Unit 6 – The Atom Vocabulary
... (1) This could be due to _____________________________________________ (2) This unstable state is called the ______________________________ ii) After the electron quickly returns to the _______________________, it ____________ the same amount of energy it absorbed. (1) The energy given off is ______ ...
... (1) This could be due to _____________________________________________ (2) This unstable state is called the ______________________________ ii) After the electron quickly returns to the _______________________, it ____________ the same amount of energy it absorbed. (1) The energy given off is ______ ...
Atoms - Issaquah Connect
... • ALL atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • All neutral atoms have no overall (net) charge, so … have the same number of electrons as protons • BUT… they can have different numbers of neutrons These are called isotopes of carbon ...
... • ALL atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • All neutral atoms have no overall (net) charge, so … have the same number of electrons as protons • BUT… they can have different numbers of neutrons These are called isotopes of carbon ...
Atoms - Issaquah Connect
... • ALL atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • All neutral atoms have no overall (net) charge, so … have the same number of electrons as protons • BUT… they can have different numbers of neutrons These are called isotopes of carbon ...
... • ALL atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • All neutral atoms have no overall (net) charge, so … have the same number of electrons as protons • BUT… they can have different numbers of neutrons These are called isotopes of carbon ...
Elements and Compounds
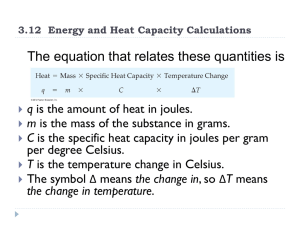
... determined charge magnitude of electrons which led to the determination of the mass • q= -1.6 x 10-19 Coulombs • Mass = 9.11 x 10-28 grams (from charge to mass ratio) ...
... determined charge magnitude of electrons which led to the determination of the mass • q= -1.6 x 10-19 Coulombs • Mass = 9.11 x 10-28 grams (from charge to mass ratio) ...
4.1 Experiencing Atoms at Tiburon 4.1 Experiencing Atoms
... • The nuclei of some isotopes of a given element are not stable. • These atoms emit a few energetic subatomic particles from their nuclei and change into different isotopes of different elements. • The emitted subatomic particles are called nuclear radiation. • The isotopes that emit them are te ...
... • The nuclei of some isotopes of a given element are not stable. • These atoms emit a few energetic subatomic particles from their nuclei and change into different isotopes of different elements. • The emitted subatomic particles are called nuclear radiation. • The isotopes that emit them are te ...
Chapter 4 Atoms and Elements
... • When an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion. • Positively charged ions are called cations. • Negatively charged ions are called anions. • Cations and anions occur together so that matter is chargeneutral. Isotopes: • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are cal ...
... • When an atom gains or loses electrons, it becomes an ion. • Positively charged ions are called cations. • Negatively charged ions are called anions. • Cations and anions occur together so that matter is chargeneutral. Isotopes: • Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are cal ...
Symbols of Elements
... occurring sulfur contains several isotopes with the following abundances Isotope % abundance 32S ...
... occurring sulfur contains several isotopes with the following abundances Isotope % abundance 32S ...
UNIT 1 Atomic Structure
... Note electrons are usually shown as far apart as possible -they have the same charge and therefore repel each other. 3. The Noble gases (Group 0) have a stable electron configuration (s2p6) with 8 electrons filling the outer s and p orbitals. This stability comes from the low energy state of this c ...
... Note electrons are usually shown as far apart as possible -they have the same charge and therefore repel each other. 3. The Noble gases (Group 0) have a stable electron configuration (s2p6) with 8 electrons filling the outer s and p orbitals. This stability comes from the low energy state of this c ...
Mendeleef`s Periodic Table
... They have inner incomplete shell. so known as transition elements. General electronic configuration is ns1 – 2 (n – 1)d1 – 10 d-block elements are generally coloured, paramagnetic and exhibit variable valency. (d) f-block elements They constitute two series 4f (lanthanoids) and 5f (actinides) in wh ...
... They have inner incomplete shell. so known as transition elements. General electronic configuration is ns1 – 2 (n – 1)d1 – 10 d-block elements are generally coloured, paramagnetic and exhibit variable valency. (d) f-block elements They constitute two series 4f (lanthanoids) and 5f (actinides) in wh ...
Q1. This question is about the first ionisation energies of some
... State the number of protons and the number of neutrons in an atom of the isotope 85Rb Number of protons ......................................................................................... Number of neutrons ....................................................................................... ...
... State the number of protons and the number of neutrons in an atom of the isotope 85Rb Number of protons ......................................................................................... Number of neutrons ....................................................................................... ...
Chapter 4 Atoms and Elements
... the nuclear theory of the atom. 1. Most of the atom’s mass and all of its positive charge are contained in a small core called the nucleus. 2. Most of the volume of the atom is empty space through which the tiny, negatively charged electrons are dispersed. 3. The number of negatively charged electro ...
... the nuclear theory of the atom. 1. Most of the atom’s mass and all of its positive charge are contained in a small core called the nucleus. 2. Most of the volume of the atom is empty space through which the tiny, negatively charged electrons are dispersed. 3. The number of negatively charged electro ...
