endocrine glands
... particular area (the target organ), where they have their effect. E.g. insulin Hormones are mainly made of PROTEIN. Some hormones are steroid based (made of lipid) e.g. male hormones Even though hormones are carried to all parts of the body in the blood stream they only affect specific areas called ...
... particular area (the target organ), where they have their effect. E.g. insulin Hormones are mainly made of PROTEIN. Some hormones are steroid based (made of lipid) e.g. male hormones Even though hormones are carried to all parts of the body in the blood stream they only affect specific areas called ...
AHA Scientific Sessions 2014 Conference Call
... toward managed care and healthcare cost containment as well as U.S. legislation affecting pharmaceutical pricing and reimbursement. Government and others’ regulations and reimbursement policies may affect the development, usage and pricing of our products. Furthermore, our research, testing, pricing ...
... toward managed care and healthcare cost containment as well as U.S. legislation affecting pharmaceutical pricing and reimbursement. Government and others’ regulations and reimbursement policies may affect the development, usage and pricing of our products. Furthermore, our research, testing, pricing ...
Endocrine System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Not serious when the thirst center is operating properly and enough water is drunk Can be life threatening in unconscious or comatose patients Hypersecretion of ADH occurs in children with meningitis, after neurosurgery or secretion from cancer cells Symptoms include retention of fluid, headache, di ...
... Not serious when the thirst center is operating properly and enough water is drunk Can be life threatening in unconscious or comatose patients Hypersecretion of ADH occurs in children with meningitis, after neurosurgery or secretion from cancer cells Symptoms include retention of fluid, headache, di ...
The MENOPAUSE Booklet - Australian Menopause Centre
... What to Expect in the First Four Months It’s important to understand that it may have taken years for your body to become hormonally imbalanced - it’s not possible to correct this instantly. Every woman will respond differently. Response will also be dependent on the particular stage of the menopau ...
... What to Expect in the First Four Months It’s important to understand that it may have taken years for your body to become hormonally imbalanced - it’s not possible to correct this instantly. Every woman will respond differently. Response will also be dependent on the particular stage of the menopau ...
Anovulation: Etiology and Management
... Evidence suggests that a cascade of neuroendocrine events that may begin with limbic system responses to psychic stimuli impairs hypothalamic-pituitary activity It has been suggested that increased hypothalamic b-endorphin is important in inhibiting gonadotropin secretion ...
... Evidence suggests that a cascade of neuroendocrine events that may begin with limbic system responses to psychic stimuli impairs hypothalamic-pituitary activity It has been suggested that increased hypothalamic b-endorphin is important in inhibiting gonadotropin secretion ...
ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Infertility
... Infertility is defined as the inability to achieve a successful pregnancy after 12 or more months of regular unprotected intercourse [1]. About 15.5% of women experience infertility [2]; however, in many women this may be temporary as time to pregnancy data show a decrease in infertility at 24 month ...
... Infertility is defined as the inability to achieve a successful pregnancy after 12 or more months of regular unprotected intercourse [1]. About 15.5% of women experience infertility [2]; however, in many women this may be temporary as time to pregnancy data show a decrease in infertility at 24 month ...
Endocrine Physiology - e-safe
... The follicles comprise a single layer of epithelial cells forming a cavity that contains colloid where the thyroid hormones are stores as thyroglobulin. C-cells, which secrete calcitonin, are found outside the follicles. Synthesis and transport of thyroid hormones Dietary iodide is concentrated by t ...
... The follicles comprise a single layer of epithelial cells forming a cavity that contains colloid where the thyroid hormones are stores as thyroglobulin. C-cells, which secrete calcitonin, are found outside the follicles. Synthesis and transport of thyroid hormones Dietary iodide is concentrated by t ...
OBSTETRICS & GYNAECOLOGY
... • Sx peak b/n 3rd-5th day and gone by 10th day. • Mood lability: elation (days 1-2), irritability, anxiety, depressed, poor concentration. • Up to 30% go on to subsequent PND (severe cases) • Treatment: reassure but be aware it may be early stages of PND ...
... • Sx peak b/n 3rd-5th day and gone by 10th day. • Mood lability: elation (days 1-2), irritability, anxiety, depressed, poor concentration. • Up to 30% go on to subsequent PND (severe cases) • Treatment: reassure but be aware it may be early stages of PND ...
