Atomic Structure Powerpoint
... has 1 proton. Its mass number is 1. 2H has 1 proton and 1 neutron. Its mass number is 2. 3H has 1 proton and 2 neutrons. Its mass number is 3. 99.98% of all hydrogen is 1H 0.018% of all hydrogen is 2H 0.002% of all hydrogen is 3H Together, they give a value of atomic mass of hydrogen equal to 1.0079 ...
... has 1 proton. Its mass number is 1. 2H has 1 proton and 1 neutron. Its mass number is 2. 3H has 1 proton and 2 neutrons. Its mass number is 3. 99.98% of all hydrogen is 1H 0.018% of all hydrogen is 2H 0.002% of all hydrogen is 3H Together, they give a value of atomic mass of hydrogen equal to 1.0079 ...
Unit Nuclear Chemistry
... › In 1928, he began to work on the acceleration of protons with Ernest Walton. › In 1932, they bombarded lithium with high energy neutrons, electrons and protons and succeeded in transmuting it into helium and other chemical elements. › This was one of the earliest experiments to change the atomic n ...
... › In 1928, he began to work on the acceleration of protons with Ernest Walton. › In 1932, they bombarded lithium with high energy neutrons, electrons and protons and succeeded in transmuting it into helium and other chemical elements. › This was one of the earliest experiments to change the atomic n ...
DO NOW
... Read “The Bohr Model and Valence Electrons” from page 141. Take Cornell Notes, defining the following terms: - Bohr Model - Valence Electrons ...
... Read “The Bohr Model and Valence Electrons” from page 141. Take Cornell Notes, defining the following terms: - Bohr Model - Valence Electrons ...
Unit 3 The History of the ATOM
... from Friday. Get out the cards and re-separate them into the two piles of isotopes. ...
... from Friday. Get out the cards and re-separate them into the two piles of isotopes. ...
NOTES: ATOMIC THEORY
... his experiment is know as the cathode –ray tube experiment. He found that the e- was almost 2000 times lighter than a hydrogen atom, which was thought to be the lightest component of matter. (1911, 1918) ERNEST RUTHERFORD = Reasoning, just like Thomson, that since the atom is an electrically NEUTRAL ...
... his experiment is know as the cathode –ray tube experiment. He found that the e- was almost 2000 times lighter than a hydrogen atom, which was thought to be the lightest component of matter. (1911, 1918) ERNEST RUTHERFORD = Reasoning, just like Thomson, that since the atom is an electrically NEUTRAL ...
pdf.format - San Diego Mesa College
... Elements are made from atoms having the same atomic number, protons Are all atoms of one particular atom the same or are they mixtures? 1) All atom nuclei for an element have the same number of protons. 2) Every atom in an element has the same number of protons & electrons. 3) However, elements are ...
... Elements are made from atoms having the same atomic number, protons Are all atoms of one particular atom the same or are they mixtures? 1) All atom nuclei for an element have the same number of protons. 2) Every atom in an element has the same number of protons & electrons. 3) However, elements are ...
Regular Chemistry - 1st Semester Final Practice Exam
... A) The atom re-emits the energy as heat. B) The atom re-emits the energy as light. C) The atom stores the energy for later use. D) The extra energy increases the speed of the electrons in their orbitals. E) none of the above 59) The atomic orbital depicted below would be found in a ________ sublevel ...
... A) The atom re-emits the energy as heat. B) The atom re-emits the energy as light. C) The atom stores the energy for later use. D) The extra energy increases the speed of the electrons in their orbitals. E) none of the above 59) The atomic orbital depicted below would be found in a ________ sublevel ...
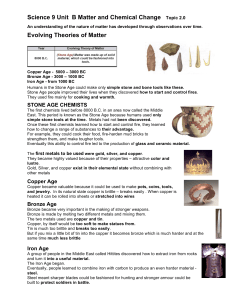
An understanding of the nature of matter has developed
... reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 98 elements exist naturally although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature.[n 1] Elements with atomic numbers from 99 to 118 have only b ...
... reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 98 elements exist naturally although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature.[n 1] Elements with atomic numbers from 99 to 118 have only b ...
Atoms and Elements
... 1. They have the same chemical and physical properties. 3. However, carbon atoms are ____________________from sulfur atoms. (Atoms of one element are different from atoms of another element.) 1. They have ________________________chemical and physical properties. 4. Atoms combine in simple, _________ ...
... 1. They have the same chemical and physical properties. 3. However, carbon atoms are ____________________from sulfur atoms. (Atoms of one element are different from atoms of another element.) 1. They have ________________________chemical and physical properties. 4. Atoms combine in simple, _________ ...
parts of the ato..
... Atomic Mass • The atomic mass on the periodic table a weighted average of the isotopes ...
