ch18 Endocrine System
... 4. Androgens secreted by the adrenal cortex usually have minimal effects. 5. An absence in the ability to produce Cortisol, from birth, causes Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia, which results in excessive androgens. This disorder has symptoms of virilism, where individual is masculinized (Clinical Conn ...
... 4. Androgens secreted by the adrenal cortex usually have minimal effects. 5. An absence in the ability to produce Cortisol, from birth, causes Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia, which results in excessive androgens. This disorder has symptoms of virilism, where individual is masculinized (Clinical Conn ...
9 Endocrine Physiology
... • A hormonal trigger is when one endocrine gland releases a hormone that stimulates another endocrine gland to release its hormone. Role of Hypothalamus • The hypothalamus is like the boss of a company; the pituitary gland is like the boss’ manager, and the thyroid gland is the worker. • The boss te ...
... • A hormonal trigger is when one endocrine gland releases a hormone that stimulates another endocrine gland to release its hormone. Role of Hypothalamus • The hypothalamus is like the boss of a company; the pituitary gland is like the boss’ manager, and the thyroid gland is the worker. • The boss te ...
Anatomical and physiological changes in pregnancy and their
... trimester. This increases to 25% by the end of the second trimester, but there is no further change in the third trimester. Stroke volume is increased by about 20% at 8 weeks and up to 30% by the end of the second trimester, then remains level until term. ...
... trimester. This increases to 25% by the end of the second trimester, but there is no further change in the third trimester. Stroke volume is increased by about 20% at 8 weeks and up to 30% by the end of the second trimester, then remains level until term. ...
General postoperative complications
... A procedure in which sutures are used to close the cervix during pregnancy to prevent preterm birth or miscarriage.Used for the treatment of cervical incompetence.It usually done after 13 week of pregnancy (between 12 -14 weeks) no earlier ,so that early abortions due to other factors will be comple ...
... A procedure in which sutures are used to close the cervix during pregnancy to prevent preterm birth or miscarriage.Used for the treatment of cervical incompetence.It usually done after 13 week of pregnancy (between 12 -14 weeks) no earlier ,so that early abortions due to other factors will be comple ...
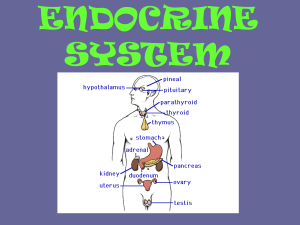
Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology
... The thyroid gland lies in the anterior portion of the neck and straddles the trachea. It secretes two hormones that play a major role in the body’s metabolism: thyroxine (T4) & triiodothyronine (T3). Absence of these hormones may decrease the body’s basal metabolic rate by 60% and an excess of th ...
... The thyroid gland lies in the anterior portion of the neck and straddles the trachea. It secretes two hormones that play a major role in the body’s metabolism: thyroxine (T4) & triiodothyronine (T3). Absence of these hormones may decrease the body’s basal metabolic rate by 60% and an excess of th ...
Novarel - Ferring Pharmaceuticals
... at puberty. HCG thus may help to predict whether or not orchiopexy will be needed in the future. Although, in some cases, descent following HCG administration is permanent, in most cases the response is temporary. Therapy is usually instituted between the ages of 4 and 9. 2. Selected cases of hypogo ...
... at puberty. HCG thus may help to predict whether or not orchiopexy will be needed in the future. Although, in some cases, descent following HCG administration is permanent, in most cases the response is temporary. Therapy is usually instituted between the ages of 4 and 9. 2. Selected cases of hypogo ...
ch18 outline
... 4. Androgens secreted by the adrenal cortex usually have minimal effects in the male but more pronounced effects in the female. a. Clinical Connection: An absence in the ability to produce Cortisol, from birth, causes Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia, which results in excessive androgens. This disorde ...
... 4. Androgens secreted by the adrenal cortex usually have minimal effects in the male but more pronounced effects in the female. a. Clinical Connection: An absence in the ability to produce Cortisol, from birth, causes Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia, which results in excessive androgens. This disorde ...
