Christopher Warner Title: Element Project Educational Filters: The
... 3.2.10 Inquiry and Design: Apply knowledge and understanding about the nature of scientific and technological knowledge. ...
... 3.2.10 Inquiry and Design: Apply knowledge and understanding about the nature of scientific and technological knowledge. ...
atomic structure studyguide key
... Atoms are always conserved during chemical and physical changes. b.Which of his points was later proven incorrect? Atoms are indivisible: Later proven they are composed of subatomic particles. Atoms of the same element are the same: Later discovered isotopes of elements and they are different ...
... Atoms are always conserved during chemical and physical changes. b.Which of his points was later proven incorrect? Atoms are indivisible: Later proven they are composed of subatomic particles. Atoms of the same element are the same: Later discovered isotopes of elements and they are different ...
If each orbital contains two electrons, the second energy level can
... clement did not have identical masses. These mass differences exist because all of the nuclei of a given element do not contain the same number of neutrons. Atoms of an element having the same atomic number but different atomic masses are called isotopes of that clement. Atoms of the isotopes of an ...
... clement did not have identical masses. These mass differences exist because all of the nuclei of a given element do not contain the same number of neutrons. Atoms of an element having the same atomic number but different atomic masses are called isotopes of that clement. Atoms of the isotopes of an ...
Atomic Number
... • Atoms are the building blocks of all materials • An atom is made of 3 parts: – Protons and Neutrons are in the nucleus (center) – Electrons orbit around the nucleus ...
... • Atoms are the building blocks of all materials • An atom is made of 3 parts: – Protons and Neutrons are in the nucleus (center) – Electrons orbit around the nucleus ...
atom
... • Use atomic mass and percent of each isotope to calculate the contribution of each isotope to the weighted average. Atomic mass 35Cl x % abundance = Atomic mass 37Cl x % abundance = • Sum is atomic mass of Cl is ...
... • Use atomic mass and percent of each isotope to calculate the contribution of each isotope to the weighted average. Atomic mass 35Cl x % abundance = Atomic mass 37Cl x % abundance = • Sum is atomic mass of Cl is ...
Chapter 5 The Periodic Table
... increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column. ...
... increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column. ...
PIB and HH - Unit 4 - Chemical Names and Formulas
... Bonded atoms attain the stable electron configuration of a noble gas. The noble gases themselves exist as isolated atoms because that is their most stable condition. For the representative elements, the number of valence electrons is equal to the element’s group number in the periodic table. The tra ...
... Bonded atoms attain the stable electron configuration of a noble gas. The noble gases themselves exist as isolated atoms because that is their most stable condition. For the representative elements, the number of valence electrons is equal to the element’s group number in the periodic table. The tra ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Spring Packet
... 1. Label each group and period with the appropriate numbers. 2. Fill in the elements for Groups 1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, and 18 and provide the names for each family, for example alkaline earth, noble gases, etc (see pg 513-514, 522 – 525 in your textbook) . List the number of valence electrons for ...
... 1. Label each group and period with the appropriate numbers. 2. Fill in the elements for Groups 1, 2, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, and 18 and provide the names for each family, for example alkaline earth, noble gases, etc (see pg 513-514, 522 – 525 in your textbook) . List the number of valence electrons for ...
Chemistry Atoms Learning Objectives Atoms Essential knowledge
... Because of Aristotle’s popularity his theory was adopted as the standard ...
... Because of Aristotle’s popularity his theory was adopted as the standard ...
File
... 25. The charge of the ion is 3+. As an element, this ion would have had 13 electrons since it has 13 protons. It then loses 3 electrons, so the ion has a charge of 3+. 26. Metals tend to lose electrons. Non-metals tend to gain electrons. 27. Atoms tend to gain or lose electrons so they have the same ...
... 25. The charge of the ion is 3+. As an element, this ion would have had 13 electrons since it has 13 protons. It then loses 3 electrons, so the ion has a charge of 3+. 26. Metals tend to lose electrons. Non-metals tend to gain electrons. 27. Atoms tend to gain or lose electrons so they have the same ...
atoms - schultz915
... a. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. b. Some but not all elements are composed of atoms. c. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of protons. d. Atoms are divisible. ...
... a. Chemical reactions occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. b. Some but not all elements are composed of atoms. c. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of protons. d. Atoms are divisible. ...
gallagher chapter 41
... charge, and a relative mass of 1 (or 1840 times that of an electron) 5. 1932 – James Chadwick confirmed the existence of the “neutron” – a particle with no charge, but a mass nearly equal to a proton ...
... charge, and a relative mass of 1 (or 1840 times that of an electron) 5. 1932 – James Chadwick confirmed the existence of the “neutron” – a particle with no charge, but a mass nearly equal to a proton ...
