Chemistry A - Montgomery County Public Schools
... describe the characteristics of protons, neutrons and electrons in terms of location, charge and mass. illustrate the structure of the atom by using the Bohr model, including the charge, relative mass and location of the sub-atomic particles. use atomic mass, atomic number, and charge to ident ...
... describe the characteristics of protons, neutrons and electrons in terms of location, charge and mass. illustrate the structure of the atom by using the Bohr model, including the charge, relative mass and location of the sub-atomic particles. use atomic mass, atomic number, and charge to ident ...
Ch. 2 Chemistry
... (b) An electron can move from one level to another only if the energy it gains or loses is exactly equal to the difference in energy between the two levels. Arrows indicate some of the step-wise changes in potential energy that are possible. Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Ben ...
... (b) An electron can move from one level to another only if the energy it gains or loses is exactly equal to the difference in energy between the two levels. Arrows indicate some of the step-wise changes in potential energy that are possible. Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Ben ...
atom
... In 1869, Mendeleev noticed that certain groups of elements had similar properties. He also found that when he listed elements in order of increasing mass, these similar properties recurred in a periodic pattern ...
... In 1869, Mendeleev noticed that certain groups of elements had similar properties. He also found that when he listed elements in order of increasing mass, these similar properties recurred in a periodic pattern ...
Student Expectation
... Key Concept 2: Electrons are located outside of the nucleus and arranged by energy levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. Key Concept 3: Electrons located in the outermost shell of the electron cloud are called “valence electrons” and h ...
... Key Concept 2: Electrons are located outside of the nucleus and arranged by energy levels in the electron cloud. There are a certain number of electrons that each energy level can hold. Key Concept 3: Electrons located in the outermost shell of the electron cloud are called “valence electrons” and h ...
Atoms/Atomic Theory PPT
... Thomson (English 1897) did more experiments to actually make the discovery he found ratio of charge of this particle to this mass of the particle since the ratio stayed constant for any metal that contained it, it must be the same in all of the metals ...
... Thomson (English 1897) did more experiments to actually make the discovery he found ratio of charge of this particle to this mass of the particle since the ratio stayed constant for any metal that contained it, it must be the same in all of the metals ...
only that they did. democritus, an early greek philosopher, even had
... Being asked what animal you'd like to be is a trick question; you're already an animal. Doug Coupland ...
... Being asked what animal you'd like to be is a trick question; you're already an animal. Doug Coupland ...
Ch 30 Nuclear Physics
... been developed for 14C dates back to about 5000 B.C. Carbon dating is widely used in archaeology, and has been used to date bones and other organic remains, charcoal from fires, beams in pyramids, the Dead Sea Scrolls, and the Shroud of Turin. ...
... been developed for 14C dates back to about 5000 B.C. Carbon dating is widely used in archaeology, and has been used to date bones and other organic remains, charcoal from fires, beams in pyramids, the Dead Sea Scrolls, and the Shroud of Turin. ...
Multiple Choice - EDU360ScienceMethods
... ESSAY: Use complete sentences and support your ideas. 1. How is the Periodic Table organized and why? What can it tell us about the elements and their properties? The periodic table is set up into columns and rows. The columns are known as groups or families. The vertical rows are called periods. Th ...
... ESSAY: Use complete sentences and support your ideas. 1. How is the Periodic Table organized and why? What can it tell us about the elements and their properties? The periodic table is set up into columns and rows. The columns are known as groups or families. The vertical rows are called periods. Th ...
C:\Users\Jim\Documents\school stuff\atomic structure.wpd
... c) When pure liquids are mixed, the combined volume often is different from the sum of the original volumes of the separate substances. This only makes sense if the liquids are made of particles which are of different sizes (imagine mixing equal volumes of sand and ping-pong balls) d) When elements ...
... c) When pure liquids are mixed, the combined volume often is different from the sum of the original volumes of the separate substances. This only makes sense if the liquids are made of particles which are of different sizes (imagine mixing equal volumes of sand and ping-pong balls) d) When elements ...
Name ____ Date
... development of various atomic models, both historic and current. 3. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, position and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atoms of different elements. 4. Correlate atomic structure and the physical and chemical properties of an element to the ...
... development of various atomic models, both historic and current. 3. Discriminate between the relative size, charge, position and number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in the atoms of different elements. 4. Correlate atomic structure and the physical and chemical properties of an element to the ...
Practice exam Part 3 Name 1) A Ca 2+ ion differs from a Ca0 atom in
... Name ______________________________ ...
... Name ______________________________ ...
Electrons
... the elements in the second row (the second period) have two orbitals for their electrons. It goes down the periodic table like that. At this time, the maximum number of electron orbitals or electron shells for any element is seven. ...
... the elements in the second row (the second period) have two orbitals for their electrons. It goes down the periodic table like that. At this time, the maximum number of electron orbitals or electron shells for any element is seven. ...
Sub Unit Plan 1 Chem Periodic Table
... II.3 Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te), and noble gases. (3.1v) II.4 Elements can be differentiated by their physical properties. Physical properties of substances, such as density, conductivity, ...