A Guide for Patients - New England Fertility
... Fibroids arise when a single muscle cell in the uterine wall multiplies rapidly to form a tumor. The exact cause of uterine fibroids is unclear, but there is evidence that they require estrogen for growth. Fibroids may grow during pregnancy, a high estrogen state. After menopause, when estrogen leve ...
... Fibroids arise when a single muscle cell in the uterine wall multiplies rapidly to form a tumor. The exact cause of uterine fibroids is unclear, but there is evidence that they require estrogen for growth. Fibroids may grow during pregnancy, a high estrogen state. After menopause, when estrogen leve ...
13 Physiologicoanatomical peculiarities of endocrine system in
... comprised of somatotroph cells of the anterior pituitary. These somatotroph adenomas are benign and grow slowly, gradually producing more and more GH. Prolonged GH excess thickens the bones of the jaw, fingers and toes. Resulting heaviness of the jaw and increased thickness of digits is referred to ...
... comprised of somatotroph cells of the anterior pituitary. These somatotroph adenomas are benign and grow slowly, gradually producing more and more GH. Prolonged GH excess thickens the bones of the jaw, fingers and toes. Resulting heaviness of the jaw and increased thickness of digits is referred to ...
consent for transfer of embryos from thawed oocytes
... College to use my frozen oocytes (eggs) for the purposes of achieving a pregnancy. I/We understand that there are several steps involved in using these frozen oocytes outlined below. Timing of oocyte thaw I/We understand that while preparing for transfer of embryos from thawed oocytes (TETO), I will ...
... College to use my frozen oocytes (eggs) for the purposes of achieving a pregnancy. I/We understand that there are several steps involved in using these frozen oocytes outlined below. Timing of oocyte thaw I/We understand that while preparing for transfer of embryos from thawed oocytes (TETO), I will ...
FIGO classification system (PALM-COEIN) for causes of abnormal
... AUB may present in the context of existing chronic AUB or might occur without such a history. Although women of reproductive age with acute AUB require immediate intervention, their follow-up may be largely dependent upon whether they require investigation and ongoing care for an underlying chronic ...
... AUB may present in the context of existing chronic AUB or might occur without such a history. Although women of reproductive age with acute AUB require immediate intervention, their follow-up may be largely dependent upon whether they require investigation and ongoing care for an underlying chronic ...
FIGO classification system (PALM-COEIN)
... AUB may present in the context of existing chronic AUB or might occur without such a history. Although women of reproductive age with acute AUB require immediate intervention, their follow-up may be largely dependent upon whether they require investigation and ongoing care for an underlying chronic ...
... AUB may present in the context of existing chronic AUB or might occur without such a history. Although women of reproductive age with acute AUB require immediate intervention, their follow-up may be largely dependent upon whether they require investigation and ongoing care for an underlying chronic ...
Regulating Plasma Hormone Levels
... bile. They may then be reabsorbed into the blood and excreted via kidneys into urine. Some is excreted with bile in feces. • Thyroid hormones (nonpeptide) are similarly metabolized by the liver. ...
... bile. They may then be reabsorbed into the blood and excreted via kidneys into urine. Some is excreted with bile in feces. • Thyroid hormones (nonpeptide) are similarly metabolized by the liver. ...
AP Biology Notes Outline Chapter 45: Hormones and the Endocrine
... CONCEPT 45.1 – The endocrine system and the nervous system act individually and together in regulating an animal’s physiology. Animals have two major regulatory systems that release chemicals; the endocrine system and the nervous system. The endocrine system secretes hormones, while the nervous syst ...
... CONCEPT 45.1 – The endocrine system and the nervous system act individually and together in regulating an animal’s physiology. Animals have two major regulatory systems that release chemicals; the endocrine system and the nervous system. The endocrine system secretes hormones, while the nervous syst ...
PREMARIN®Editorial change.(conjugated estrogens tablets, USP)
... PREMARIN® (conjugated estrogens tablets, USP) for oral administration contains a mixture of conjugated estrogens obtained exclusively from natural sources, occurring as the sodium salts of water-soluble estrogen sulfates blended to represent the average composition of material derived ...
