Solve Systems with Elimination (Multiplication)
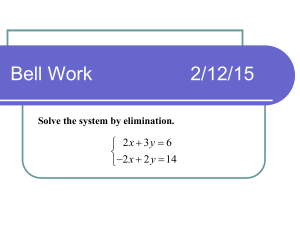
... equation by to eliminate the x’s? 3x + y = 4 6x + 4y = 6 ...
... equation by to eliminate the x’s? 3x + y = 4 6x + 4y = 6 ...
Equations Rectangular Coordinates
... Points in Quadrant 2 have negative x but positive y coordinates. Points in Quadrant 3 have negative x and negative y coordinates. Points in Quadrant 4 have positive x but negative y coordinates. ...
... Points in Quadrant 2 have negative x but positive y coordinates. Points in Quadrant 3 have negative x and negative y coordinates. Points in Quadrant 4 have positive x but negative y coordinates. ...
PHYS4330 Theoretical Mechanics HW #1 Due 6 Sept 2011
... where τ is a positive constant, and starts from rest at x = 0 and t = 0. Find the velocity v(t) = ẋ(t) and position x(t) as functions of time. Also find the velocity v(t) for times t � τ . (2) A particle of mass m moves in two dimensions according to plane polar coordinates r and φ. It is acted on ...
... where τ is a positive constant, and starts from rest at x = 0 and t = 0. Find the velocity v(t) = ẋ(t) and position x(t) as functions of time. Also find the velocity v(t) for times t � τ . (2) A particle of mass m moves in two dimensions according to plane polar coordinates r and φ. It is acted on ...
Lagrange`s equations of motion in generalized coordinates
... An important case occurs when a system is scleronomic, i.e., there is no explicit dependency on time in the coordinate transformation, we then have ...
... An important case occurs when a system is scleronomic, i.e., there is no explicit dependency on time in the coordinate transformation, we then have ...
Domain and Range
... belong to a certain function, we write them as an equation with two variables, usually x and y Examples: d = 5t y = 5x ...
... belong to a certain function, we write them as an equation with two variables, usually x and y Examples: d = 5t y = 5x ...
[2012 question paper]
... [2] Consider a particle of mass µ in three dimensions. It is subjected to an attractive central force of magnitude F (r) where r is the distance from the origin. For such a particle, (a) Write down the Lagrangian and set up the Euler-Lagrange equations. (b) Show that the motion is planar (c) Show th ...
... [2] Consider a particle of mass µ in three dimensions. It is subjected to an attractive central force of magnitude F (r) where r is the distance from the origin. For such a particle, (a) Write down the Lagrangian and set up the Euler-Lagrange equations. (b) Show that the motion is planar (c) Show th ...
Physics 200A Theoretical Mechanics Fall 2013 Topics
... Principle of Least Action, Generalized Coordinates, Lagrange’s Equations b.) Symmetries and Conservation Laws, Noether’s theorem c.) Constraints and constraint forces d.) Hamiltonians and Hamilton’s equations ...
... Principle of Least Action, Generalized Coordinates, Lagrange’s Equations b.) Symmetries and Conservation Laws, Noether’s theorem c.) Constraints and constraint forces d.) Hamiltonians and Hamilton’s equations ...













![[2012 question paper]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008881815_1-f519c09d51fa08989c44092ef48b677c-300x300.png)