Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... • Which parts of an atom make up the mass of the atom? • Elements are made up of? • The element lead is made up of what kind of atoms? ...
... • Which parts of an atom make up the mass of the atom? • Elements are made up of? • The element lead is made up of what kind of atoms? ...
Chemistry Chapter 4 (Due October 24) [Test
... ____ 15. Dalton hypothesized that atoms are indivisible and that all atoms of an element are identical. It is now known that ____. a. all of Dalton's hypotheses are correct b. atoms of an element can have different numbers of protons c. atoms are divisible d. all atoms of an element are not identic ...
... ____ 15. Dalton hypothesized that atoms are indivisible and that all atoms of an element are identical. It is now known that ____. a. all of Dalton's hypotheses are correct b. atoms of an element can have different numbers of protons c. atoms are divisible d. all atoms of an element are not identic ...
The History of the Periodic Table
... other workers had reported. For the rest of the 19th century, atomic masses were continually revised and improved and new elements were rapidly being discovered By 1817, it was recognized that some elements could be placed into groups, using their physical and chemical properties. Elements with clos ...
... other workers had reported. For the rest of the 19th century, atomic masses were continually revised and improved and new elements were rapidly being discovered By 1817, it was recognized that some elements could be placed into groups, using their physical and chemical properties. Elements with clos ...
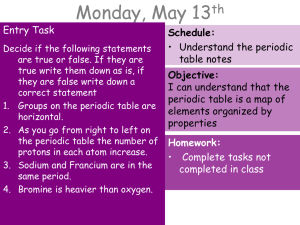
Entry Task
... • If a group has more than 4 they take electrons- making them – ions • If they have 4 they can do either • What they do with their electrons determines what other elements they bond with – Oxygen has 6 electrons and Hydrogen has 1 electron – H2 O is two hydrogen (2 electrons) and one oxygen (6 elect ...
... • If a group has more than 4 they take electrons- making them – ions • If they have 4 they can do either • What they do with their electrons determines what other elements they bond with – Oxygen has 6 electrons and Hydrogen has 1 electron – H2 O is two hydrogen (2 electrons) and one oxygen (6 elect ...
File
... w/ metals (NaCl, FeO2, and CaCl2 ) and usually form covalent bonds when combined w/ other nonmetals (CO2, O2, C6H12O6) ...
... w/ metals (NaCl, FeO2, and CaCl2 ) and usually form covalent bonds when combined w/ other nonmetals (CO2, O2, C6H12O6) ...
Chapter 16 Physical Science The Periodic Table Parts of an Atom
... (NaCl, FeO2, and CaCl2 ) and usually form covalent bonds when combined w/ other nonmetals (CO2, O2, C6H12O6) – Asbestos – substance once used for its fire retardant characteristics but is no longer used because of it’s a carcinogen. – Carbon – the element on which all life is based. ...
... (NaCl, FeO2, and CaCl2 ) and usually form covalent bonds when combined w/ other nonmetals (CO2, O2, C6H12O6) – Asbestos – substance once used for its fire retardant characteristics but is no longer used because of it’s a carcinogen. – Carbon – the element on which all life is based. ...
Atomic Number
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • John Dalton (1766-1844), an English schoolteacher and chemist, • Studied the theories and the results of experiments by other scientists. • He formed a hypothesis, experimented, and came up with a theory. • Dalton proposed his atomic theory of matter in 1803. ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • John Dalton (1766-1844), an English schoolteacher and chemist, • Studied the theories and the results of experiments by other scientists. • He formed a hypothesis, experimented, and came up with a theory. • Dalton proposed his atomic theory of matter in 1803. ...
Chapter 4, Lesson 2: The Periodic Table
... or neutron). The majority of the atomic mass is contributed by the protons and neutrons. For any element in the periodic table, the number of electrons in an atom of that element always equals the number of protons in the nucleus. But this is not true for neutrons. Atoms of the same element can have ...
