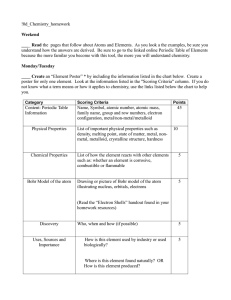
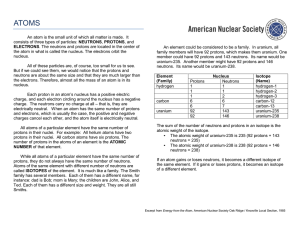
ATOMIC THEORY
... alike, but we know that is not completely true. So what is alike? 1. All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. 2. If the atom is neutral, that means they also have the same number of electrons. 3. The number of neutrons, however, can ...
... alike, but we know that is not completely true. So what is alike? 1. All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. 2. If the atom is neutral, that means they also have the same number of electrons. 3. The number of neutrons, however, can ...
10_Chemistry homework
... Answer: The atomic number for sulfur is 16. The number of neutrons = A - Z = 33 - 16 = 17 An atom contains 24 neutrons and 25 protons, what is the mass number of the atom? Answer: Mass number = A = number protons + number of neutrons = 24 + 25 = 49 An atom with a mass number of 39 contains 20 neutro ...
... Answer: The atomic number for sulfur is 16. The number of neutrons = A - Z = 33 - 16 = 17 An atom contains 24 neutrons and 25 protons, what is the mass number of the atom? Answer: Mass number = A = number protons + number of neutrons = 24 + 25 = 49 An atom with a mass number of 39 contains 20 neutro ...
Document
... blocks, of elements according to the subshells that are last to fill, s, p, d, or f. ►Beginning at the top left corner of the periodic table, the first row contains only two elements, H and He. The 1s subshell is being filled here. ►The second row begins with two s-block elements (Li and Be) and con ...
... blocks, of elements according to the subshells that are last to fill, s, p, d, or f. ►Beginning at the top left corner of the periodic table, the first row contains only two elements, H and He. The 1s subshell is being filled here. ►The second row begins with two s-block elements (Li and Be) and con ...
04 Atom notes
... John Dalton (English chemist & schoolteacher, _____________) using _______________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ How was John Dalton able to study atoms even though he was unable to see them directly? What eviden ...
... John Dalton (English chemist & schoolteacher, _____________) using _______________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ How was John Dalton able to study atoms even though he was unable to see them directly? What eviden ...
The Atom
... • His theory explained some observations but could not provide enough evidence to convince people that atoms really existed ...
... • His theory explained some observations but could not provide enough evidence to convince people that atoms really existed ...
Chapter 3
... blocks, of elements according to the subshells that are last to fill, s, p, d, or f. ▶Beginning at the top left corner of the periodic table, the first row contains only two elements, H and He. The 1s subshell is being filled here. ▶The second row begins with two s-block elements (Li and Be) and con ...
... blocks, of elements according to the subshells that are last to fill, s, p, d, or f. ▶Beginning at the top left corner of the periodic table, the first row contains only two elements, H and He. The 1s subshell is being filled here. ▶The second row begins with two s-block elements (Li and Be) and con ...
Academic Chemistry Midterm Study Guide Chapters 1
... 35. Explain the steps needed to successfully light a Bunsen burner and obtain a blue (non-luminous) flame. 1. Turn on the gas, use striker to light 2. Adjust the gas to produce a flame of proper height 3. Open the air holes until a blue flame is produced 36. List five safety rules that must be follo ...
... 35. Explain the steps needed to successfully light a Bunsen burner and obtain a blue (non-luminous) flame. 1. Turn on the gas, use striker to light 2. Adjust the gas to produce a flame of proper height 3. Open the air holes until a blue flame is produced 36. List five safety rules that must be follo ...
atomic mass - Cloudfront.net
... because of its protons. • In a neutral atom the proton # = electron # • B = Boron = __p+, __e• Cl = Chlorine = ____p+, ____e- ...
... because of its protons. • In a neutral atom the proton # = electron # • B = Boron = __p+, __e• Cl = Chlorine = ____p+, ____e- ...
