1.3 Lifecycle of stars
... A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line—it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a su ...
... A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line—it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a su ...
01_test_bank
... A) Stars are fixed and never move. B) Stars move, but they move very slowly—only a few kilometers in a thousand years. C) Although most stars move through the sky, the brightest stars do not, and these are the ones that trace the patterns we see in the constellations. D) The stars in our sky actuall ...
... A) Stars are fixed and never move. B) Stars move, but they move very slowly—only a few kilometers in a thousand years. C) Although most stars move through the sky, the brightest stars do not, and these are the ones that trace the patterns we see in the constellations. D) The stars in our sky actuall ...
Some Examples of Virtual Observatory Enabled Science What Are the Some Distinguishing
... • In order to study QSOs (and other AGN), we first have to find them, in large numbers, and hopefully in a systematic fashion – This is especially important for studies of their evolution ...
... • In order to study QSOs (and other AGN), we first have to find them, in large numbers, and hopefully in a systematic fashion – This is especially important for studies of their evolution ...
Study Guide Presentation
... How can spectra of elements be used to determine the composition of stars and galaxies? How can spectra of elements be used to determine how fast galaxies are moving away from us? Spectra: Label the three types of spectrum and what causes it: ...
... How can spectra of elements be used to determine the composition of stars and galaxies? How can spectra of elements be used to determine how fast galaxies are moving away from us? Spectra: Label the three types of spectrum and what causes it: ...
Zodiac Party Game - Home - DMNS Galaxy Guide Portal
... o PRECESSION--The very slow wobbling motion of the Earth on its axis. This motion has two effects: 1. It shifts the celestial sphere toward the east by one constellation every 2,200 years. 2. It alters which star, if any, is the North Star. A north star is a star that appears to be located directly ...
... o PRECESSION--The very slow wobbling motion of the Earth on its axis. This motion has two effects: 1. It shifts the celestial sphere toward the east by one constellation every 2,200 years. 2. It alters which star, if any, is the North Star. A north star is a star that appears to be located directly ...
STELLAR CLASSIFICATIONS: TYPE “O” STARS
... The one biggest plus to “M” class stars is that they live a very long time. 56 billion years on average. With lifespans more than 5 times that of the sun, there’s plenty of time for life to evolve around a star such as this. Color: These stars appear orange-red in the visible spectrum, but emit most ...
... The one biggest plus to “M” class stars is that they live a very long time. 56 billion years on average. With lifespans more than 5 times that of the sun, there’s plenty of time for life to evolve around a star such as this. Color: These stars appear orange-red in the visible spectrum, but emit most ...
The Cosmic Perspective Our Galaxy
... a) We're in the middle of one of its arms and thus have no perspective. b) It is very large and the edges are far away and faint. c) Dust blocks our view when we look toward the center or in the disk. d) We cannot see it from the outside. e) all of the above © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... a) We're in the middle of one of its arms and thus have no perspective. b) It is very large and the edges are far away and faint. c) Dust blocks our view when we look toward the center or in the disk. d) We cannot see it from the outside. e) all of the above © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Parallax - The Universe Adventure
... What is Parallax? Parallax is when an object appears to change position when you view it from a different angle. Astronomers see the effects of parallax when they look at stars from different points on Earth’s orbit around the sun. Stars that are nearer to Earth appear to move compared to other star ...
... What is Parallax? Parallax is when an object appears to change position when you view it from a different angle. Astronomers see the effects of parallax when they look at stars from different points on Earth’s orbit around the sun. Stars that are nearer to Earth appear to move compared to other star ...
chapter 7 review questions
... 23. The binding energy of the first level in an atom is 2.210-18 J, and the binding energy of the second energy level is 1.610-18 J. What is the energy of the photon that is emitted if an electron moves from the second level to the first? a. ...
... 23. The binding energy of the first level in an atom is 2.210-18 J, and the binding energy of the second energy level is 1.610-18 J. What is the energy of the photon that is emitted if an electron moves from the second level to the first? a. ...
Goal: To understand clusters of stars
... • All stars star in clusters. • Open clusters are young clusters in the disk of our galaxy which only stay for about a billion years. • Globular clusters are old and lie on the outskirts of our galaxy. ...
