EPSc 446 STABLE ISOTOPE GEOCHEMISTRY Instructor: Bob Criss
... Found that a few α particles were deflected through large angles- up to 180°. ...
... Found that a few α particles were deflected through large angles- up to 180°. ...
Building Atoms - Community Science Workshop Network
... There are three main parts in each element’s squares. One or two letters represent the name of each element, and the first letter is always capitalized. For some elements one or two letters from th ...
... There are three main parts in each element’s squares. One or two letters represent the name of each element, and the first letter is always capitalized. For some elements one or two letters from th ...
Chapter 4 Atomic Structure
... atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. (3.) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine to form compounds. ...
... atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. (3.) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine to form compounds. ...
atomic number
... • The identity of an element is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus. the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. For example, any atom with 6 protons in the nucleus is a Carbon atom. • Elements are arranged in the periodic table by their atomic number. ...
... • The identity of an element is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus. the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is called the atomic number. For example, any atom with 6 protons in the nucleus is a Carbon atom. • Elements are arranged in the periodic table by their atomic number. ...
1 - kurtniedenzu
... a. fall back to lower energy levels b. are gained by a neutral atom c. are emitted by the nucleus as beta particles d. move to higher energy levels 2. Compared with an atom of C-12, an atom of C-14 has a. More protons b. Fewer protons c. More neutrons d. Fewer neutrons 3. How many electrons are pres ...
... a. fall back to lower energy levels b. are gained by a neutral atom c. are emitted by the nucleus as beta particles d. move to higher energy levels 2. Compared with an atom of C-12, an atom of C-14 has a. More protons b. Fewer protons c. More neutrons d. Fewer neutrons 3. How many electrons are pres ...
3 chemical foundations: elements, atoms and ions
... Lothar Meyer. Mendeleev gets the title of “Father of Modern Chemistry” because Meyer did not make any further use of his table. Mendeleev (and Meyer) noted that many of the known elements have very similar physical and chemical properties. Those atoms with such similar properties were put in columns ...
... Lothar Meyer. Mendeleev gets the title of “Father of Modern Chemistry” because Meyer did not make any further use of his table. Mendeleev (and Meyer) noted that many of the known elements have very similar physical and chemical properties. Those atoms with such similar properties were put in columns ...
Flavors of the Atom
... Atoms are the smallest particle of an element that can enter into a chemical reaction. Protons and neutrons make up the dense, positive nucleus. Electrons occupy the empty space outside the nucleus. A neutral atom contains the same number of electrons and protons. ...
... Atoms are the smallest particle of an element that can enter into a chemical reaction. Protons and neutrons make up the dense, positive nucleus. Electrons occupy the empty space outside the nucleus. A neutral atom contains the same number of electrons and protons. ...
Test 3 Review
... Wave Mechanical Model. The Bohr model successfully explained the bright line spectra for hydrogen, but could not explain the spectra of atoms with more electrons. The wave mechanical model solved the problem. The wave mechanical model describes the location of electrons a their most probable locatio ...
... Wave Mechanical Model. The Bohr model successfully explained the bright line spectra for hydrogen, but could not explain the spectra of atoms with more electrons. The wave mechanical model solved the problem. The wave mechanical model describes the location of electrons a their most probable locatio ...
Chapter 4 and 25 Study Guide
... 28. True or false? Between protons in a nucleus, attraction due to nuclear force is greater than repulsion due to electrostatic force. True 29. What happens to unstable nuclei? It undergoes radioactive decay 30. What is a beta particle? Symbol ; also called an electron 31. What is the change in the ...
... 28. True or false? Between protons in a nucleus, attraction due to nuclear force is greater than repulsion due to electrostatic force. True 29. What happens to unstable nuclei? It undergoes radioactive decay 30. What is a beta particle? Symbol ; also called an electron 31. What is the change in the ...
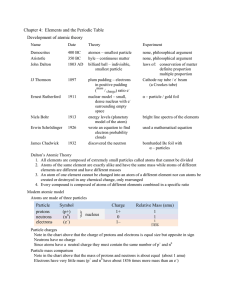
Chapter 4: Elements and the Periodic Table Development of atomic
... Some plants form a symbiotic relationship with bacteria that can fix N2 Nitrogen is a major component of most fertilizers Phosphorus is the only other nonmetal in group 15 Phosphorus compounds are used to make matches Phosphorus is needed for the backbone of DNA but this is the element that is the l ...
... Some plants form a symbiotic relationship with bacteria that can fix N2 Nitrogen is a major component of most fertilizers Phosphorus is the only other nonmetal in group 15 Phosphorus compounds are used to make matches Phosphorus is needed for the backbone of DNA but this is the element that is the l ...
The atom CP and H ONLINE
... Write the [answers] to the following: (Just write the answers) Name plates! IDS! Turn in Classroom Contracts Now if you have not- into the hulk-hand-in. 1) When should you have your ID on? 2) If you are sitting in the lab and you leave that area, what should you do? 3) If the teacher starts counting ...
... Write the [answers] to the following: (Just write the answers) Name plates! IDS! Turn in Classroom Contracts Now if you have not- into the hulk-hand-in. 1) When should you have your ID on? 2) If you are sitting in the lab and you leave that area, what should you do? 3) If the teacher starts counting ...
Notes without questions - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... sugar molecule in its excited state (potential energy) until you release the energy via digestion, allowing the electron to “drop back” to a lower orbit (kinetic/chemical/heat energy) ...