... Atomic Mass • The atomic mass on the periodic table a weighted average of the isotopes ...
apbio ch 2 study guide
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
How many protons, electrons and neutrons are in an atom of krypton
... The interesting thing here is that adding or removing neutrons from an atom does not create a different element. Rather, it creates a heavier or lighter version of that element. These different versions are called isotopes and most elements are actually a mixture of different isotopes. If you could ...
... The interesting thing here is that adding or removing neutrons from an atom does not create a different element. Rather, it creates a heavier or lighter version of that element. These different versions are called isotopes and most elements are actually a mixture of different isotopes. If you could ...
Atomic Structure
... • Electrons give off energy when they “jump” back down to the more stable ground state. • Ground State – when the electrons in an atom are arranged in the lowest possible energy level. ...
... • Electrons give off energy when they “jump” back down to the more stable ground state. • Ground State – when the electrons in an atom are arranged in the lowest possible energy level. ...
Species Number of protons Number of
... Do not penalize for e(g). Accept loss of electron on LHS. 5th electron removed from energy level closer to nucleus/5th electron removed from 3rd energy level and 4th electron from 4th energy ...
... Do not penalize for e(g). Accept loss of electron on LHS. 5th electron removed from energy level closer to nucleus/5th electron removed from 3rd energy level and 4th electron from 4th energy ...
Chemistry Syllabus - Madison County Schools
... 3b. Analyze patterns and trends in the organization of elements in the periodic table and compare their relationship to position in the periodic table. (DOK 2) Chemical characteristics of each region Periodic properties (e.g., metal/nonmetal/metalloid behavior, electrical/heat conductivity, elec ...
... 3b. Analyze patterns and trends in the organization of elements in the periodic table and compare their relationship to position in the periodic table. (DOK 2) Chemical characteristics of each region Periodic properties (e.g., metal/nonmetal/metalloid behavior, electrical/heat conductivity, elec ...
KD 1
... Atomic Number Atoms are composed of identical protons, neutrons, and electrons How then are atoms of one element different from another element? Elements are different because they contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
... Atomic Number Atoms are composed of identical protons, neutrons, and electrons How then are atoms of one element different from another element? Elements are different because they contain different numbers of PROTONS The “atomic number” of an element is the number of protons in the nucleus ...
Chap 4 Review with answers
... at what the atom was made of. They had to make inferences from the results of many different experiments. It was like trying to describe a picture, such as the one on the next slide, with only small portions visible. ...
... at what the atom was made of. They had to make inferences from the results of many different experiments. It was like trying to describe a picture, such as the one on the next slide, with only small portions visible. ...
Chemistry Syllabus
... 3b. Analyze patterns and trends in the organization of elements in the periodic table and compare their relationship to position in the periodic table. (DOK 2) Atomic number, atomic mass, mass number, and number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in isotopes of elements Average atomic mass calc ...
... 3b. Analyze patterns and trends in the organization of elements in the periodic table and compare their relationship to position in the periodic table. (DOK 2) Atomic number, atomic mass, mass number, and number of protons, electrons, and neutrons in isotopes of elements Average atomic mass calc ...
Chapter 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
... • Elements gain or lose electrons to acquire the electron configuration of the noble gases. Periodic Properties of the Elements ...
... • Elements gain or lose electrons to acquire the electron configuration of the noble gases. Periodic Properties of the Elements ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... • A covalent bond is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms • In a covalent bond, the shared electrons count as part of each atom’s valence shell – A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds – A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of on ...
... • A covalent bond is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons by two atoms • In a covalent bond, the shared electrons count as part of each atom’s valence shell – A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds – A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of on ...
the Atom Regents Review Worksheets with answers.
... 25. Isotopes of an element must have different A. atomic numbers C. numbers of protons B. mass numbers D. numbers of electrons 26. What is the total number of neutrons in an at om of an element that has a mass number of 19 and an atomic number of 9? ...
... 25. Isotopes of an element must have different A. atomic numbers C. numbers of protons B. mass numbers D. numbers of electrons 26. What is the total number of neutrons in an at om of an element that has a mass number of 19 and an atomic number of 9? ...
Atomic Mass
... neutrons is the mass number = 12 atomic mass units Mass Number (A) = # protons + # neutrons NOT on the periodic table…(Round the AVERAGE atomic mass on the table) A boron atom can have ...
... neutrons is the mass number = 12 atomic mass units Mass Number (A) = # protons + # neutrons NOT on the periodic table…(Round the AVERAGE atomic mass on the table) A boron atom can have ...
Atoms - TeacherWeb
... nucleus are called valence electrons. These electrons form chemical bonds with other atoms and give elements their chemical properties. Atoms combine with other atoms to complete their outermost or last energy level, called the valence shell. ...
... nucleus are called valence electrons. These electrons form chemical bonds with other atoms and give elements their chemical properties. Atoms combine with other atoms to complete their outermost or last energy level, called the valence shell. ...