... • All stars star in clusters. • Open clusters are young clusters in the disk of our galaxy which only stay for about a billion years. • Globular clusters are old and lie on the outskirts of our galaxy. ...
Goal: To understand clusters of stars
... • All stars star in clusters. • Open clusters are young clusters in the disk of our galaxy which only stay for about a billion years. • Globular clusters are old and lie on the outskirts of our galaxy. ...
... • All stars star in clusters. • Open clusters are young clusters in the disk of our galaxy which only stay for about a billion years. • Globular clusters are old and lie on the outskirts of our galaxy. ...
ASTR-264-Lecture
... Interaction between light and matter determine the appearance of everything around us Chair looks red because only the red light is coming out Windows are both mirrors and transmitters Rose is red because rose reflects red light 5.2 what is light? Light can either act like a wave or a particle Photo ...
... Interaction between light and matter determine the appearance of everything around us Chair looks red because only the red light is coming out Windows are both mirrors and transmitters Rose is red because rose reflects red light 5.2 what is light? Light can either act like a wave or a particle Photo ...
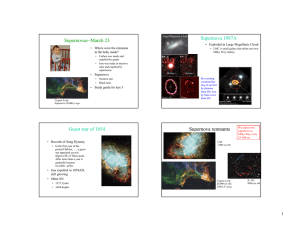
Supernovae March 23 − Supernova 1987A
... • Gas expelled in 1054AD, still glowing • Other SN • 1572 Tycho • 1604 Kepler ...
... • Gas expelled in 1054AD, still glowing • Other SN • 1572 Tycho • 1604 Kepler ...
1-structure-of-the-universe-and-the-big-bang
... A) red shift in the light from distant galaxies B) change in the swing direction of a Foucault pendulum on Earth C) parallelism of Earth's axis in orbit D) spiral shape of the Milky Way Galaxy 16. According to the big bang theory, the universe began as an explosion and is still expanding. This theor ...
... A) red shift in the light from distant galaxies B) change in the swing direction of a Foucault pendulum on Earth C) parallelism of Earth's axis in orbit D) spiral shape of the Milky Way Galaxy 16. According to the big bang theory, the universe began as an explosion and is still expanding. This theor ...
Life and Death of Stars - UM Research Repository
... circulation can be measured, hence they can be referred for directions, as well as the measurement of time. Stars are one of the beautiful objects which come out at night which becomes the symbolic of the hundreds of thousands of the members of heaven. The stars life cycles are following some stages ...
... circulation can be measured, hence they can be referred for directions, as well as the measurement of time. Stars are one of the beautiful objects which come out at night which becomes the symbolic of the hundreds of thousands of the members of heaven. The stars life cycles are following some stages ...
Think about the universe
... objects in the sky with much greater precision than ever before. Observations using telescopes showed that many different types of objects in the sky could be identified. These included single or double stars, groups of stars called galaxies, clusters of galaxies, and clouds of gas and dust called n ...
... objects in the sky with much greater precision than ever before. Observations using telescopes showed that many different types of objects in the sky could be identified. These included single or double stars, groups of stars called galaxies, clusters of galaxies, and clouds of gas and dust called n ...
Color and Temperature of Stars
... emits a broad spectrum (band) of colors. You can see that starlight consists of many colors by using a prism to separate and spread the colors of the light of the sun, a yellow star. The visible spectrum includes all the colors of the rainbow. These colors range from red, produced by the photons (pa ...
... emits a broad spectrum (band) of colors. You can see that starlight consists of many colors by using a prism to separate and spread the colors of the light of the sun, a yellow star. The visible spectrum includes all the colors of the rainbow. These colors range from red, produced by the photons (pa ...
Sample
... never really reverse their direction of travel in their orbits. This makes it easy to use analogies—for example, when students try the demonstration in Figure 2.27, they never say that their friend really moves backward as they pass by, only that the friend appears to move backward against the backg ...
... never really reverse their direction of travel in their orbits. This makes it easy to use analogies—for example, when students try the demonstration in Figure 2.27, they never say that their friend really moves backward as they pass by, only that the friend appears to move backward against the backg ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.