... sugar molecule in its excited state (potential energy) until you release the energy via digestion, allowing the electron to “drop back” to a lower orbit (kinetic/chemical/heat energy) ...
Unit 3-The Atom Chapter Packet
... _________ _________, that the ratio of the masses of elements in any given compound is always the same. The law of ____________ ___________ , proposed soon after, states that the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of another element in different compounds are in simple, whole-numbe ...
... _________ _________, that the ratio of the masses of elements in any given compound is always the same. The law of ____________ ___________ , proposed soon after, states that the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of another element in different compounds are in simple, whole-numbe ...
Document
... The nucleus is held together by a poorly understood force, the Nuclear Force IAEA ...
... The nucleus is held together by a poorly understood force, the Nuclear Force IAEA ...
Chapter 2 Law of Conservation of Mass Law of Conservation of Mass
... • Some groups have descriptive names that are commonly used instead of their group numbers. – Halogens (Halides) • Group 17 (VIIA) nonmetals • exist naturally as diatomic molecules – Noble gases • Group 18 (VIIIA) nonmetals • are also called inert gases • are so named because they do not chemically ...
... • Some groups have descriptive names that are commonly used instead of their group numbers. – Halogens (Halides) • Group 17 (VIIA) nonmetals • exist naturally as diatomic molecules – Noble gases • Group 18 (VIIIA) nonmetals • are also called inert gases • are so named because they do not chemically ...
Review for Test
... 3. If Fred had two bar magnets, could he have placed them near the screen without causing any distortion in the image? Explain. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 3. If Fred had two bar magnets, could he have placed them near the screen without causing any distortion in the image? Explain. __________________________________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ ...
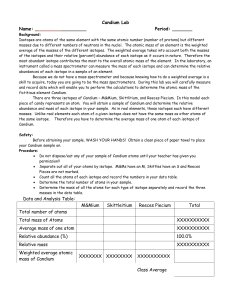
Candium Lab - OCPS TeacherPress
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number (number of protons) but different masses due to different numbers of neutrons in the nuclei. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of the different isotopes. The weighted average takes into account both ...
... Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number (number of protons) but different masses due to different numbers of neutrons in the nuclei. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of the different isotopes. The weighted average takes into account both ...
Unit Expectations – Periodic Table
... C4.10 Neutral Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes - A neutral atom of any element will contain the same number of protons and electrons. Ions are charged particles with an unequal number of protons and electrons. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons and essentially the sam ...
... C4.10 Neutral Atoms, Ions, and Isotopes - A neutral atom of any element will contain the same number of protons and electrons. Ions are charged particles with an unequal number of protons and electrons. Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons and essentially the sam ...
Atomic Structure LO Teacher
... 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of 2 or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements are joined in a definite, wholenumber ratio, such as 1:1, 2:1, or 3:2. Dalton’s essential ideas are still useful today, but several modifications to his theory have been made… ...
... 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of 2 or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements are joined in a definite, wholenumber ratio, such as 1:1, 2:1, or 3:2. Dalton’s essential ideas are still useful today, but several modifications to his theory have been made… ...
Atomic Structure LO Teacher
... 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of 2 or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements are joined in a definite, wholenumber ratio, such as 1:1, 2:1, or 3:2. Dalton’s essential ideas are still useful today, but several modifications to his theory have been made… ...
... 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of 2 or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements are joined in a definite, wholenumber ratio, such as 1:1, 2:1, or 3:2. Dalton’s essential ideas are still useful today, but several modifications to his theory have been made… ...
Atoms and Periodic Table Unit Name
... 25 - These are good conductors of heat and electricity. They also have luster and a high density 27 - Metals are considered this if they can be made into wire. 29 - There are this many known quarks? 30 - The attraction that holds atoms close to each other 32 - Group of nitrogenous organic compounds ...
... 25 - These are good conductors of heat and electricity. They also have luster and a high density 27 - Metals are considered this if they can be made into wire. 29 - There are this many known quarks? 30 - The attraction that holds atoms close to each other 32 - Group of nitrogenous organic compounds ...
3lectouttch
... 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of 2 or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements are joined in a definite, wholenumber ratio, such as 1:1, 2:1, or 3:2. Dalton’s essential ideas are still useful today, but several modifications to his theory have been made… ...
... 3. Compounds are formed by the joining of atoms of 2 or more elements. In any compound, the atoms of the different elements are joined in a definite, wholenumber ratio, such as 1:1, 2:1, or 3:2. Dalton’s essential ideas are still useful today, but several modifications to his theory have been made… ...
SCH 3U - othsmath
... 1) When reacting chemically, metals tend to lose one or more valence electrons to form positive ions. Going down a group, a new energy level is added with each subsequent atom, ensuring the valence electrons are moved further and further from the nucleus. This increases the shielding provided by non ...
... 1) When reacting chemically, metals tend to lose one or more valence electrons to form positive ions. Going down a group, a new energy level is added with each subsequent atom, ensuring the valence electrons are moved further and further from the nucleus. This increases the shielding provided by non ...
Niels BOHR Bohr`s model was the first proposal that predicted the
... Quantum mechanics treats the electrons as waves and models THAT behavior! - To describe the electrons, we use WAVEFUNCTIONs - which are mathematical descriptions of the behavior or electrons. - The wavefunction describes the probability of finding an electron in a given space - For larger objects, t ...
... Quantum mechanics treats the electrons as waves and models THAT behavior! - To describe the electrons, we use WAVEFUNCTIONs - which are mathematical descriptions of the behavior or electrons. - The wavefunction describes the probability of finding an electron in a given space - For larger objects, t ...