Unit 1
... observing comets, and kept finding objects that while fuzzy, were not comets – He made a list (or catalog) of these undesired objects, so he could avoid seeing them – They became known as Messier Objects, a number preceded by an M. – M31 (the Andromeda galaxy) is one such object ...
... observing comets, and kept finding objects that while fuzzy, were not comets – He made a list (or catalog) of these undesired objects, so he could avoid seeing them – They became known as Messier Objects, a number preceded by an M. – M31 (the Andromeda galaxy) is one such object ...
A Universe of Galaxies - Pennsylvania State University
... Quasars: Fast, distant, and very bright Quasars have enormous redshifts, indicating that they are moving away from us at more than 90% of the speed of light. Stars in the Milky Way cannot move that fast. The only way to achieve such a high speed is if they are incredibly far away. They are therefor ...
... Quasars: Fast, distant, and very bright Quasars have enormous redshifts, indicating that they are moving away from us at more than 90% of the speed of light. Stars in the Milky Way cannot move that fast. The only way to achieve such a high speed is if they are incredibly far away. They are therefor ...
Document
... Hubble space telescope, tracing emission from nitrogen (red), hydrogen (green), oxygen (blue) and helium (violet). ...
... Hubble space telescope, tracing emission from nitrogen (red), hydrogen (green), oxygen (blue) and helium (violet). ...
WORD - UWL faculty websites
... o Observing which wavelengths are missing after reflection tells you about the composition of the reflecting surface! o Observing which wavelengths are missing after passing through material (e.g. atmosphere of a planet or star) tells you about that material Most of the stuff in the universe is hy ...
... o Observing which wavelengths are missing after reflection tells you about the composition of the reflecting surface! o Observing which wavelengths are missing after passing through material (e.g. atmosphere of a planet or star) tells you about that material Most of the stuff in the universe is hy ...
Applications of Light to Astronomy
... o Observing which wavelengths are missing after reflection tells you about the composition of the reflecting surface! o Observing which wavelengths are missing after passing through material (e.g. atmosphere of a planet or star) tells you about that material Most of the stuff in the universe is hy ...
... o Observing which wavelengths are missing after reflection tells you about the composition of the reflecting surface! o Observing which wavelengths are missing after passing through material (e.g. atmosphere of a planet or star) tells you about that material Most of the stuff in the universe is hy ...
Celestial Objects
... a) red shiftshift- shift toward longer red wavelengths of energy showing that an object is moving AWAY from Earth 1) the farther away the galaxy, the greater the red shift 2) almost all galaxies show a red shiftshiftproof that the universe is expanding (Edwin Hubble was the first to realize this!) ...
... a) red shiftshift- shift toward longer red wavelengths of energy showing that an object is moving AWAY from Earth 1) the farther away the galaxy, the greater the red shift 2) almost all galaxies show a red shiftshiftproof that the universe is expanding (Edwin Hubble was the first to realize this!) ...
Watch the episode titled “The Milky Way” from the series “The
... What do astronomers think came first, the galaxy or the black hole? Besides being sucked into the black hole, what else is happening at the edges of a black hole? Once formed at the edge of a black hole, what is likely to happen to that star? About how many times has our solar system been orbited ar ...
... What do astronomers think came first, the galaxy or the black hole? Besides being sucked into the black hole, what else is happening at the edges of a black hole? Once formed at the edge of a black hole, what is likely to happen to that star? About how many times has our solar system been orbited ar ...
Chapter 30 Study Notes
... During the main sequence stage, ________ hydrogen helium to generate energy in a fuses into _______ star’s core. ...
... During the main sequence stage, ________ hydrogen helium to generate energy in a fuses into _______ star’s core. ...
notes_chapter1 - Auburn University
... The Sun is 8.3 light minutes (~93 million miles) away A light year measures a distance of 5.87 trillion miles. The visible Universe is > 13 billion light years away ...
... The Sun is 8.3 light minutes (~93 million miles) away A light year measures a distance of 5.87 trillion miles. The visible Universe is > 13 billion light years away ...