What is acromegaly
... This expansion causes the headaches and visual disturbances that are often symptoms of acromegaly. In addition, ...
... This expansion causes the headaches and visual disturbances that are often symptoms of acromegaly. In addition, ...
29.6 The Endocrine System and Hormones
... growth, development, and digestion. • It is a collection of physically disconnected organs • responds to environment May control: • Cell division • Cell death • Sexual development • Body temperature • Alertness • Salt levels… ...
... growth, development, and digestion. • It is a collection of physically disconnected organs • responds to environment May control: • Cell division • Cell death • Sexual development • Body temperature • Alertness • Salt levels… ...
The Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
... organism for studying neurological circuits because its entire nervous system contains only 302 neurons. In this species oxytocin helps the individual worms nd and recognize mates. A function of oxytocin in the mammalian brain seems to be the enhancement of speci c neuronal circuits over others. In ...
... organism for studying neurological circuits because its entire nervous system contains only 302 neurons. In this species oxytocin helps the individual worms nd and recognize mates. A function of oxytocin in the mammalian brain seems to be the enhancement of speci c neuronal circuits over others. In ...
First-Trimester Emergencies: A Practical Approach To Abdominal
... 1. Ectopic pregnancy: a. is defined as the implantation of a fertilized ovum outside the endometrial cavity of the uterus. b. may be more common than is reported because of advances in the diagnosis and treatment of ectopic pregnancy in the past few decades, a substantial decrease in inpatient hos ...
... 1. Ectopic pregnancy: a. is defined as the implantation of a fertilized ovum outside the endometrial cavity of the uterus. b. may be more common than is reported because of advances in the diagnosis and treatment of ectopic pregnancy in the past few decades, a substantial decrease in inpatient hos ...
University of Buea University of Buea
... ____ 36. Which characteristic below is not shared by both lipophilic and hydrophilic hormones? a. amplification of hormone actions in the target cell. b. transport via plasma proteins. c. regulation of metabolic reactions. d. initiation of second messenger systems. e. Both (b) and (d) above. ____ 37 ...
... ____ 36. Which characteristic below is not shared by both lipophilic and hydrophilic hormones? a. amplification of hormone actions in the target cell. b. transport via plasma proteins. c. regulation of metabolic reactions. d. initiation of second messenger systems. e. Both (b) and (d) above. ____ 37 ...
Endocrine System
... autonomic nervous system. By controlling the pituitary, the hypothalamus exerts control over the the other endocrine glands, as well as over many other ograns in the body. ...
... autonomic nervous system. By controlling the pituitary, the hypothalamus exerts control over the the other endocrine glands, as well as over many other ograns in the body. ...
HORMONES…..
... function, sensory pereception sleep, excretion, lactation, stress, growth and development movement, reproduction, and mood. Hormones affect distant cells by binding to specific receptor proteins in the target cell resulting in a change in cell function. When a hormone binds to the receptor, it resul ...
... function, sensory pereception sleep, excretion, lactation, stress, growth and development movement, reproduction, and mood. Hormones affect distant cells by binding to specific receptor proteins in the target cell resulting in a change in cell function. When a hormone binds to the receptor, it resul ...
Human Physiology
... Episodic secretion of hormones • The most prominent episodes of release occur with a frequency of about one hour—referred to as circhoral • An episode of release longer than an hour, but less than 24 hours, the rhythm is referred to as ultradian • If the periodicity is approximately 24 hours, the r ...
... Episodic secretion of hormones • The most prominent episodes of release occur with a frequency of about one hour—referred to as circhoral • An episode of release longer than an hour, but less than 24 hours, the rhythm is referred to as ultradian • If the periodicity is approximately 24 hours, the r ...
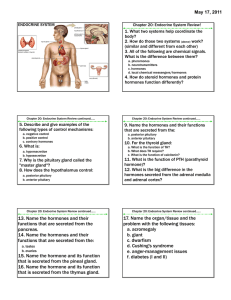
13. Name the hormones and their functions that are secreted from
... 1. What two systems help coordinate the body? 2. How do those two systems (above) work? (similar and different from each other) 3. All of the following are chemical signals. What is the difference between them? a. pheromones b. neurotransmitters c. hormones d. local chemical messengers/hormones ...