... II.3 Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te), and noble gases. (3.1v) II.4 Elements can be differentiated by their physical properties. Physical properties of substances, such as density, conductivity, ...
atomic number
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qQNpucos9wc http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RIg1Vh7uPyw&list=TL9l iUotc3avVG69w_AB1a0zk9sCfDLWVc&safe=active ...
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qQNpucos9wc http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RIg1Vh7uPyw&list=TL9l iUotc3avVG69w_AB1a0zk9sCfDLWVc&safe=active ...
The Periodic Table
... as how readily an atom can lose an electron. From right to left across a period, metallic character increases because the attraction between valence electron and the nucleus is weaker, enabling an easier loss of electrons. Metallic character increases as you move down a group because the atomic ...
... as how readily an atom can lose an electron. From right to left across a period, metallic character increases because the attraction between valence electron and the nucleus is weaker, enabling an easier loss of electrons. Metallic character increases as you move down a group because the atomic ...
Atoms & Elements2013
... chemical reaction. Word origin: atom comes from the Greek word atomos meaning “ indivisible” ...
... chemical reaction. Word origin: atom comes from the Greek word atomos meaning “ indivisible” ...
Chapter 3 – Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter - Hatboro
... This idea succeeded for about _______years. Neither view was supported by __________ _________ until ________. ...
... This idea succeeded for about _______years. Neither view was supported by __________ _________ until ________. ...
PS_Module 4 - Leon County Schools
... ways it can react to form new materials. • Chemical properties cannot be measured or studied without changing the composition of the substance. – Flammability and other tendencies to react with oxygen – Reaction with acids and bases – Reaction with water – Decomposition caused by light or heat – Ten ...
... ways it can react to form new materials. • Chemical properties cannot be measured or studied without changing the composition of the substance. – Flammability and other tendencies to react with oxygen – Reaction with acids and bases – Reaction with water – Decomposition caused by light or heat – Ten ...
Chapter 12 –Radioactivity
... discovered more radioactive elements including polonium and radium. • She used the word radioactivity to describe the property of certain substances to give off invisible “radiations” that could be detected by films. • Scientists soon realised that there were three different types of radiation. • Th ...
... discovered more radioactive elements including polonium and radium. • She used the word radioactivity to describe the property of certain substances to give off invisible “radiations” that could be detected by films. • Scientists soon realised that there were three different types of radiation. • Th ...
Do not forget to study your polyatomic ions! Honors Chemistry
... 18. The number of significant figures in the measured value 0.032 0 g is a. 2. b. 3. c. 4. d. 5. 19. Which orbitals can be modeled as dumbbell shaped? a. s b. p c. d d. f 20. The most massive particle in an atom is the a. proton. b. neutron. c. electron. d. None of the above 21. The molar mass of an ...
... 18. The number of significant figures in the measured value 0.032 0 g is a. 2. b. 3. c. 4. d. 5. 19. Which orbitals can be modeled as dumbbell shaped? a. s b. p c. d d. f 20. The most massive particle in an atom is the a. proton. b. neutron. c. electron. d. None of the above 21. The molar mass of an ...
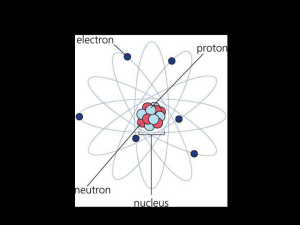
The atomic number tells how many protons Protons make an atom
... to put two together, they push away from each other. ...
... to put two together, they push away from each other. ...
The Atom Review Packet
... 7. The total number of electrons in a neutral atom of every element is always equal to the atom’s (1) mass number (2) number of neutrons (3) number of protons (4) number of nucleons 8. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of (1) neutrons in the atom (2) protons in the atom (3) neutron ...
... 7. The total number of electrons in a neutral atom of every element is always equal to the atom’s (1) mass number (2) number of neutrons (3) number of protons (4) number of nucleons 8. The atomic number of an atom is equal to the number of (1) neutrons in the atom (2) protons in the atom (3) neutron ...
Atomic Theory 1
... Number. E.g. All hydrogen (H) atoms have 1 proton in their nuclei, while all carbon (C) atoms have 6 protons in their nuclei). HOWEVER, an element can have a VARIABLE number of neutrons in its nuclei. (This does NOT alter the identity of the element (#p same), but DOES make the element heavier or li ...
... Number. E.g. All hydrogen (H) atoms have 1 proton in their nuclei, while all carbon (C) atoms have 6 protons in their nuclei). HOWEVER, an element can have a VARIABLE number of neutrons in its nuclei. (This does NOT alter the identity of the element (#p same), but DOES make the element heavier or li ...
Atomic Theory Part 1
... Number. E.g. All hydrogen (H) atoms have 1 proton in their nuclei, while all carbon (C) atoms have 6 protons in their nuclei). HOWEVER, an element can have a VARIABLE number of neutrons in its nuclei. (This does NOT alter the identity of the element (#p same), but DOES make the element heavier or li ...
... Number. E.g. All hydrogen (H) atoms have 1 proton in their nuclei, while all carbon (C) atoms have 6 protons in their nuclei). HOWEVER, an element can have a VARIABLE number of neutrons in its nuclei. (This does NOT alter the identity of the element (#p same), but DOES make the element heavier or li ...