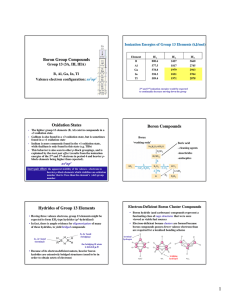
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... Indium is more commonly found in the +1 oxidation state, while thallium is only found in this state (e.g. TlBr) This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by the inert pair effect (results from the ionization energies of the 2nd and 3rd electrons in period 4 and heavier ...
... Indium is more commonly found in the +1 oxidation state, while thallium is only found in this state (e.g. TlBr) This behavior is also seen in other p-block groupings, and is explained by the inert pair effect (results from the ionization energies of the 2nd and 3rd electrons in period 4 and heavier ...
Science Focus 10 Unit 1 Energy and Matter in Chemical
... • group number describes how many electrons are found in the valence or outermost energy level (eg. lithium is in group 1 and has 1 valence electron) • for groups 13 – 18, we use the last number to designate the number of valence electrons (eg. elements in group 16 have 6 valence electrons) • electr ...
... • group number describes how many electrons are found in the valence or outermost energy level (eg. lithium is in group 1 and has 1 valence electron) • for groups 13 – 18, we use the last number to designate the number of valence electrons (eg. elements in group 16 have 6 valence electrons) • electr ...
Chapter 10
... Explanation: Straight-forward enough? Are you acquainted with friends who feel a straight answer can’t be the one to pick—that there’s always a trick? Ask with a straight face, “What really is 1 + 1.” Is there a long pause in answering? ...
... Explanation: Straight-forward enough? Are you acquainted with friends who feel a straight answer can’t be the one to pick—that there’s always a trick? Ask with a straight face, “What really is 1 + 1.” Is there a long pause in answering? ...
9.6
... Atomic Radius Across a Period Atomic radius decreases • Going from left to right across a period. • As more protons increase nuclear attraction for valence electrons. ...
... Atomic Radius Across a Period Atomic radius decreases • Going from left to right across a period. • As more protons increase nuclear attraction for valence electrons. ...
Atom
... of only one kind of atom, and a compound is composed of particles that are chemical combinations of different kinds of atoms. ...
... of only one kind of atom, and a compound is composed of particles that are chemical combinations of different kinds of atoms. ...
Atom
... Elements are different because they contain different number of protons. Atomic number – of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. Example – all hydrogen atoms have 1 proton and the atomic number of hydrogen is 1. The atomic number identifies an element. ...
... Elements are different because they contain different number of protons. Atomic number – of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom of that element. Example – all hydrogen atoms have 1 proton and the atomic number of hydrogen is 1. The atomic number identifies an element. ...
Atomic_structure
... The atomic number tells you how many protons there are in one atom of an element. The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons, which is why the atom has no overall charge. Since the mass of the atom is made up of the neutrons and protons, the number of neutrons in an atom is calculated ...
... The atomic number tells you how many protons there are in one atom of an element. The number of electrons is equal to the number of protons, which is why the atom has no overall charge. Since the mass of the atom is made up of the neutrons and protons, the number of neutrons in an atom is calculated ...
Essential Question: What type of model did Thompson ,Rutherford
... Corresponds to group number in the periodic table. Group 2 elements have 2 valence electrons: ...
... Corresponds to group number in the periodic table. Group 2 elements have 2 valence electrons: ...
By 1911 the components of the atom had been discovered
... spread out throughout the atom. Then, if he shot high velocity radioactive alpha particles (helium nuclei, positively charged) at an atom then there would be very little to deflect the alpha particles. He decided to test this with a thin film of gold atoms. As expected, most alpha particles went rig ...
... spread out throughout the atom. Then, if he shot high velocity radioactive alpha particles (helium nuclei, positively charged) at an atom then there would be very little to deflect the alpha particles. He decided to test this with a thin film of gold atoms. As expected, most alpha particles went rig ...
Lecture 4
... chemically combined • Two or more substances in different proportions • Substances that can be separated by physical methods Example: Pasta and water can be separated with a strainer. ...
... chemically combined • Two or more substances in different proportions • Substances that can be separated by physical methods Example: Pasta and water can be separated with a strainer. ...
The Structure of Atoms
... • The equation can be solved for the hydrogen atom to produce the values that are allowed for the electron in the hydrogen atom. Each solution (or set of values) can be described by a set of quantum numbers. More complex equations are required for atoms with many electrons. • Four quantum are necess ...
... • The equation can be solved for the hydrogen atom to produce the values that are allowed for the electron in the hydrogen atom. Each solution (or set of values) can be described by a set of quantum numbers. More complex equations are required for atoms with many electrons. • Four quantum are necess ...