Separable Differential Equations
... Mon Jan 04 Do Now Find the original function if F’(x) = 3x + 1 and f(0) = 2 ...
... Mon Jan 04 Do Now Find the original function if F’(x) = 3x + 1 and f(0) = 2 ...
Now!
... Algebra 3.4: Solve Equations with Variables on Both Sides, Pages 154-156 Objective: I will be able to solve equations with variables on both sides. Vocabulary: identity Solve by bringing variables to one side. Check your work. ...
... Algebra 3.4: Solve Equations with Variables on Both Sides, Pages 154-156 Objective: I will be able to solve equations with variables on both sides. Vocabulary: identity Solve by bringing variables to one side. Check your work. ...
Formula Sheet - Blank File
... (B2) Ch. 12&13 Thermodynamics Linear expansion: Rate of heat transfer by conduction: ...
... (B2) Ch. 12&13 Thermodynamics Linear expansion: Rate of heat transfer by conduction: ...
Algebra I - MCPMathReadingFun9
... Can I use “s” and “t” as variables for my first equation and “x” and “y” as variables for my second ...
... Can I use “s” and “t” as variables for my first equation and “x” and “y” as variables for my second ...
8-1 Solving Systems of Equations
... Step1 –Choose a variable to solve for in either equation. I will choose x from the first equation because it has a coefficient of 1 (there is no number next to it) and it will be easy to solve for x. X= 1- 4y Step 2- Now I will take 1-4y and substitute it into the other equation. I will “substitute” ...
... Step1 –Choose a variable to solve for in either equation. I will choose x from the first equation because it has a coefficient of 1 (there is no number next to it) and it will be easy to solve for x. X= 1- 4y Step 2- Now I will take 1-4y and substitute it into the other equation. I will “substitute” ...
A_4.pdf
... 8. Find |u + v| and θ given |u| = 78 kilograms and |v| = 45 kilograms. 9. Find |u| and |v|, the magnitudes of the horizontal and vertical components of u + v given |u + v| = 390 miles per hour and θ = 6º. 10. Given u = 〈−1,2〉 , v = 〈3,−2〉 , and w = 〈0,−2〉 , find (a) u + v, (b) u - v, and (c) 2u - v ...
... 8. Find |u + v| and θ given |u| = 78 kilograms and |v| = 45 kilograms. 9. Find |u| and |v|, the magnitudes of the horizontal and vertical components of u + v given |u + v| = 390 miles per hour and θ = 6º. 10. Given u = 〈−1,2〉 , v = 〈3,−2〉 , and w = 〈0,−2〉 , find (a) u + v, (b) u - v, and (c) 2u - v ...
A variable needs to be eliminated to solve the system of equations
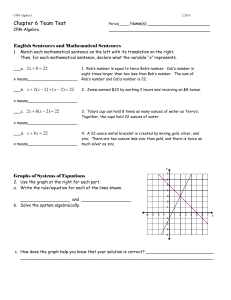
... 1. Rob’s number is equal to twice Bob’s number. Cob’s number is eight times larger than two less than Bob’s number. The sum of Rob’s number and Cob’s number is 22. 2. Jenna earned $22 by working 2 hours and receiving an $8 bonus. ...
... 1. Rob’s number is equal to twice Bob’s number. Cob’s number is eight times larger than two less than Bob’s number. The sum of Rob’s number and Cob’s number is 22. 2. Jenna earned $22 by working 2 hours and receiving an $8 bonus. ...
Mechanics
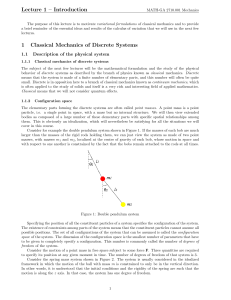
... A set of generalized coordinates can be used to replace the Cartesian coordinates. qm = qm(x11,…, xN3, t) xil = xil(q1, …, qf, t) Generalized coordinates need not be distances ...
... A set of generalized coordinates can be used to replace the Cartesian coordinates. qm = qm(x11,…, xN3, t) xil = xil(q1, …, qf, t) Generalized coordinates need not be distances ...