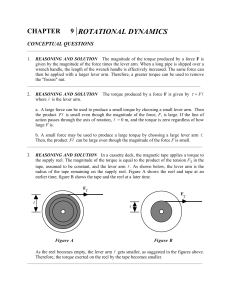
Ch 08) Rotational Motion
... will be the same for all points. Thus, v and a are properties of the rotating object as a whole. With v measured in radians per second and t in seconds, a has units of radians per second squared Arad兾s2 B. Each point or particle of a rotating object has, at any moment, a linear velocity v and a line ...
... will be the same for all points. Thus, v and a are properties of the rotating object as a whole. With v measured in radians per second and t in seconds, a has units of radians per second squared Arad兾s2 B. Each point or particle of a rotating object has, at any moment, a linear velocity v and a line ...
14.7 M - Thierry Karsenti
... Level 1. Priority A. Linear Algebra 1 and Calculus 3 is prerequisite. (Note overlap with Vector Analysis) Vectors, Velocity and Acceleration: Dot product, cross product, triple products. Derivatives of vectors, Integrals of vectors. Relative velocity and acceleration. Tangential and normal accelerat ...
... Level 1. Priority A. Linear Algebra 1 and Calculus 3 is prerequisite. (Note overlap with Vector Analysis) Vectors, Velocity and Acceleration: Dot product, cross product, triple products. Derivatives of vectors, Integrals of vectors. Relative velocity and acceleration. Tangential and normal accelerat ...
Dahler and Sciven 1963
... From this, the continuity equation, and the transport and divergence theorems it follows that at every point a ( ~ ) p t + v . ( u=~R) X F + G - v . ( ~ x R ) + v . c . ...
... From this, the continuity equation, and the transport and divergence theorems it follows that at every point a ( ~ ) p t + v . ( u=~R) X F + G - v . ( ~ x R ) + v . c . ...
Chapter 7:Rotation of a Rigid Body
... Rigid body is defined as a body with definite shape that doesn’t change, so that the particles that compose it stay in fixed position relative to one another even though a force is exerted on it. If the rigid body is in equilibrium, means the body is translational and rotational equilibrium. There a ...
... Rigid body is defined as a body with definite shape that doesn’t change, so that the particles that compose it stay in fixed position relative to one another even though a force is exerted on it. If the rigid body is in equilibrium, means the body is translational and rotational equilibrium. There a ...
3 Newton`s First Law of Motion—Inertia
... If a sheet of paper is held in midair, the heavyweight champion of the world could not strike the paper with a force of 200 N (45 pounds). The paper is not capable of exerting a reaction force of 200 N, and you cannot have an action force without a reaction force. If the paper is against the wall, t ...
... If a sheet of paper is held in midair, the heavyweight champion of the world could not strike the paper with a force of 200 N (45 pounds). The paper is not capable of exerting a reaction force of 200 N, and you cannot have an action force without a reaction force. If the paper is against the wall, t ...
POP4e: Ch. 10 Problems
... has a mass of 0.420 kg, and the pulley is a hollow cylinder with a mass of 0.350 kg, an inner radius of 0.020 0 m, and an outer radius of 0.030 0 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.250. The pulley turns without friction on its axle. The light cor ...
... has a mass of 0.420 kg, and the pulley is a hollow cylinder with a mass of 0.350 kg, an inner radius of 0.020 0 m, and an outer radius of 0.030 0 m. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is 0.250. The pulley turns without friction on its axle. The light cor ...
Lecture 6. Momentum
... molecules of a solid are also in motion, but they can move only a small amount because the atoms are very close together. The closer the molecules are together, the less free they are to move. The liquid state is between the gaseous and solid states. The molecules of a liquid are less free of move t ...
... molecules of a solid are also in motion, but they can move only a small amount because the atoms are very close together. The closer the molecules are together, the less free they are to move. The liquid state is between the gaseous and solid states. The molecules of a liquid are less free of move t ...
3 Newton`s First Law of Motion—Inertia
... weighed in the same location? Answer: Two kilograms of anything has twice the inertia and twice the mass of one kilogram of anything else. In the same location, where mass and weight are proportional, two kilograms of anything will weigh twice as much as one kilogram of anything. Except for volume, ...
... weighed in the same location? Answer: Two kilograms of anything has twice the inertia and twice the mass of one kilogram of anything else. In the same location, where mass and weight are proportional, two kilograms of anything will weigh twice as much as one kilogram of anything. Except for volume, ...
3 Newton`s First Law of Motion—Inertia
... weighed in the same location? Answer: Two kilograms of anything has twice the inertia and twice the mass of one kilogram of anything else. In the same location, where mass and weight are proportional, two kilograms of anything will weigh twice as much as one kilogram of anything. Except for volume, ...
... weighed in the same location? Answer: Two kilograms of anything has twice the inertia and twice the mass of one kilogram of anything else. In the same location, where mass and weight are proportional, two kilograms of anything will weigh twice as much as one kilogram of anything. Except for volume, ...