... PREMARIN® (conjugated estrogens tablets, USP) for oral administration contains a mixture of conjugated estrogens obtained exclusively from natural sources, occurring as the sodium salts of water-soluble estrogen sulfates blended to represent the average composition of material derived ...
Hormones in Wellness and Disease Prevention: Common Practices
... over the course of 3 years, oral conjugated estrogen taken alone or with synthetic progestins or micronized progesterone was associated with clinically significant improvement in lipoprotein profile and lowered fibrinogen levels. PEPI also demonstrated significant losses in high-density lipoprotein ...
... over the course of 3 years, oral conjugated estrogen taken alone or with synthetic progestins or micronized progesterone was associated with clinically significant improvement in lipoprotein profile and lowered fibrinogen levels. PEPI also demonstrated significant losses in high-density lipoprotein ...
Hormones in Wellness and Disease Prevention
... over the course of 3 years, oral conjugated estrogen taken alone or with synthetic progestins or micronized progesterone was associated with clinically significant improvement in lipoprotein profile and lowered fibrinogen levels. PEPI also demonstrated significant losses in high-density lipoprotein ...
... over the course of 3 years, oral conjugated estrogen taken alone or with synthetic progestins or micronized progesterone was associated with clinically significant improvement in lipoprotein profile and lowered fibrinogen levels. PEPI also demonstrated significant losses in high-density lipoprotein ...
Introduction to the Endocrine System
... Maturation of reproductive organs such as the uterus and vagina ...
... Maturation of reproductive organs such as the uterus and vagina ...
Development of low-dose reproductive hormone therapies in China
... hormone deficiency. The most obvious postmenopausal complications are the menopausal syndrome, urogenital tract atrophy, osteoporosis, atherosclerotic vascular diseases and dementia. There are other complications, which affect every organ system and are only now being appreciated [4]. The menopausal ...
... hormone deficiency. The most obvious postmenopausal complications are the menopausal syndrome, urogenital tract atrophy, osteoporosis, atherosclerotic vascular diseases and dementia. There are other complications, which affect every organ system and are only now being appreciated [4]. The menopausal ...
product monograph
... From the original HERS trial, 2321 women consented to participate in an open label extension of HERS, known as HERS II. Average follow-up in HERS II was an additional 2.7 years, for a total of 6.8 years overall. After 6.8 years, hormone therapy did not reduce the risk of cardiovascular events in wo ...
... From the original HERS trial, 2321 women consented to participate in an open label extension of HERS, known as HERS II. Average follow-up in HERS II was an additional 2.7 years, for a total of 6.8 years overall. After 6.8 years, hormone therapy did not reduce the risk of cardiovascular events in wo ...
Glucose Homeostasis
... • Prolonged fasting leads to phase V • Less dependence on gluconeogenesis • All body tissues mainly use FA and KB oxidation for energy production • Gluconeogenesis somewhat maintains blood glucose level in this phase ...
... • Prolonged fasting leads to phase V • Less dependence on gluconeogenesis • All body tissues mainly use FA and KB oxidation for energy production • Gluconeogenesis somewhat maintains blood glucose level in this phase ...
L6- Glucose Homeostasis
... • Prolonged fasting leads to phase V • Less dependence on gluconeogenesis • All body tissues mainly use FA and KB oxidation for energy production • Gluconeogenesis somewhat maintains blood glucose level in this phase ...
... • Prolonged fasting leads to phase V • Less dependence on gluconeogenesis • All body tissues mainly use FA and KB oxidation for energy production • Gluconeogenesis somewhat maintains blood glucose level in this phase ...
endocrine system - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Gonadal hormones ~ estrogen, testosterone Adrenalcorticoids hormones ~ corticosteroids Eicosanoids (eye cos an oids) Increase inflammation & cause swelling NON-CIRCULATING hormones ~ act locally only Released from most cell membranes & have a highly localized response Prostaglandins ~ most common ...
... Gonadal hormones ~ estrogen, testosterone Adrenalcorticoids hormones ~ corticosteroids Eicosanoids (eye cos an oids) Increase inflammation & cause swelling NON-CIRCULATING hormones ~ act locally only Released from most cell membranes & have a highly localized response Prostaglandins ~ most common ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.