I Biology I Lecture Outline Basic Chemistry Life
... 4. Chemists have identified 92 naturally occurring elements. Some examples include hydrogen, helium, nurogen, carbon, etc. 5. Of these 92 naturally occurring elements, only 6 elements are basic to life and make up about 95% of the body weight of organisms. These six are: (CHNOPS) A. Carbon - p ...
... 4. Chemists have identified 92 naturally occurring elements. Some examples include hydrogen, helium, nurogen, carbon, etc. 5. Of these 92 naturally occurring elements, only 6 elements are basic to life and make up about 95% of the body weight of organisms. These six are: (CHNOPS) A. Carbon - p ...
Atoms - Issaquah Connect
... • ALL atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • All neutral atoms have no overall (net) charge, so … have the same number of electrons as protons • BUT… they can have different numbers of neutrons These are called isotopes of carbon ...
... • ALL atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. • All neutral atoms have no overall (net) charge, so … have the same number of electrons as protons • BUT… they can have different numbers of neutrons These are called isotopes of carbon ...
Structure of the Atom
... All the bound protons and neutrons in an atom make up a tiny atomic nucleus, and are collectively called nucleons. The radius of a nucleus is approximately equal to , where A is the total number of nucleons. This is much smaller than the radius of the atom, which is on the order of 105 fm. The nucle ...
... All the bound protons and neutrons in an atom make up a tiny atomic nucleus, and are collectively called nucleons. The radius of a nucleus is approximately equal to , where A is the total number of nucleons. This is much smaller than the radius of the atom, which is on the order of 105 fm. The nucle ...
Document
... The first draft of the periodic table was developed between 1879 and 1871, and published by Dmitri Mendeleev. Note that this was before the subatomic particles were discovered, so it was not based on atomic number. The 63 known elements were arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass, and ...
... The first draft of the periodic table was developed between 1879 and 1871, and published by Dmitri Mendeleev. Note that this was before the subatomic particles were discovered, so it was not based on atomic number. The 63 known elements were arranged in order of increasing relative atomic mass, and ...
Atomic Structure
... Below you will practice figuring out the different protons, electrons, and neutrons for the table. I have left some open to help you out, but once you have an answer click on the cell shade to reveal the answers. If you need the periodic table click on the animal below to go to the periodic table. ...
... Below you will practice figuring out the different protons, electrons, and neutrons for the table. I have left some open to help you out, but once you have an answer click on the cell shade to reveal the answers. If you need the periodic table click on the animal below to go to the periodic table. ...
Atomic
... • Not all atoms of the same element have the same number of neutrons. Most Carbon atoms have 6 neutrons, although some have more and some have less. Atoms of the same element with differing numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. The number of neutrons does not change the atom or the element it mak ...
... • Not all atoms of the same element have the same number of neutrons. Most Carbon atoms have 6 neutrons, although some have more and some have less. Atoms of the same element with differing numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. The number of neutrons does not change the atom or the element it mak ...
Isotopes
... e have seen that an atom has a nucleus with a positive charge due to its protons and has electrons in the space surrounding the nucleus at relatively large distances from it. As an example, consider a sodium atom, which has 11 protons in its nucleus. Because an atom has no overall charge, the number ...
... e have seen that an atom has a nucleus with a positive charge due to its protons and has electrons in the space surrounding the nucleus at relatively large distances from it. As an example, consider a sodium atom, which has 11 protons in its nucleus. Because an atom has no overall charge, the number ...
Lesson 1 & 2 Periodic table trends and formation
... 2. What is the atomic mass of an element? The atomic mass is the mass of an atom of a particular element. It is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of a particular element, averaged over all the isotopes of the element. (Note: students may not have studied isotopes yet ...
... 2. What is the atomic mass of an element? The atomic mass is the mass of an atom of a particular element. It is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom of a particular element, averaged over all the isotopes of the element. (Note: students may not have studied isotopes yet ...
Structure of the Atom
... The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons (except in the case of hydrogen-1, which is the only stable nuclide wit ...
... The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons (except in the case of hydrogen-1, which is the only stable nuclide wit ...
Atomic Model Unit Plan with SCTS
... configurations to form substances. There are one or more—but never many—kinds of these atoms for each of the approximately 100 elements. - There are distinct patterns of properties among the elements. There are groups of elements that have similar properties, including highly reactive metals, less-r ...
... configurations to form substances. There are one or more—but never many—kinds of these atoms for each of the approximately 100 elements. - There are distinct patterns of properties among the elements. There are groups of elements that have similar properties, including highly reactive metals, less-r ...
Reason for Fractional Atomic Masses of Elements
... The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons (except in the case of hydrogen-1, which is the only stable nuclide wit ...
... The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons (except in the case of hydrogen-1, which is the only stable nuclide wit ...
atomic mass
... A) These reactions are called nuclear reactions, as they involve changes in the nucleus. ...
... A) These reactions are called nuclear reactions, as they involve changes in the nucleus. ...