Periodic Table Trends - Magoffin County Schools
... decrease left to right along a period, so group 1 atoms are generally larger than group 18 atoms. • This is because, within a period, the number of principle energy levels (PELs) in each element generally remains constant. • For example, all elements in Period 3 have three energy levels. However, th ...
... decrease left to right along a period, so group 1 atoms are generally larger than group 18 atoms. • This is because, within a period, the number of principle energy levels (PELs) in each element generally remains constant. • For example, all elements in Period 3 have three energy levels. However, th ...
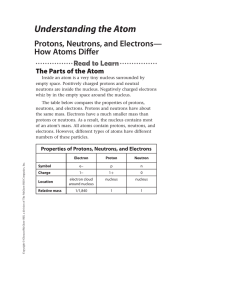
An atom is the small unit of which all matter is made. It consists of
... An atom is the small unit of which all matter is made. It consists of three types of particles: NEUTRONS, PROTONS, and ELECTRONS. The neutrons and protons are located in the center of the atom in what is called the nucleus. The electrons orbit the nucleus. All of these particles are, of course, too ...
... An atom is the small unit of which all matter is made. It consists of three types of particles: NEUTRONS, PROTONS, and ELECTRONS. The neutrons and protons are located in the center of the atom in what is called the nucleus. The electrons orbit the nucleus. All of these particles are, of course, too ...
Chapter 4 powerpoint
... beta (charge of 1–), and gamma (no charge). • The neutron-to-proton ratio of an atom’s nucleus determines its stability. ...
... beta (charge of 1–), and gamma (no charge). • The neutron-to-proton ratio of an atom’s nucleus determines its stability. ...
Intro to the atom - thsicp-23
... The term matter describes all of the physical substances around us: your table, your body, a pencil, water, and so forth ...
... The term matter describes all of the physical substances around us: your table, your body, a pencil, water, and so forth ...
Follow the steps to find the number
... 3. The number of electrons in a sodium +1 ion. Multiply by the number of protons in an atom of Sn. Divide by the number of neutrons in at atom of H-2. Multiply by the number of electrons in an atom of neutral barium. 4. The number of electrons in Cu. Subtract the number of neutrons in F. Multiply by ...
... 3. The number of electrons in a sodium +1 ion. Multiply by the number of protons in an atom of Sn. Divide by the number of neutrons in at atom of H-2. Multiply by the number of electrons in an atom of neutral barium. 4. The number of electrons in Cu. Subtract the number of neutrons in F. Multiply by ...
Course Outline
... In a neutral atom, the number of protons in the nucleus equals th number the b off electrons. l t ...
... In a neutral atom, the number of protons in the nucleus equals th number the b off electrons. l t ...
September 22 Bellwork
... isotopes. 78.70% of Magnesium atoms exist as Magnesium-24 (23.9850 g/mol), 10.03% exist as Magnesium-25 (24.9858 g/mol) and 11.17% exist as Magnesium-26 (25.9826 g/mol). What is the average atomic mass of Magnesium? Atomic Mass of Magnesium= ...
... isotopes. 78.70% of Magnesium atoms exist as Magnesium-24 (23.9850 g/mol), 10.03% exist as Magnesium-25 (24.9858 g/mol) and 11.17% exist as Magnesium-26 (25.9826 g/mol). What is the average atomic mass of Magnesium? Atomic Mass of Magnesium= ...
Understanding the Atom
... covered a photographic plate with black paper, this energy would pass through the paper and expose the film. An image of the mineral appeared on the plate. One day, Becquerel left the mineral in a drawer next to a wrapped, unexposed plate. Later, he unwrapped the plate and found that it contained an ...
... covered a photographic plate with black paper, this energy would pass through the paper and expose the film. An image of the mineral appeared on the plate. One day, Becquerel left the mineral in a drawer next to a wrapped, unexposed plate. Later, he unwrapped the plate and found that it contained an ...
Explaining the Periodic Table (6.7)
... Explaining the Periodic Table (6.7) • If elements are the building blocks of all other matter, what are they made of? • There are three particles that make up an atom or element: • protons • electrons • neutrons • These are called subatomic particles because they are smaller or below an atom. ...
