Two-port network
... parameters. Once this is done, the isolated part of the circuit becomes a "black box" with a set of distinctive properties, enabling us to abstract away its specific physical buildup, thus simplifying analysis. Any linear circuit with four terminals can be transformed into a two-port network provide ...
... parameters. Once this is done, the isolated part of the circuit becomes a "black box" with a set of distinctive properties, enabling us to abstract away its specific physical buildup, thus simplifying analysis. Any linear circuit with four terminals can be transformed into a two-port network provide ...
FTT-10A Free Topology Twisted Pair Tranceiver Datasheet
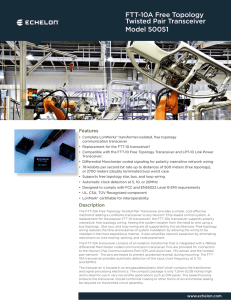
... The transceiver is housed in an encapsulated plastic shell which contains the transformer and signal processing electronics. The compact package is only 7.2mm (0.28 inches) high and is ideal for use in very low profile applications such as DIN packs. The sealed housing protects the transceiver shoul ...
... The transceiver is housed in an encapsulated plastic shell which contains the transformer and signal processing electronics. The compact package is only 7.2mm (0.28 inches) high and is ideal for use in very low profile applications such as DIN packs. The sealed housing protects the transceiver shoul ...
Analysis of Series-Parallel Resonant Inductive Coupling Circuit
... is more appropriate to call it resonant inductive coupling rather than merely inductive coupling. All topology has certain advantage and disadvantage and their choice mainly depends on type of application. There has been research to find out most suitable topology for particular application such as ...
... is more appropriate to call it resonant inductive coupling rather than merely inductive coupling. All topology has certain advantage and disadvantage and their choice mainly depends on type of application. There has been research to find out most suitable topology for particular application such as ...
Lecture 1
... Identify enclosed, non-overlapping areas in circuit Circuit elements bounding these areas form mesh loops Mesh currents flow around the mesh loops ...
... Identify enclosed, non-overlapping areas in circuit Circuit elements bounding these areas form mesh loops Mesh currents flow around the mesh loops ...
FTT-10A Free Topology Twisted Pair Transceiver
... The FTT-10A transceiver also provides electrical isolation for I/O devices that are grounded, allowing such devices to be used on a link power network segment. Each segment of a link power network utilizes a non-isolated design with a single ground point at the LPI-10 Link Power Interface. Proper op ...
... The FTT-10A transceiver also provides electrical isolation for I/O devices that are grounded, allowing such devices to be used on a link power network segment. Each segment of a link power network utilizes a non-isolated design with a single ground point at the LPI-10 Link Power Interface. Proper op ...
Lab 4
... motion by closing a switch. If the alarm goes off the instant the switch is closed, there would be a lot of false alarms. On the other hand, once the alarm is on, it should stay on for some time after the motion stops and the switch opens, to encourage the bad guys to leave. In this design, the manu ...
... motion by closing a switch. If the alarm goes off the instant the switch is closed, there would be a lot of false alarms. On the other hand, once the alarm is on, it should stay on for some time after the motion stops and the switch opens, to encourage the bad guys to leave. In this design, the manu ...
Chapter 3 - Loop Analysis(PowerPoint Format)
... • To keep the analysis as systematic as possible, we use (if possible) only meshes to perform loop analysis (mesh analysis). • There are cases (when a mesh traverses a current source) when we must use a loop in place of a mesh. ...
... • To keep the analysis as systematic as possible, we use (if possible) only meshes to perform loop analysis (mesh analysis). • There are cases (when a mesh traverses a current source) when we must use a loop in place of a mesh. ...
Chapter 4 (Techniques of Circuit Analysis)
... Voltage Sources and the Supernode If there is a DC voltage source between two non-reference nodes, you can get into trouble when trying to use KCL between the two nodes because the current through the voltage source may not be known, and an equation cannot be written for it. Therefore, we create a ...
... Voltage Sources and the Supernode If there is a DC voltage source between two non-reference nodes, you can get into trouble when trying to use KCL between the two nodes because the current through the voltage source may not be known, and an equation cannot be written for it. Therefore, we create a ...
image sensor
... An image sensor is a device that converts an optical image into an electronic signal. It is used mostly in digital cameras and other imaging ...
... An image sensor is a device that converts an optical image into an electronic signal. It is used mostly in digital cameras and other imaging ...
RC Circuits
... circuit have on the time to charge the capacitor? a) The charging time will decrease because the rate of charge flowing to the plates will increase. b) The charging time will decrease because the rate of charge flowing to the plates will decrease. c) The charging time will not change because the cha ...
... circuit have on the time to charge the capacitor? a) The charging time will decrease because the rate of charge flowing to the plates will increase. b) The charging time will decrease because the rate of charge flowing to the plates will decrease. c) The charging time will not change because the cha ...
Capacitance graphs support
... explain the similarities and differences between graphs showing charging and discharging of a capacitor and be able to sketch them all explain the meaning of the time constant and be able to find it from the equations and from a graph find the energy stored in a capacitor from the equations and also ...
... explain the similarities and differences between graphs showing charging and discharging of a capacitor and be able to sketch them all explain the meaning of the time constant and be able to find it from the equations and from a graph find the energy stored in a capacitor from the equations and also ...
OHM`S LAW Objectives: a. To find the unknown resistance of an
... Where, “A” is area of cross-section of the wire of length “l” Experiments: Part 1: Finding the value of R1 In this exercise you will apply different potential differences across an ohmic resistor and measure the corresponding currents. The different potential difference are created through the disch ...
... Where, “A” is area of cross-section of the wire of length “l” Experiments: Part 1: Finding the value of R1 In this exercise you will apply different potential differences across an ohmic resistor and measure the corresponding currents. The different potential difference are created through the disch ...
Topology (electrical circuits)
The topology of an electronic circuit is the form taken by the network of interconnections of the circuit components. Different specific values or ratings of the components are regarded as being the same topology. Topology is not concerned with the physical layout of components in a circuit, nor with their positions on a circuit diagram. It is only concerned with what connections exist between the components. There may be numerous physical layouts and circuit diagrams that all amount to the same topology.Strictly speaking, replacing a component with one of an entirely different type is still the same topology. In some contexts, however, these can loosely be described as different topologies. For instance, interchanging inductors and capacitors in a low-pass filter results in a high-pass filter. These might be described as high-pass and low-pass topologies even though the network topology is identical. A more correct term for these classes of object (that is, a network where the type of component is specified but not the absolute value) is prototype network.Electronic network topology is related to mathematical topology, in particular, for networks which contain only two-terminal devices, circuit topology can be viewed as an application of graph theory. In a network analysis of such a circuit from a topological point of view, the network nodes are the vertices of graph theory and the network branches are the edges of graph theory.Standard graph theory can be extended to deal with active components and multi-terminal devices such as integrated circuits. Graphs can also be used in the analysis of infinite networks.