File
... *This explains why no hydrogen lines are seen in the spectrum of a type Ia supernova explosion—white dwarfs contain very little hydrogen. ...
... *This explains why no hydrogen lines are seen in the spectrum of a type Ia supernova explosion—white dwarfs contain very little hydrogen. ...
Sample
... never really reverse their direction of travel in their orbits. This makes it easy to use analogies—for example, when students try the demonstration in Figure 2.27, they never say that their friend really moves backward as they pass by, only that the friend appears to move backward against the backg ...
... never really reverse their direction of travel in their orbits. This makes it easy to use analogies—for example, when students try the demonstration in Figure 2.27, they never say that their friend really moves backward as they pass by, only that the friend appears to move backward against the backg ...
5. cosmic distance ladder ii: standard candles
... easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequently, if you can identify a star as being one of these special types, you know its luminosity. Then you only have to measure its brightness to be able to compute its distance. ...
... easily calculated. However, some special types of variable and exploding stars do have known, standard luminosities. Consequently, if you can identify a star as being one of these special types, you know its luminosity. Then you only have to measure its brightness to be able to compute its distance. ...
Moitinho et al. - Wiley Online Library
... (Martı́nez-Delgado et al. 2005). The youth of the BP also explains why no 1–2 Gyr red clump is evident at 8 kpc. Fig. 2 also reveals the presence of a few other BPs. These would also be considered a non-Galactic population, but in this case they are much closer than the proposed distance to the CMa ...
... (Martı́nez-Delgado et al. 2005). The youth of the BP also explains why no 1–2 Gyr red clump is evident at 8 kpc. Fig. 2 also reveals the presence of a few other BPs. These would also be considered a non-Galactic population, but in this case they are much closer than the proposed distance to the CMa ...
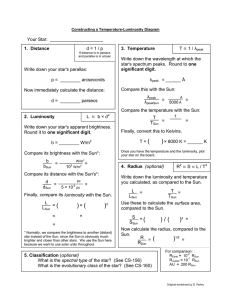
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... In this exercise, we will use the observed properties (parallax, apparent brightness, and spectrum peak) of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns i ...
... In this exercise, we will use the observed properties (parallax, apparent brightness, and spectrum peak) of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns i ...
Astrophysics notes - School
... Magnitude is a measure of how bright a star is. There are, however, two different ways of indicating a stars magnitude; apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. The scale we use to measure magnitude is based on that created by the ancient Greeks which ran from 1 to 6. On the ancient Greek scale 1 ...
... Magnitude is a measure of how bright a star is. There are, however, two different ways of indicating a stars magnitude; apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. The scale we use to measure magnitude is based on that created by the ancient Greeks which ran from 1 to 6. On the ancient Greek scale 1 ...
Sep 2014 - Bays Mountain Park
... Sullivan South student, who shared her open cluster research with members. I want to thank her for all the work and her willingness to stand up in front of a group. August's constellation quest was Cygnus, the swan. This constellation was a very good one to see with the naked eye or with binoculars. ...
... Sullivan South student, who shared her open cluster research with members. I want to thank her for all the work and her willingness to stand up in front of a group. August's constellation quest was Cygnus, the swan. This constellation was a very good one to see with the naked eye or with binoculars. ...
Galaxies
... Galaxy mass measurements show that galaxies need between 3 and 10 times more mass than can be observed to explain their rotation curves. The discrepancy is even larger in galaxy clusters, which need 10 to 100 times more mass. The total needed is more than the sum of the dark matter associated with e ...
... Galaxy mass measurements show that galaxies need between 3 and 10 times more mass than can be observed to explain their rotation curves. The discrepancy is even larger in galaxy clusters, which need 10 to 100 times more mass. The total needed is more than the sum of the dark matter associated with e ...
Orion – The Hunter - Guild of Students
... built to mirror the three stars of Orion's belt. Osiris was born in Thebes in Upper Egypt, the heavenly mirror-world that the Egyptians believed existed in the sky, to Nut and Geb. His grandfather Ra made him heir to the throne and so when his father Geb retired he took over as the fourth divine pha ...
... built to mirror the three stars of Orion's belt. Osiris was born in Thebes in Upper Egypt, the heavenly mirror-world that the Egyptians believed existed in the sky, to Nut and Geb. His grandfather Ra made him heir to the throne and so when his father Geb retired he took over as the fourth divine pha ...
Reflecting telescopes - School
... Magnitude is a measure of how bright a star is. There are, however, two different ways of indicating a stars magnitude; apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. The scale we use to measure magnitude is based on that created by the ancient Greeks which ran from 1 to 6. On the ancient Greek scale 1 ...
