A Look at Chapter 4: Circuit Characterization and Performance
... of the course text). • Capacitances for the Ground and VDD nodes have been excluded from the picture, why? • Provide the time constant or propagation delay () for this gate ...
... of the course text). • Capacitances for the Ground and VDD nodes have been excluded from the picture, why? • Provide the time constant or propagation delay () for this gate ...
CircuitI_exp021411060340
... current controlled current source (CCCS). Figure 11 shows the PSPICE diagrams of these dependent sources. Each diagram is divided into an ammeter at the left side and a source (voltage or current) at the right side. The ammeter must be connected in series with the required current that is to be meas ...
... current controlled current source (CCCS). Figure 11 shows the PSPICE diagrams of these dependent sources. Each diagram is divided into an ammeter at the left side and a source (voltage or current) at the right side. The ammeter must be connected in series with the required current that is to be meas ...
PDF
... voltage of the elements for the three-level NPC topology can be one-half that of the two-level topology, and thus the three-level NPC topology is a suitable configuration for high-voltage power converters. For improved efficiency, however, the three-level bidirectional switch topology is more advant ...
... voltage of the elements for the three-level NPC topology can be one-half that of the two-level topology, and thus the three-level NPC topology is a suitable configuration for high-voltage power converters. For improved efficiency, however, the three-level bidirectional switch topology is more advant ...
6.01SC Software Lab 8: Describing Circuits
... We can represent a set of equations using an instance of the class le.EquationSet. This class takes no parameters at initialization time, and returns an object that represents an empty set of equations. Equations can then be added using the addEquation method, whose input is an instance of le.Equati ...
... We can represent a set of equations using an instance of the class le.EquationSet. This class takes no parameters at initialization time, and returns an object that represents an empty set of equations. Equations can then be added using the addEquation method, whose input is an instance of le.Equati ...
Slide 1
... • Mesh: More popular as voltage sources do exist physically. • Nodal: Less popular as current sources do not exist physically except in models of electronics circuits. ...
... • Mesh: More popular as voltage sources do exist physically. • Nodal: Less popular as current sources do not exist physically except in models of electronics circuits. ...
i Kim B
... If a crystalline solid substance is heated to the melting state and then cooled down, it solidifies at a fixed temperature Ts , called temperature of solidification, also called the melting point of the substance. The traditional method to determine Ts is to follow the change in temperature with tim ...
... If a crystalline solid substance is heated to the melting state and then cooled down, it solidifies at a fixed temperature Ts , called temperature of solidification, also called the melting point of the substance. The traditional method to determine Ts is to follow the change in temperature with tim ...
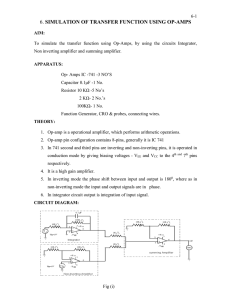
6-SIMULATION OF TRANSFER FUNCTION USING OP
... 1. Connect the circuit as per the circuit diagram shown in fig (i). 2. A square wave input is given to both the integrator and non inverting amplifier circuits. 3. +Vcc and –Vee are applied as +10v and -10v at 7 and 4 pins respectively for every circuit shown in the circuit diagram. 4. Individual ou ...
... 1. Connect the circuit as per the circuit diagram shown in fig (i). 2. A square wave input is given to both the integrator and non inverting amplifier circuits. 3. +Vcc and –Vee are applied as +10v and -10v at 7 and 4 pins respectively for every circuit shown in the circuit diagram. 4. Individual ou ...
Systematic Circuit Analysis
... • The dependent source will be dependent on some voltage or current in the circuit • You will need to express that voltage or current in terms of the unknown node voltages • The idea is to only use the node voltages in finding the currents so that there will be as many KCL equations as variables ...
... • The dependent source will be dependent on some voltage or current in the circuit • You will need to express that voltage or current in terms of the unknown node voltages • The idea is to only use the node voltages in finding the currents so that there will be as many KCL equations as variables ...
Loop and Nodal Analysis and Op Amps
... Create loop current labels that include every circuit branch where each loop contains a branch included by no other loop and no loops cross each other. Perform KVL around each loop expressing all voltages in terms of loop currents. ...
... Create loop current labels that include every circuit branch where each loop contains a branch included by no other loop and no loops cross each other. Perform KVL around each loop expressing all voltages in terms of loop currents. ...
Topology (electrical circuits)
The topology of an electronic circuit is the form taken by the network of interconnections of the circuit components. Different specific values or ratings of the components are regarded as being the same topology. Topology is not concerned with the physical layout of components in a circuit, nor with their positions on a circuit diagram. It is only concerned with what connections exist between the components. There may be numerous physical layouts and circuit diagrams that all amount to the same topology.Strictly speaking, replacing a component with one of an entirely different type is still the same topology. In some contexts, however, these can loosely be described as different topologies. For instance, interchanging inductors and capacitors in a low-pass filter results in a high-pass filter. These might be described as high-pass and low-pass topologies even though the network topology is identical. A more correct term for these classes of object (that is, a network where the type of component is specified but not the absolute value) is prototype network.Electronic network topology is related to mathematical topology, in particular, for networks which contain only two-terminal devices, circuit topology can be viewed as an application of graph theory. In a network analysis of such a circuit from a topological point of view, the network nodes are the vertices of graph theory and the network branches are the edges of graph theory.Standard graph theory can be extended to deal with active components and multi-terminal devices such as integrated circuits. Graphs can also be used in the analysis of infinite networks.