3.2 Lesson - FHS PAP Algebra 2
... Step 2: ADD the revised equations from Step 1. Combining like terms will eliminate one of the variables. Solve for the remaining variables. Step 3: SUBSTITUTE the value obtained in Step 2 into either of the original equations and solve for the other variable. ...
... Step 2: ADD the revised equations from Step 1. Combining like terms will eliminate one of the variables. Solve for the remaining variables. Step 3: SUBSTITUTE the value obtained in Step 2 into either of the original equations and solve for the other variable. ...
Name:______________________________________________ Date:________ Period:_______
... Name:______________________________________________ ...
... Name:______________________________________________ ...
Solving Two-Variable Systems of Linear Equations
... Systems of linear equations in two variables have either no solutions, one solution, or infinitely many solutions. y y y ...
... Systems of linear equations in two variables have either no solutions, one solution, or infinitely many solutions. y y y ...
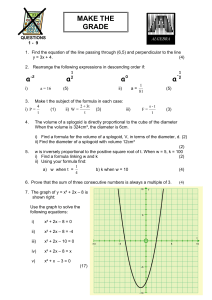
Find the equation of the line passing through (6,5) and
... can find the equation of a perpendicular line can evaluate algebraic expressions involving negative and fractional powers can rearrange more complex formulae including when variables are given twice can solve direct proportion problems can solve inverse proportion problems can prove simple statement ...
... can find the equation of a perpendicular line can evaluate algebraic expressions involving negative and fractional powers can rearrange more complex formulae including when variables are given twice can solve direct proportion problems can solve inverse proportion problems can prove simple statement ...
PowerPoint 1
... A linear equation in one variable is an equation that can be written in the form ax = b where a and b are constants and a 0. A number is a solution of an equation if the statement is true when the number is substituted for the variable. Two equations are equivalent if they have the same solutions. ...
... A linear equation in one variable is an equation that can be written in the form ax = b where a and b are constants and a 0. A number is a solution of an equation if the statement is true when the number is substituted for the variable. Two equations are equivalent if they have the same solutions. ...
The Cubic formula
... is 40. .... and thus far does arithmetical subtlety go, of which this, the extreme, is, as I have said, so subtle that it is useless.” (MACTUTOR) ...
... is 40. .... and thus far does arithmetical subtlety go, of which this, the extreme, is, as I have said, so subtle that it is useless.” (MACTUTOR) ...
Partial differential equation

In mathematics, a partial differential equation (PDE) is a differential equation that contains unknown multivariable functions and their partial derivatives. (A special case are ordinary differential equations (ODEs), which deal with functions of a single variable and their derivatives.) PDEs are used to formulate problems involving functions of several variables, and are either solved by hand, or used to create a relevant computer model.PDEs can be used to describe a wide variety of phenomena such as sound, heat, electrostatics, electrodynamics, fluid flow, elasticity, or quantum mechanics. These seemingly distinct physical phenomena can be formalised similarly in terms of PDEs. Just as ordinary differential equations often model one-dimensional dynamical systems, partial differential equations often model multidimensional systems. PDEs find their generalisation in stochastic partial differential equations.