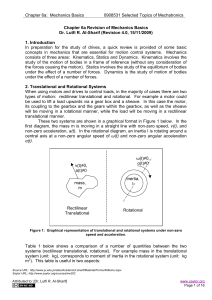
APPARENT MASSES AND INERTIA MOMENTS OF THE PARAFOIL
... into account by increasing the body mass. This additional mass is known as the apparent mass. The above described an unsteady aerodynamic effect, causing that the moving body can be treated as the body with greater mass and inertia moment, is called “the apparent mass effect”. It should be underline ...
... into account by increasing the body mass. This additional mass is known as the apparent mass. The above described an unsteady aerodynamic effect, causing that the moving body can be treated as the body with greater mass and inertia moment, is called “the apparent mass effect”. It should be underline ...
PSI AP Physics I
... 61. A solid cylinder (I = ½ MR2) of mass 0.56 kg and radius 0.042 m rolls, without slipping, down an incline of height 0.67 m. What is the speed of the cylinder at the bottom of the incline? Does its speed depend on the mass and radius of the cylinder? 62. Two uniform spheres (I = 2/5 MR2) roll, wit ...
... 61. A solid cylinder (I = ½ MR2) of mass 0.56 kg and radius 0.042 m rolls, without slipping, down an incline of height 0.67 m. What is the speed of the cylinder at the bottom of the incline? Does its speed depend on the mass and radius of the cylinder? 62. Two uniform spheres (I = 2/5 MR2) roll, wit ...
Orbits, shapes and currents
... The contribution from each family to the shell energy is given by ...
... The contribution from each family to the shell energy is given by ...
textbook_week_3
... First, convert the angular displacement to radians and the angular speeds to rad/s: ...
... First, convert the angular displacement to radians and the angular speeds to rad/s: ...
ap physics 1
... change of linear momentum and angular impulse, and change of angular momentum. (LO 3.F.3.1) 3. TSW justifies that a torque exerted on an object can change the angular momentum of an object. (EK 3.F.3) 4. TSW will recognize the presence of a net torque along any axis causes a rigid system to change i ...
... change of linear momentum and angular impulse, and change of angular momentum. (LO 3.F.3.1) 3. TSW justifies that a torque exerted on an object can change the angular momentum of an object. (EK 3.F.3) 4. TSW will recognize the presence of a net torque along any axis causes a rigid system to change i ...
2565 Opt B Part 1
... if a force acts directly through the centre of mass of an object, then linear acceleration will occur (Newton's second law), no turning or rotating ...
... if a force acts directly through the centre of mass of an object, then linear acceleration will occur (Newton's second law), no turning or rotating ...
unit 12: rotational motion
... According to Newton's second law an object will undergo a linear acceleration a when it is subjected to a linear force r r where F = ma . Let's postulate that a similar law can be formulated for rotational motion in which a torque τ is proportional to an angular acceleration α. If we define the € co ...
... According to Newton's second law an object will undergo a linear acceleration a when it is subjected to a linear force r r where F = ma . Let's postulate that a similar law can be formulated for rotational motion in which a torque τ is proportional to an angular acceleration α. If we define the € co ...
Physics Chapter 3 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best
... B Newton’s first law holds that your body moves along with Earth because it is not compelled to change its motion by an unbalanced force. C Newton’s second law holds that the acceleration produced by the force of gravity is offset by the force of friction on your feet. D Newton’s third law holds tha ...
... B Newton’s first law holds that your body moves along with Earth because it is not compelled to change its motion by an unbalanced force. C Newton’s second law holds that the acceleration produced by the force of gravity is offset by the force of friction on your feet. D Newton’s third law holds tha ...