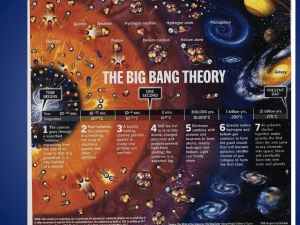
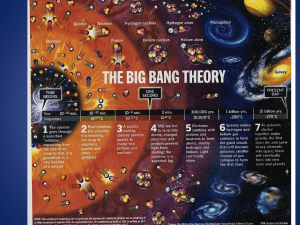
The Big Bang Theory
... • The universe has grown from the size of an atom to larger than the size a grapefruit • E=mc2 • energy froze into matter according to Albert Einstein’s equation. • This basically says that like snowflakes freezing, energy forms matter into clumps that today we call protons, neutrons and electrons. ...
... • The universe has grown from the size of an atom to larger than the size a grapefruit • E=mc2 • energy froze into matter according to Albert Einstein’s equation. • This basically says that like snowflakes freezing, energy forms matter into clumps that today we call protons, neutrons and electrons. ...
Space Science Ch. 1 Notes - Mr. Ruggiero`s Science 8-2
... Galileo started it all with his hand-held telescope. It was powerful enough to see some of Jupiter’s moons and show that the Earth isn’t the center of the universe. Space exploration has mushroomed in the past 50 years. Rockets that originally lofted weapons during World War II were converted to car ...
... Galileo started it all with his hand-held telescope. It was powerful enough to see some of Jupiter’s moons and show that the Earth isn’t the center of the universe. Space exploration has mushroomed in the past 50 years. Rockets that originally lofted weapons during World War II were converted to car ...
The Big Bang Theory
... • The universe has grown from the size of an atom to larger than the size a grapefruit • E=mc2 • energy froze into matter according to Albert Einstein’s equation. • This basically says that like snowflakes freezing, energy forms matter into clumps that today we call protons, neutrons and electrons. ...
... • The universe has grown from the size of an atom to larger than the size a grapefruit • E=mc2 • energy froze into matter according to Albert Einstein’s equation. • This basically says that like snowflakes freezing, energy forms matter into clumps that today we call protons, neutrons and electrons. ...
hubble_refurb
... Joining Mikulski as an advocate for servicing Hubble was NASA's Chief Scientist, physicist John Grunsfeld, who was present at the meeting when O'Keefe announced the cancellation of the mission.[18] A veteran astronaut of four shuttle missions, including two Hubble servicing missions, Grunsfeld had d ...
... Joining Mikulski as an advocate for servicing Hubble was NASA's Chief Scientist, physicist John Grunsfeld, who was present at the meeting when O'Keefe announced the cancellation of the mission.[18] A veteran astronaut of four shuttle missions, including two Hubble servicing missions, Grunsfeld had d ...
Lecture - Ann Arbor Earth Science
... Types of Galaxies Elliptical galaxies range from nearly spherical to lensshaped. Their stars are concentrated in their centers, and they have no arms. Elliptical galaxies contain far less interstellar gas and dust (than spiral galaxies), and contain ...
... Types of Galaxies Elliptical galaxies range from nearly spherical to lensshaped. Their stars are concentrated in their centers, and they have no arms. Elliptical galaxies contain far less interstellar gas and dust (than spiral galaxies), and contain ...
Which of the following is the best description of an Sc galaxy? A) a
... a. regions within a molecular cloud that are not moving relative to the rest of the cloud. b. the upper energy level of the 21-cm transition in the hydrogen atom. c. the lower energy level of the 21-cm transition in the hydrogen atom. d. the boundary layers between HI regions and the hotter interclo ...
... a. regions within a molecular cloud that are not moving relative to the rest of the cloud. b. the upper energy level of the 21-cm transition in the hydrogen atom. c. the lower energy level of the 21-cm transition in the hydrogen atom. d. the boundary layers between HI regions and the hotter interclo ...
Telescopes
... Telescopes Stars are too far away to ever study directly. It would take 19,000 years to reach the nearest star, a mere 4 light years away traveling at 240,000 km/hr (150,000 miles/hr) the world record for current space travel speed! So all the evidence we gather about stars to form our theories of t ...
... Telescopes Stars are too far away to ever study directly. It would take 19,000 years to reach the nearest star, a mere 4 light years away traveling at 240,000 km/hr (150,000 miles/hr) the world record for current space travel speed! So all the evidence we gather about stars to form our theories of t ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.