... Explaining the Periodic Table (6.7) • If elements are the building blocks of all other matter, what are they made of? • There are three particles that make up an atom or element: • protons • electrons • neutrons • These are called subatomic particles because they are smaller or below an atom. ...
Class 9 CBSE Test paper Solved Chapter 3: Structure of...
... there in one atom of this radon isotope? Ans: protons = 86 neutrons = 222 - 86 = 136 electrons = 86 Long Answer Questions Q.9) Why do isotopes show similar chemical properties? Ans: This is because isotopes have same no of electrons ...
... there in one atom of this radon isotope? Ans: protons = 86 neutrons = 222 - 86 = 136 electrons = 86 Long Answer Questions Q.9) Why do isotopes show similar chemical properties? Ans: This is because isotopes have same no of electrons ...
File
... 25. The average isotopic mass of chlorine is 35.5. Which mixture of isotopes (shown as percents) produces this average mass? A) 50% 12C and 50% 13C B) 50% 35Cl and 50% 37Cl C) 75% 35Cl and 25% 37Cl D) 75% 12C and 25% 13C 26. A sample of element X contains 90. percent 35X atoms, 8.0 percent 37X atoms ...
... 25. The average isotopic mass of chlorine is 35.5. Which mixture of isotopes (shown as percents) produces this average mass? A) 50% 12C and 50% 13C B) 50% 35Cl and 50% 37Cl C) 75% 35Cl and 25% 37Cl D) 75% 12C and 25% 13C 26. A sample of element X contains 90. percent 35X atoms, 8.0 percent 37X atoms ...
Masses of Atoms and the Periodic Table
... neutrons in an atom is the mass number – A fluoride atom with 9 protons and 10 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A sodium atom with 11 protons and 12 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 0 neutrons has a mass number of ________ ...
... neutrons in an atom is the mass number – A fluoride atom with 9 protons and 10 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A sodium atom with 11 protons and 12 neutrons has a mass number of _________ – A hydrogen atom with 1 proton and 0 neutrons has a mass number of ________ ...
Atoms and Molecules - Library Video Company
... groups of atoms called molecules. Atoms themselves are made of subatomic particles called electrons, protons and neutrons.The nucleus of every atom is made of a certain number of protons and neutrons and orbiting this nucleus are smaller particles called electrons.These particles each have an electr ...
... groups of atoms called molecules. Atoms themselves are made of subatomic particles called electrons, protons and neutrons.The nucleus of every atom is made of a certain number of protons and neutrons and orbiting this nucleus are smaller particles called electrons.These particles each have an electr ...
lecture CH2 chem121pikul
... soccer ball. A component of soot, this form of carbon was not discovered until 1985. Its unusual name stems from its shape, which resembles the geodesic dome invented by R. Buckminster Fuller. ...
... soccer ball. A component of soot, this form of carbon was not discovered until 1985. Its unusual name stems from its shape, which resembles the geodesic dome invented by R. Buckminster Fuller. ...
Atoms and Molecules - Distribution Access
... groups of atoms called molecules. Atoms themselves are made of subatomic particles called electrons, protons and neutrons.The nucleus of every atom is made of a certain number of protons and neutrons and orbiting this nucleus are smaller particles called electrons.These particles each have an electr ...
... groups of atoms called molecules. Atoms themselves are made of subatomic particles called electrons, protons and neutrons.The nucleus of every atom is made of a certain number of protons and neutrons and orbiting this nucleus are smaller particles called electrons.These particles each have an electr ...
atom
... be. Atoms with electrons in higher energy levels have additional electron clouds of different shapes that also show where those electrons are likely to be. For more information, click here: http://regentsprep.org/Regents/physics/phys05/catomodel/cloud.htm ...
... be. Atoms with electrons in higher energy levels have additional electron clouds of different shapes that also show where those electrons are likely to be. For more information, click here: http://regentsprep.org/Regents/physics/phys05/catomodel/cloud.htm ...
History of Periodic Table
... Dmitri Mendeleev (1871) • Developed the first Periodic Table • He arranged his table so that elements in the same column (groups) have similar properties; increasing atomic mass ...
... Dmitri Mendeleev (1871) • Developed the first Periodic Table • He arranged his table so that elements in the same column (groups) have similar properties; increasing atomic mass ...