even g-rays – wider sample of universe than MW (e.g. range of metallicities, star formation rate etc etc) to be studied in detail ...
... IR, x-ray sources and even g-rays – wider sample of universe than MW (e.g. range of metallicities, star formation rate etc etc) to be studied in detail ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1
... compact, these regions spin and shrink and begin to form a flattened disk. The disk has a central concentration of matter called a protostar. • The protostar continues to contract and increase in temperature for several million years. Eventually the gas in the region becomes so hot that its electron ...
... compact, these regions spin and shrink and begin to form a flattened disk. The disk has a central concentration of matter called a protostar. • The protostar continues to contract and increase in temperature for several million years. Eventually the gas in the region becomes so hot that its electron ...
mass loss of massive stars - of /proceedings
... Stars more massive than 25 M (et solar metallicity) end their lives as Wolf-Rayet stars (WR). The WR phase takes up to 5% of the star’s lifetime. Typically, a 40 M star will spend 0.2 Myr as a WR for a total lifetime of 5 Myr. During that phase, Wolf-Rayet stars have strong stellar winds character ...
... Stars more massive than 25 M (et solar metallicity) end their lives as Wolf-Rayet stars (WR). The WR phase takes up to 5% of the star’s lifetime. Typically, a 40 M star will spend 0.2 Myr as a WR for a total lifetime of 5 Myr. During that phase, Wolf-Rayet stars have strong stellar winds character ...
Lesson 3: Calculating distances to stars
... 1. The trigonometric parallax can be used to calculate the distance to nearby stars. 2. The parallax angle is the angle that a star is observed to make, compared to the background stars, due to the movement of the Earth around the Sun. 3. A star that has a parallax angle of 1 arc second has a distan ...
... 1. The trigonometric parallax can be used to calculate the distance to nearby stars. 2. The parallax angle is the angle that a star is observed to make, compared to the background stars, due to the movement of the Earth around the Sun. 3. A star that has a parallax angle of 1 arc second has a distan ...
Multi-physics simulations using a hierarchical interchangeable
... Stellar masses are assigned using a Salpeter (1955) IMF between 0.1 and 100 M⊙ , with an additional constraint that the most massive star is ∼ 22 M⊙ . This maximum mass is based on the most massive star naively expected for a cluster with this number of stars and mass function Kroupa & Weidner (2003 ...
... Stellar masses are assigned using a Salpeter (1955) IMF between 0.1 and 100 M⊙ , with an additional constraint that the most massive star is ∼ 22 M⊙ . This maximum mass is based on the most massive star naively expected for a cluster with this number of stars and mass function Kroupa & Weidner (2003 ...
Field Star Distributions of the Hercules Thick Disk Cloud
... The Hercules Thick Disk Cloud (Larsen et al. 2009) was initially discovered as an excess in the number of faint blue stars between quadrants I and IV of the Galaxy. The field stars responsible for the excess, are between 2 and 4 kiloparsecs from the Sun, 1.2 kpc above the Galactic plane, and the asy ...
... The Hercules Thick Disk Cloud (Larsen et al. 2009) was initially discovered as an excess in the number of faint blue stars between quadrants I and IV of the Galaxy. The field stars responsible for the excess, are between 2 and 4 kiloparsecs from the Sun, 1.2 kpc above the Galactic plane, and the asy ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.