... 1. What two systems help coordinate the body? 2. How do those two systems (above) work? (similar and different from each other) 3. All of the following are chemical signals. What is the difference between them? a. pheromones b. neurotransmitters c. hormones d. local chemical messengers/hormones ...
Egg Donation
... 1. Blood drawing and medication injections- mild discomfort and a risk of developing a bruise at the needle site. 2. Fertility drugs and other medications used to stimulate the ovaries may cause: a) Hyperstimulation - The fertility drugs/medications previously described may cause excessive ovarian ...
... 1. Blood drawing and medication injections- mild discomfort and a risk of developing a bruise at the needle site. 2. Fertility drugs and other medications used to stimulate the ovaries may cause: a) Hyperstimulation - The fertility drugs/medications previously described may cause excessive ovarian ...
6: Diagnosis of Infertility
... cycle, when estrogen levels are rising, the BBT remains at resting level, approximately 98.00 F. When ovulation occurs, estrogen levels decline and progesterone levels rise, which causes an upward shift in BBT to 98.40 F or higher, @here may also be a slight decrease in BBT immediately before the up ...
... cycle, when estrogen levels are rising, the BBT remains at resting level, approximately 98.00 F. When ovulation occurs, estrogen levels decline and progesterone levels rise, which causes an upward shift in BBT to 98.40 F or higher, @here may also be a slight decrease in BBT immediately before the up ...
The Effect of Relaxation and Positive Self
... of the issues or cognitive distortions related to that subject. Instead of paying attention to external, environmental, genetic, heredity and childhood event factors, cognitive therapists concentrate on the individual’s thoughts, reforming their understanding, interpretations, and attitudes (22). Th ...
... of the issues or cognitive distortions related to that subject. Instead of paying attention to external, environmental, genetic, heredity and childhood event factors, cognitive therapists concentrate on the individual’s thoughts, reforming their understanding, interpretations, and attitudes (22). Th ...
Chemistry Problem Solving Drill
... system uses chemical messengers, called neurotransmitters, at each synapse (the gap between neurons or between a neuron and a target tissue, such as a muscle cell), and thus represents a point-to-point system of connection. However, there is a second communication system in your body. The endocrine ...
... system uses chemical messengers, called neurotransmitters, at each synapse (the gap between neurons or between a neuron and a target tissue, such as a muscle cell), and thus represents a point-to-point system of connection. However, there is a second communication system in your body. The endocrine ...
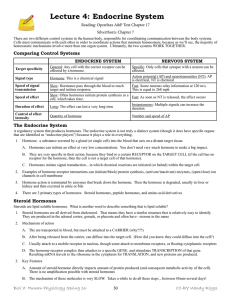
Lecture 4: Endocrine System
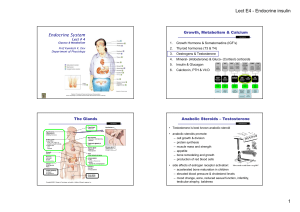
... the adrenal glands (located on top of the kidneys) to secrete cortisol, which promotes the breakdown of proteins and fats and helps the body adapt to stress. Cortisol functions to provide the body with fuel by breaking down the materials of the body. This is a catabolic process. Under normal conditi ...
... the adrenal glands (located on top of the kidneys) to secrete cortisol, which promotes the breakdown of proteins and fats and helps the body adapt to stress. Cortisol functions to provide the body with fuel by breaking down the materials of the body. This is a catabolic process. Under normal conditi ...
1. the thyroid gland
... upper pole of the gland, which increases during systole. When enlarged TG is pressing on the trachea, in auscultation a whistling sound is determined. Examination of patients with thyroid disease must include assessment of the behavior of the patient, the detection of hand tremor, eye symptoms, and ...
... upper pole of the gland, which increases during systole. When enlarged TG is pressing on the trachea, in auscultation a whistling sound is determined. Examination of patients with thyroid disease must include assessment of the behavior of the patient, the detection of hand tremor, eye symptoms, and ...
Endometriosis
... breakdown and bleeding of this tissue each month also can cause scar tissue, called adhesions, to form. Sometimes adhesions can cause organs to stick together. The bleeding, inflammation, and scarring can cause pain, especially before and during menstruation. ...
... breakdown and bleeding of this tissue each month also can cause scar tissue, called adhesions, to form. Sometimes adhesions can cause organs to stick together. The bleeding, inflammation, and scarring can cause pain, especially before and during menstruation. ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.