* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RC Circuits
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Electric battery wikipedia , lookup
Crossbar switch wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Rechargeable battery wikipedia , lookup
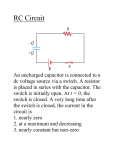
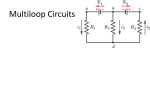
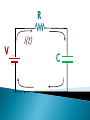
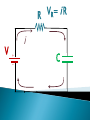
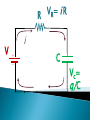
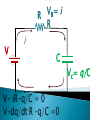
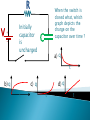
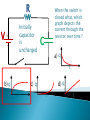
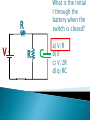
R V i(t) + - C V = i R R R V i + - C V = i R R R V i + - C Vc= q/C V = i R R R V i + - C V- iR-q/C = 0 V-dq/dt R –q/C =0 Vc= q/C RC Circuits, Charging a Capacitor: 27.9: RC Circuits, Time Constant: The product RC is called the capacitive time constant of the circuit and is represented with the symbol t: At time t= t =( RC), the charge on the initially uncharged capacitor increases from zero to: During the first time constant t the charge has increased from zero to 63% of its final value CE. R V+ - Initially capacitor is uncharged When the switch is closed what, which graph depicts the charge on the capacitor over time ? C a) q t b) q d) q c) q t t t RC Circuits, Discharging a Capacitor: A simple circuit consists of a resistor R, a capacitor C charged to a potential Vo, and a switch that is initially open but then thrown closed. Immediately after the switch is thrown closed, the current in the circuit is A) Vo/R. B) zero. C) need more information R V+ - Initially capacitor is uncharged When the switch is closed what, which graph depicts the current through the resistor over time ? C a) q t b) q d) q c) q t t t What is the initial I through the battery when the switch is closed? R V+ - R C a) V/R b) 0 c) V/2R d) q/RC R V+ - R C What is current through the battery after a long time? a) V/R b) 0 c) V/2R d) q/RC R V+ - R C What is the charge on the capacitor after a long time? a) CV b) CV/4 c) 2CV d) CV/2 With capacitor charged, we open the circuit. What happens immediately after? R V+ - i1 R i2 C a) b) c) d) i1=0, i2= -V/2R i1=0, i2= V/2R i1=V/2R, i2= V/2R i1=V/R , i2=0 What effect, if any, does increasing the battery emf in an RC circuit have on the time to charge the capacitor? a) The charging time will decrease because the rate of charge flowing to the plates will increase. b) The charging time will decrease because the rate of charge flowing to the plates will decrease. c) The charging time will not change because the charging time does not depend on the battery emf. d) The charging time will increase because the emf is increased. e) The charging time will decrease because potential difference across the plates will be larger. In physics lab, Rebecca measured the voltage across an unknown capacitor in an RC circuit, every ten seconds after a switch in the circuit that allows the capacitor to discharge is closed. The capacitor was initially fully charged. Using the graph, estimate the time constant. a) 7.5 s b) 15 s c) 30 s d) 45 s e) 60 s












![Sample_hold[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008409180_1-2fb82fc5da018796019cca115ccc7534-150x150.png)