
LookatSlideFiveforHW
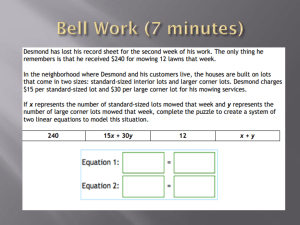
... represent the number of interior lots mowed and y to represent the number of corner lots mowed, set up a system of two linear equations to model this situation. ...
... represent the number of interior lots mowed and y to represent the number of corner lots mowed, set up a system of two linear equations to model this situation. ...
m1-] 63 NOTE ON THE NUMBER OF LINEARLY INDEPEND
... ls,*--—-i. T h e roots of D{k) are [T, p . 338] 0, — 1, both simple, and y/a/2, — y/a/2 of multiplicities which we will denote by p and n respectively. Then, 0-l+%(a)ll2(p-n) ...
... ls,*--—-i. T h e roots of D{k) are [T, p . 338] 0, — 1, both simple, and y/a/2, — y/a/2 of multiplicities which we will denote by p and n respectively. Then, 0-l+%(a)ll2(p-n) ...
Graphing Linear Equations
... Graphing Linear Equations using Coordinate Points: (x, y) is a _____________________ __________. “x” is the x-coordinate and “y” is the y-coordinate. We count to the right (positive) or left (negative) using the ___ - coordinate and up (positive) or down (negative) using the ___-coordinate. We can g ...
... Graphing Linear Equations using Coordinate Points: (x, y) is a _____________________ __________. “x” is the x-coordinate and “y” is the y-coordinate. We count to the right (positive) or left (negative) using the ___ - coordinate and up (positive) or down (negative) using the ___-coordinate. We can g ...
Algebra Worksheet - Cape Cornwall School
... 2 a Write down all of the whole number values of x, such that 5 x 3 b Represent the inequality 5 x 3 on a number line. 3 Remove the brackets and then simplify: a 3(5x + y) + 2(3y − 2x) b 5(2m + 3) − 3(4 − m) 4 Here are the first five numbers of a sequence. ...
... 2 a Write down all of the whole number values of x, such that 5 x 3 b Represent the inequality 5 x 3 on a number line. 3 Remove the brackets and then simplify: a 3(5x + y) + 2(3y − 2x) b 5(2m + 3) − 3(4 − m) 4 Here are the first five numbers of a sequence. ...
solutions
... If x is not 0, then dividing the first equation through by x gives λ = −4. Then the second equation gives 2y = −16y, which means that y = 0. The third then says that x2 = 4, so x = −2 or x = 2. This gives two points: (x, y) = (−2, 0) and (x, y) = (2, 0). We have f (−2, 0) = −16 and f (2, 0) = −16. ...
... If x is not 0, then dividing the first equation through by x gives λ = −4. Then the second equation gives 2y = −16y, which means that y = 0. The third then says that x2 = 4, so x = −2 or x = 2. This gives two points: (x, y) = (−2, 0) and (x, y) = (2, 0). We have f (−2, 0) = −16 and f (2, 0) = −16. ...
PES 3210 Classical Mechanics I
... Given the equation of a force in some region, be able to calculate the work it would take to move a particle from one position to another along a specified path. ...
... Given the equation of a force in some region, be able to calculate the work it would take to move a particle from one position to another along a specified path. ...
notes on Kinematics Equations
... When given problems to solve, you will be expected to “show your work” COMPLETELY! “Showing work” means that you will be expected to include the following pieces in your full answer (or you will not receive full credit for the problem…) ...
... When given problems to solve, you will be expected to “show your work” COMPLETELY! “Showing work” means that you will be expected to include the following pieces in your full answer (or you will not receive full credit for the problem…) ...











![m1-] 63 NOTE ON THE NUMBER OF LINEARLY INDEPEND](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/012997862_1-d2f38d28dd32ef9691afaab3955d0a2a-300x300.png)