... Magnitude is a measure of how bright a star is. There are, however, two different ways of indicating a stars magnitude; apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. The scale we use to measure magnitude is based on that created by the ancient Greeks which ran from 1 to 6. On the ancient Greek scale 1 ...
Galaxy / Cluster Ecosystem Ming Sun (University of Alabama in Huntsville)
... W. Forman, C. Jones, A. Vikhlinin, B. Zhang (CfA); M. Fumagalli ...
... W. Forman, C. Jones, A. Vikhlinin, B. Zhang (CfA); M. Fumagalli ...
Physics- HSC- Module 9.7 Astrophysics
... During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, astronomers obtained spectra and parallax distances for many stars, a powerful tool was discovered for classifying and understanding stars. Around 1911-13, Enjar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell independently found that stars could be divided into t ...
... During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, astronomers obtained spectra and parallax distances for many stars, a powerful tool was discovered for classifying and understanding stars. Around 1911-13, Enjar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell independently found that stars could be divided into t ...
Pulsating Variable Stars and The Hertzsprung - Chandra X
... brightness due to physical changes within the interior of the star. The pulsations are due to the periodic expansion and contraction of the surface layers of the stars. The change in size is observed as a change in apparent magnitude. Stars pulsate because they are not in hydrostatic equilibrium: th ...
... brightness due to physical changes within the interior of the star. The pulsations are due to the periodic expansion and contraction of the surface layers of the stars. The change in size is observed as a change in apparent magnitude. Stars pulsate because they are not in hydrostatic equilibrium: th ...
Apparent Magnitude - RanelaghALevelPhysics
... emitted per second (units of Watts). • The Sun’s luminosity is about 4 x 1026 W. • The most luminous stars have a luminosity of about million times that of the Sun! ...
... emitted per second (units of Watts). • The Sun’s luminosity is about 4 x 1026 W. • The most luminous stars have a luminosity of about million times that of the Sun! ...
1-structure-of-the-universe-and-the-big-bang
... A) red shift in the light from distant galaxies B) change in the swing direction of a Foucault pendulum on Earth C) parallelism of Earth's axis in orbit D) spiral shape of the Milky Way Galaxy 16. According to the big bang theory, the universe began as an explosion and is still expanding. This theor ...
... A) red shift in the light from distant galaxies B) change in the swing direction of a Foucault pendulum on Earth C) parallelism of Earth's axis in orbit D) spiral shape of the Milky Way Galaxy 16. According to the big bang theory, the universe began as an explosion and is still expanding. This theor ...
ph507lecnote06
... Spectrograph with a resolving power of 105 will have a pixel scale ~ 10-5 c ~ few km/s Therefore, specialized techniques that can measure radial velocity shifts of ~10-3 of a pixel stably over many years are required High sensitivity to small radial velocity shifts is achieved by: • comparing high S ...
... Spectrograph with a resolving power of 105 will have a pixel scale ~ 10-5 c ~ few km/s Therefore, specialized techniques that can measure radial velocity shifts of ~10-3 of a pixel stably over many years are required High sensitivity to small radial velocity shifts is achieved by: • comparing high S ...
FROM MOLECULAR CLOUDS TO STARS 1 Star formation and the
... density enhancements in relatively small, cold regions called ”Dense Cores”. Stars form inside these cores and the mass of the dense cores settles the upper limit of the star masses. The masses of the Dense Cores have a lower limit given by the Jeans Mass (see § 3), that depends on the temperature o ...
... density enhancements in relatively small, cold regions called ”Dense Cores”. Stars form inside these cores and the mass of the dense cores settles the upper limit of the star masses. The masses of the Dense Cores have a lower limit given by the Jeans Mass (see § 3), that depends on the temperature o ...
Ursa Major

Ursa Major /ˈɜrsə ˈmeɪdʒər/ (also known as the Great Bear and Charles' Wain) is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by Ptolemy (second century AD), it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. It can be visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. Its name, Latin for ""the greater (or larger) she-bear"", stands as a reference to and in direct contrast with Ursa Minor, ""the smaller she-bear"", with which it is frequently associated in mythology and amateur astronomy. The constellation's most recognizable asterism, a group of seven relatively bright stars commonly known as the ""Big Dipper"", ""the Wagon"" or ""the Plough"" (among others), both mimicks the shape of the lesser bear (the ""Little Dipper"") and is commonly used as a navigational pointer towards the current northern pole star, Polaris in Ursa Minor. The Big Dipper and the constellation as a whole have mythological significance in numerous world cultures, usually as a symbol of the north.The third largest constellation in the sky, Ursa Major is home to many deep-sky objects including seven Messier objects, four other NGC objects and I Zwicky 18, the youngest known galaxy in the visible universe.