chapter 28 pages 747-752
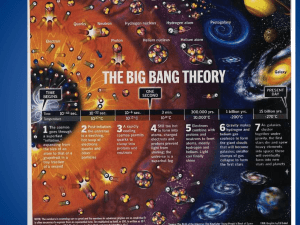
... • Red shift • Edwin Hubble saw that galaxies are moving away from earth based on the red shifts he saw in 1929 • In a medium that is uniformly expanding, all points are moving away from all other points, and no point has to be at the center ...
... • Red shift • Edwin Hubble saw that galaxies are moving away from earth based on the red shifts he saw in 1929 • In a medium that is uniformly expanding, all points are moving away from all other points, and no point has to be at the center ...
Active Galactic Nuclei - University of Toronto
... inward, it heats up and glows brightly, getting hotter and hotter the closer it is to the event horizon. Some of the gas is blown away from the disk like steam from a kettle. As this gas streams off the disk, the intense radiation generated by the very hot gas near the event horizon forces the escap ...
... inward, it heats up and glows brightly, getting hotter and hotter the closer it is to the event horizon. Some of the gas is blown away from the disk like steam from a kettle. As this gas streams off the disk, the intense radiation generated by the very hot gas near the event horizon forces the escap ...
Galaxies - schoolphysics
... the trip across our galaxy. This means that the light that we see from the stars on the other side of the galaxy started out on its journey over eighty thousand years ago! If we could shrink the whole solar system out to the orbit of Pluto to the size of a grain of sand 1mm across then on the same s ...
... the trip across our galaxy. This means that the light that we see from the stars on the other side of the galaxy started out on its journey over eighty thousand years ago! If we could shrink the whole solar system out to the orbit of Pluto to the size of a grain of sand 1mm across then on the same s ...
Groups of Stars
... nebula • This means they formed at about the same time and they are all about the same distance from Earth ...
... nebula • This means they formed at about the same time and they are all about the same distance from Earth ...
Galaxies - science9atsouthcarletonhs
... Galaxy Clusters • Most galaxies are not alone in the vast expanse of space, but are connected to one or more other galaxies by gravity • These collections of galaxies are known as galaxy clusters and they too appear to be organized into larger “superclusters” ...
... Galaxy Clusters • Most galaxies are not alone in the vast expanse of space, but are connected to one or more other galaxies by gravity • These collections of galaxies are known as galaxy clusters and they too appear to be organized into larger “superclusters” ...
Wadhurst Astronomical Society Newsletter May 2017
... of the star as it passes behind mountains on the limb of the Moon from several positions at right angle to the path of the Moon and at the same time. These timings are used by reporting centres to refine the position and tilt of the Earth and also to predict Baily’s Beads during a Solar Eclipse wher ...
... of the star as it passes behind mountains on the limb of the Moon from several positions at right angle to the path of the Moon and at the same time. These timings are used by reporting centres to refine the position and tilt of the Earth and also to predict Baily’s Beads during a Solar Eclipse wher ...
Document
... The Universe is filled with these star systems which themselves cluster together into larger systems. ...
... The Universe is filled with these star systems which themselves cluster together into larger systems. ...
Galaxies
... The Universe is filled with these star systems which themselves cluster together into larger systems. ...
... The Universe is filled with these star systems which themselves cluster together into larger systems. ...
June 2013 Kepler Space Telescope Update
... "We were concerned that HXMM01's intense brightness at sub-millimetre wavelengths might be due to gravitational lensing – the bending of light caused by foreground massive objects. In some cases, that can strongly magnify the appearance of a background galaxy," explains co-author Asantha Cooray, als ...
... "We were concerned that HXMM01's intense brightness at sub-millimetre wavelengths might be due to gravitational lensing – the bending of light caused by foreground massive objects. In some cases, that can strongly magnify the appearance of a background galaxy," explains co-author Asantha Cooray, als ...
UniverseofGalaxies
... Dwarf galaxies • Dwarf galaxies – Low surface brightness – Less than 5000 ly across – Some are irregular, some are elliptical – Various star formation histories ...
... Dwarf galaxies • Dwarf galaxies – Low surface brightness – Less than 5000 ly across – Some are irregular, some are elliptical – Various star formation histories ...
The Extragalactic Distance Database: Color–Magnitude Diagrams
... tables hold information about the measurement of a single star per row. There are, among others, columns that describe a star’s position on the image, and its apparent magnitude in both flight and groundbased filters, as well as several characterizations of the quality of the measurement. If there a ...
... tables hold information about the measurement of a single star per row. There are, among others, columns that describe a star’s position on the image, and its apparent magnitude in both flight and groundbased filters, as well as several characterizations of the quality of the measurement. If there a ...