... or neutron). The majority of the atomic mass is contributed by the protons and neutrons. For any element in the periodic table, the number of electrons in an atom of that element always equals the number of protons in the nucleus. But this is not true for neutrons. Atoms of the same element can have ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
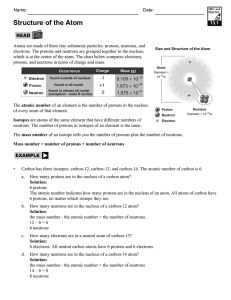
... The atomic number (also called “proton number”) of an atom is the number of protons it contains. All the atoms of a particular element have the same atomic number (number of protons). The atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons. For example, all oxygen atoms have 8 protons and ...
... The atomic number (also called “proton number”) of an atom is the number of protons it contains. All the atoms of a particular element have the same atomic number (number of protons). The atoms of different elements have different numbers of protons. For example, all oxygen atoms have 8 protons and ...
Investigating Atoms and Atomic Theory
... The morale of Matterville is stable as long as each negative Electron brother is balanced out by one positive Proton sister. The number of residents in Matterville depends on the Proton and Neutron families. Challenge: What would happen to the morale of Matterville if one Elliott Electron was kidna ...
... The morale of Matterville is stable as long as each negative Electron brother is balanced out by one positive Proton sister. The number of residents in Matterville depends on the Proton and Neutron families. Challenge: What would happen to the morale of Matterville if one Elliott Electron was kidna ...
Atomic Structure Paper Plate Model Plate 1: Front
... Back- Write a brief explanation about how you formed your ion. Did your element need to gain or lose electrons? How many? Why? What is the overall charge on your Ion? (+1, +2, or -1) Plate 3: Front- Draw an Isotope that represents your element. Label the features that make this an isotope compared t ...
... Back- Write a brief explanation about how you formed your ion. Did your element need to gain or lose electrons? How many? Why? What is the overall charge on your Ion? (+1, +2, or -1) Plate 3: Front- Draw an Isotope that represents your element. Label the features that make this an isotope compared t ...
DEFINING THE ATOM - Southgate Schools
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in ...
... Part B True-False Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 11. The atomic number of an element is the sum of the protons and electrons in an atom of that element. ________ 12. The atomic number of an atom is the total number of protons in ...
- Dr.Divan Fard
... Different electrons have different amounts of energy and thus occupy different regions within the atom. The energies of electrons are quantized, or restricted to having only certain values. The electrons in an atom are grouped around the nucleus into shells. Within the shells, electrons are further ...
... Different electrons have different amounts of energy and thus occupy different regions within the atom. The energies of electrons are quantized, or restricted to having only certain values. The electrons in an atom are grouped around the nucleus into shells. Within the shells, electrons are further ...
10C The Periodic Table
... table charts, and information about them, in your local library or on the Internet. A periodic table holds an amazing amount of information. In this skill sheet, you will use a periodic table to identify information about specific elements, make calculations, and make predictions. Read: ...
... table charts, and information about them, in your local library or on the Internet. A periodic table holds an amazing amount of information. In this skill sheet, you will use a periodic table to identify information about specific elements, make calculations, and make predictions. Read: ...
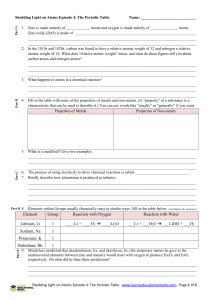
Element Group Reaction with Oxygen Reaction with Water Lithium
... 9. Mendeleev predicted that ekaaluminium, Ea, and ekasilicon, Es, (the temporary names he gave to the undiscovered elements between zinc and arsenic) would react with oxygen to produce Ea2O3 and EsO2 respectively. On what did he base these predictions? ...
... 9. Mendeleev predicted that ekaaluminium, Ea, and ekasilicon, Es, (the temporary names he gave to the undiscovered elements between zinc and arsenic) would react with oxygen to produce Ea2O3 and EsO2 respectively. On what did he base these predictions? ...
