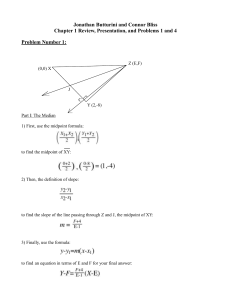
Jonathan Butturini and Connor Bliss Chapter 1 Review
... 1) Here are the values given to you in order to create a quadratic equation: ...
... 1) Here are the values given to you in order to create a quadratic equation: ...
Solving Two-Step Equations: It is called a two
... Adding and Subtracting Think Money Think Temperature ...
... Adding and Subtracting Think Money Think Temperature ...
Topics covered in PH111 - Rose
... Electric charges, electric potential, equipotential lines, lines of force, force on a charge in a electric field. Magnetism: Magnetic field, lines of force and equipotential lines for a magnetic field, Earth as a magnet, force on a moving charge in a magnetic field. Work: Work done by a force from a ...
... Electric charges, electric potential, equipotential lines, lines of force, force on a charge in a electric field. Magnetism: Magnetic field, lines of force and equipotential lines for a magnetic field, Earth as a magnet, force on a moving charge in a magnetic field. Work: Work done by a force from a ...
Second Mid-Term Exam Solution
... Thursday, October 24, 2002 – 5-6:30 PM Hammond Auditorium Room 120 Engineering Building You may not consult any books, notes, or inanimate references. You may not consult with another person. You may not copy another student’s solutions. ...
... Thursday, October 24, 2002 – 5-6:30 PM Hammond Auditorium Room 120 Engineering Building You may not consult any books, notes, or inanimate references. You may not consult with another person. You may not copy another student’s solutions. ...
Dynamics
... kinematic properties of object. We indirectly control position, velocity, and acceleration by exerting forces and torques Current position f ...
... kinematic properties of object. We indirectly control position, velocity, and acceleration by exerting forces and torques Current position f ...
Advanced Mechanics 241, Spring 2008 Examination Questions and Problems Part I. Questions
... 1. Formulate Hamilton’s principle (the principle of least action) and use it to derive Lagrange’s equations of motion for a system with s degrees of freedom. What is called the number of degrees of freedom? What are the properties of the Lagrangian of a mechanical system? What is the Lagrangian for ...
... 1. Formulate Hamilton’s principle (the principle of least action) and use it to derive Lagrange’s equations of motion for a system with s degrees of freedom. What is called the number of degrees of freedom? What are the properties of the Lagrangian of a mechanical system? What is the Lagrangian for ...
Chapter 3: Graphing
... Equations where the graphs result in a straight line are called linear equations Notice from your graph on the previous page that y – 0.81x + 2 is a linear equation . For each of the following equations, find the corresponding y values for the given x values plot the coordinates on the graph ...
... Equations where the graphs result in a straight line are called linear equations Notice from your graph on the previous page that y – 0.81x + 2 is a linear equation . For each of the following equations, find the corresponding y values for the given x values plot the coordinates on the graph ...
Revision
... August 31, 2006 – Sarah Donaldson Prompt In an Algebra 1 class some students began solving a quadratic equation as follows: Solve for x: ...
... August 31, 2006 – Sarah Donaldson Prompt In an Algebra 1 class some students began solving a quadratic equation as follows: Solve for x: ...
Equations of Motion Computational Physics Orbital Motion
... Radial Force dependent on position only: Angular Momentum conserved; Motion in a plane. ...
... Radial Force dependent on position only: Angular Momentum conserved; Motion in a plane. ...