What MSU Astronomers Will Do with the SOAR
... • Recently formed test details of “bottom-up” formation scenario • Evolution of cluster population sensitive probe of Dark Matter and Dark Energy • Best “fair sample” of matter content of Universe • Dark vs. normal matter ...
... • Recently formed test details of “bottom-up” formation scenario • Evolution of cluster population sensitive probe of Dark Matter and Dark Energy • Best “fair sample” of matter content of Universe • Dark vs. normal matter ...
What Can We See in the Night Sky?
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
... • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies • Open clusters – contain about 50 to 1000 stars – dispersed along the Milky Way’s main band ...
AAO Techniques Workshop (April 2001) 12 Mbytes
... Structure of the Universe Origin and Evolution of Galaxies History of the Milky Way Birth and Formation of Stars Origin of Planetary Systems ...
... Structure of the Universe Origin and Evolution of Galaxies History of the Milky Way Birth and Formation of Stars Origin of Planetary Systems ...
The Closest New Stars To Earth
... Along with the Lupus molecular clouds (about 600 light years distant), these dark, lightblocking patches are virtually unknown to most sky watchers in the northern hemisphere, as they're all southern hemisphere objects. In visible light, these clouds appear predominantly as dark patches, obscuring a ...
... Along with the Lupus molecular clouds (about 600 light years distant), these dark, lightblocking patches are virtually unknown to most sky watchers in the northern hemisphere, as they're all southern hemisphere objects. In visible light, these clouds appear predominantly as dark patches, obscuring a ...
Astr 40 Final Exam Review ()
... binaries, optical doubles are not true binaries because they are not gravitationally bound. 50. Because stars in clusters all have similar age and distance, the main underlying physical cause of their different appearances is their mass. 51. If one region of the sky shows nearby stars but no distant ...
... binaries, optical doubles are not true binaries because they are not gravitationally bound. 50. Because stars in clusters all have similar age and distance, the main underlying physical cause of their different appearances is their mass. 51. If one region of the sky shows nearby stars but no distant ...
Introduction to the Earth
... distance measurement called the Light- year 1 light-year is the distance light travels in one ...
... distance measurement called the Light- year 1 light-year is the distance light travels in one ...
Galaxy Notes File
... Types of Galaxies = Spirals Spirals are classified according to how tightly or loosely wound the arms are. The brightness of the central nucleus is correlated to the tightness of the arm. The galaxies M 104 (below) and M 51 (right) respectively show tightly and loosely wounds. Notice the effects of ...
... Types of Galaxies = Spirals Spirals are classified according to how tightly or loosely wound the arms are. The brightness of the central nucleus is correlated to the tightness of the arm. The galaxies M 104 (below) and M 51 (right) respectively show tightly and loosely wounds. Notice the effects of ...
Lec12
... move into spiral arms 2. Squeezing of clouds triggers star formation 3. Young stars flow out of spiral arms ...
... move into spiral arms 2. Squeezing of clouds triggers star formation 3. Young stars flow out of spiral arms ...
Galaxies Powerpoint
... gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
... gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
Main Types of Galaxies
... gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
... gas, and dust in space that are held together by gravity. • The largest galaxies contain more than a trillion stars. Smaller galaxies may have only a few million. • Scientists estimate the number of stars from the size and brightness of the galaxy. ...
Hubble Deep Field

The Hubble Deep Field (HDF) is an image of a small region in the constellation Ursa Major, constructed from a series of observations by the Hubble Space Telescope. It covers an area 2.5 arcminutes across, about one 24-millionth of the whole sky, which is equivalent in angular size to a 65 mm tennis ball at a distance of 100 metres. The image was assembled from 342 separate exposures taken with the Space Telescope's Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 over ten consecutive days between December 18 and December 28, 1995.The field is so small that only a few foreground stars in the Milky Way lie within it; thus, almost all of the 3,000 objects in the image are galaxies, some of which are among the youngest and most distant known. By revealing such large numbers of very young galaxies, the HDF has become a landmark image in the study of the early universe, with the associated scientific paper having received over 900 citations by the end of 2014.Three years after the HDF observations were taken, a region in the south celestial hemisphere was imaged in a similar way and named the Hubble Deep Field South. The similarities between the two regions strengthened the belief that the universe is uniform over large scales and that the Earth occupies a typical region in the Universe (the cosmological principle). A wider but shallower survey was also made as part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey. In 2004 a deeper image, known as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF), was constructed from a few months of light exposure. The HUDF image was at the time the most sensitive astronomical image ever made at visible wavelengths, and it remained so until the Hubble Extreme Deep Field (XDF) was released in 2012.