Chap8
... The object is stable as long as the direction of the torque due to its weight, τw tends to keep it upright. This occurs as long as the object’s center of mass lies above its base. To tip the object over, you must rotate its center of mass around the axis of rotation until it is no longer above the b ...
... The object is stable as long as the direction of the torque due to its weight, τw tends to keep it upright. This occurs as long as the object’s center of mass lies above its base. To tip the object over, you must rotate its center of mass around the axis of rotation until it is no longer above the b ...
Review Rotational Motion and Equilibrium and Elasticity
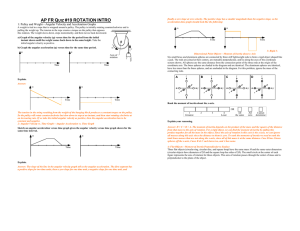
... 20.) A machinist turns on the power on to a grinding wheel at time t = 0 s. The wheel accelerates uniformly from rest for 10 s and reaches the operating angular speed of 58 rad/s. The wheel is run at that angular velocity for 30 s, and then power is shut off. The wheel slows down uniformly at until ...
... 20.) A machinist turns on the power on to a grinding wheel at time t = 0 s. The wheel accelerates uniformly from rest for 10 s and reaches the operating angular speed of 58 rad/s. The wheel is run at that angular velocity for 30 s, and then power is shut off. The wheel slows down uniformly at until ...
Chapter 1 Rotation of an Object About a Fixed Axis
... or because a string passes over the pulley and does not slip against it. In those cases the string exerts a force on the pulley which is tangential, and we use this fact in computing the torque on the pulley. But see the next point. . . • When a string does pass over a real pulley (i.e. it has mass ...
... or because a string passes over the pulley and does not slip against it. In those cases the string exerts a force on the pulley which is tangential, and we use this fact in computing the torque on the pulley. But see the next point. . . • When a string does pass over a real pulley (i.e. it has mass ...
PSE4_Lecture_Ch10 - Rotational Motion
... velocities and accelerations. A carousel is initially at rest. At t = 0 it is given a constant angular acceleration α = 0.060 rad/s2, which increases its angular velocity for 8.0 s. At t = 8.0 s, determine the magnitude of the following quantities: (a) the angular velocity of the carousel; (b) the l ...
... velocities and accelerations. A carousel is initially at rest. At t = 0 it is given a constant angular acceleration α = 0.060 rad/s2, which increases its angular velocity for 8.0 s. At t = 8.0 s, determine the magnitude of the following quantities: (a) the angular velocity of the carousel; (b) the l ...
Vectors & Scalars - The Grange School Blogs
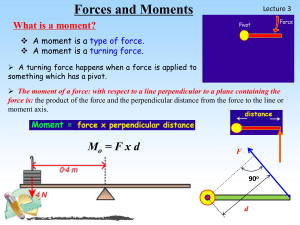
... Note that we take moments about point P. This is because there is a third force which acts on the shelf; this is the contact force (or ‘reaction’) of the wall on the shelf. We do not know its magnitude or direction but, since it acts through point P, it has no turning effect about P. ...
... Note that we take moments about point P. This is because there is a third force which acts on the shelf; this is the contact force (or ‘reaction’) of the wall on the shelf. We do not know its magnitude or direction but, since it acts through point P, it has no turning effect about P. ...
lectures 2014
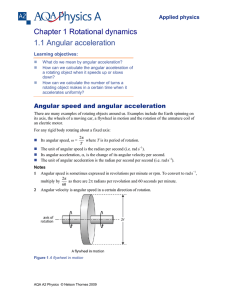
... the place of the mass, and it is a measure of a body’s reluctance to change its state of angular motion. The larger the moment of inertia, the slower the rate of change of angular velocity for a given applied moment of a force. Like the mass, the moment of inertia is a scalar quantity, usually ...
... the place of the mass, and it is a measure of a body’s reluctance to change its state of angular motion. The larger the moment of inertia, the slower the rate of change of angular velocity for a given applied moment of a force. Like the mass, the moment of inertia is a scalar quantity, usually ...