5 Equilibrium of a Rigid Body Chapter Objectives
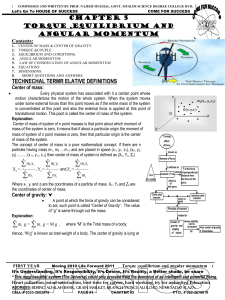
... Conditions for Rigid Equilibrium Free-Body Diagrams Equations of Equilibrium Two and Three-Force Members Free Body Diagrams Equations of Equilibrium Constraints and Statical Determinacy ...
... Conditions for Rigid Equilibrium Free-Body Diagrams Equations of Equilibrium Two and Three-Force Members Free Body Diagrams Equations of Equilibrium Constraints and Statical Determinacy ...
Document
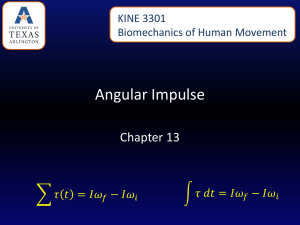
... After the torque is applied to the rigid bar the angular velocity increases to 5.27 r/s. If the rigid bar has a moment of inertia of 0.8 kg∙m2 what was the final angular momentum? If the torque was applied for t = 0.9 s, what was the angular impulse? ...
... After the torque is applied to the rigid bar the angular velocity increases to 5.27 r/s. If the rigid bar has a moment of inertia of 0.8 kg∙m2 what was the final angular momentum? If the torque was applied for t = 0.9 s, what was the angular impulse? ...
r - De Anza
... Analysis models introduced so far cannot be used to analyze all motion. We can model the motion of an extended object by modeling it as a system of many particles. § The analysis is simplified if the object is assumed to be a rigid object. A rigid object is one that is non-deformable. § The relative ...
... Analysis models introduced so far cannot be used to analyze all motion. We can model the motion of an extended object by modeling it as a system of many particles. § The analysis is simplified if the object is assumed to be a rigid object. A rigid object is one that is non-deformable. § The relative ...
Questions and Problems
... is the magnitude of the angular velocity vz) must increase in order for the magnitude of Lz = Ivz to remain constant. 8-13 (d) The angular momentum L of a system is conserved only if no net torque acts on the system. This isn’t the case for either the pulley or the disk: A net torque due to the ten ...
... is the magnitude of the angular velocity vz) must increase in order for the magnitude of Lz = Ivz to remain constant. 8-13 (d) The angular momentum L of a system is conserved only if no net torque acts on the system. This isn’t the case for either the pulley or the disk: A net torque due to the ten ...
Ch 08 B1 QFD.cwk (WP)
... A lawn roller in the form of a hollow cylinder of mass M is pulled horizontally with constant force F applied by a handle attached to the axle. If it rolls without slipping then find the acceleration of the roller and the friction force that act on it. Answer in terms of F and M. The rotational iner ...
... A lawn roller in the form of a hollow cylinder of mass M is pulled horizontally with constant force F applied by a handle attached to the axle. If it rolls without slipping then find the acceleration of the roller and the friction force that act on it. Answer in terms of F and M. The rotational iner ...
ExamView - C_Rotation_MC_2008 practice.tst
... B) his angular velocity remains the same. E) his rotational inertia decreases. C) his angular momentum remains the same. 15. A top spinning on the floor precesses because the torque due to gravity, about the point of contact of the top with the floor, is: A) parallel to the angular momentum vector. ...
... B) his angular velocity remains the same. E) his rotational inertia decreases. C) his angular momentum remains the same. 15. A top spinning on the floor precesses because the torque due to gravity, about the point of contact of the top with the floor, is: A) parallel to the angular momentum vector. ...