02 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 1. Write the element symbol.. 2. Determine the number of valence electrons the element has. Remember the valence electrons = group number. 3. Place the number of valence electrons as dots around the element symbol. ...
... 1. Write the element symbol.. 2. Determine the number of valence electrons the element has. Remember the valence electrons = group number. 3. Place the number of valence electrons as dots around the element symbol. ...
SUBATOMIC PARTICLES The three main subatomic particles found
... of rare isotopes that may not be included in the percentages when calculating atomic mass. ...
... of rare isotopes that may not be included in the percentages when calculating atomic mass. ...
CHEMISTRY OLYMPICS 2nd 6 weeks What particles form the
... • A) that electrons orbit the nucleus • B) that atoms are made of positively and negatively charged particles • C) that most of an atom’s mass is concentrated in a relatively small portion of the atom’s entire volume • D) that all neutrons are located in the nucleus ...
... • A) that electrons orbit the nucleus • B) that atoms are made of positively and negatively charged particles • C) that most of an atom’s mass is concentrated in a relatively small portion of the atom’s entire volume • D) that all neutrons are located in the nucleus ...
The number of neutrons in the nucleus of a specific atom is equal to its
... Quantum physics requires the speed of light to be a constant value. Classical physics requires that only certain, allowed values for energy be used. Quantum physics requires that only certain, allowed values for energy be used. Quantum physics can only describe the behavior of very small objects, li ...
... Quantum physics requires the speed of light to be a constant value. Classical physics requires that only certain, allowed values for energy be used. Quantum physics requires that only certain, allowed values for energy be used. Quantum physics can only describe the behavior of very small objects, li ...
Bohr Model - TeacherWeb
... But when it comes to reacting with other elements, it is the electrons that do all the work. Of course the electrons would not be with the atom if it weren’t for the positive charge of the protons keeping them there. ...
... But when it comes to reacting with other elements, it is the electrons that do all the work. Of course the electrons would not be with the atom if it weren’t for the positive charge of the protons keeping them there. ...
Chemistry Note PowerPoint
... • An atom’s valance electrons are those that have the highest energy levels and are held most loosely. • The number of valance electrons determine many properties of that element, including the ways in which the atom combines with other atoms ...
... • An atom’s valance electrons are those that have the highest energy levels and are held most loosely. • The number of valance electrons determine many properties of that element, including the ways in which the atom combines with other atoms ...
Atoms, Elements, and Compounds
... graduate research under the guidance of the man who discovered the electron, J. J. Thomson. Through his research with Thomson, Rutherford became interested in studying radioactivity. In 1898 he described two kinds of particles emitted from radioactive atoms, calling them alpha and beta particles. He ...
... graduate research under the guidance of the man who discovered the electron, J. J. Thomson. Through his research with Thomson, Rutherford became interested in studying radioactivity. In 1898 he described two kinds of particles emitted from radioactive atoms, calling them alpha and beta particles. He ...
Ch 17 Notes
... electrons are very small& do not significantly contribute to the atomic mass of atom mass of electron is small compared to mass of a nucleon in a electrically neutral atom: the number of electrons equals the number of protons ...
... electrons are very small& do not significantly contribute to the atomic mass of atom mass of electron is small compared to mass of a nucleon in a electrically neutral atom: the number of electrons equals the number of protons ...
1. Which sublevel is filled immediately before the 5p orbital? a. 4s b
... b. Some electrons in the atom going from higher to lower energy levels. c. The metal reacting with oxygen. d. Some electrons in the atom going from lower to higher energy levels. e. The atom ionizing. ...
... b. Some electrons in the atom going from higher to lower energy levels. c. The metal reacting with oxygen. d. Some electrons in the atom going from lower to higher energy levels. e. The atom ionizing. ...
Physical Science
... mixtures of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons. ...
... mixtures of isotopes. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that differ in the number of neutrons. ...