Supervised Learning
... object concept or action is represented by the pattern of activity object, across a population of neurons. Note that this is very different to the way conventional computers represent information using symbols. The connections can learn to translate from one pattern of input to another th pattern. t ...
... object concept or action is represented by the pattern of activity object, across a population of neurons. Note that this is very different to the way conventional computers represent information using symbols. The connections can learn to translate from one pattern of input to another th pattern. t ...
Chapter 6 - RaduegePsychology
... Principles of Conditioning Extinction: After repeated presentation of the conditioned stimulus (CS) without the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) the conditioned response (CR) fades away and eventually stops. ...
... Principles of Conditioning Extinction: After repeated presentation of the conditioned stimulus (CS) without the unconditioned stimulus (UCS) the conditioned response (CR) fades away and eventually stops. ...
Step Up To: Psychology - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... neurotransmitter such as serotonin would involve the reabsorption of serotonin into a(n): A) axon terminal. B) receiving neuron. C) myelin sheath. D) glial cell. ...
... neurotransmitter such as serotonin would involve the reabsorption of serotonin into a(n): A) axon terminal. B) receiving neuron. C) myelin sheath. D) glial cell. ...
02 The Visual System
... wavelength of light B. Striate cortex: Orientation selectivity, direction selectivity, and binocularity C. Extrastriate cortical areas: Selective responsive to complex shapes; e.g., Faces Psychology 355 ...
... wavelength of light B. Striate cortex: Orientation selectivity, direction selectivity, and binocularity C. Extrastriate cortical areas: Selective responsive to complex shapes; e.g., Faces Psychology 355 ...
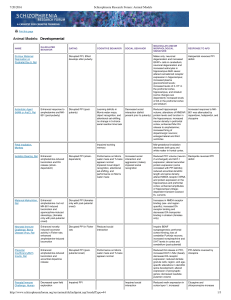
Developmental - Schizophrenia Research Forum
... reelin- and parvalbuminexpressing neurons in PFC; reduced DA levels and D1 receptors in PFC; increased TH expression in striatum; reduced density of cerebellar Purkinje cells; delayed myelination of hippocampus; reduced parvalbuminexpressing neurons in the hippocampus; enlargement of lateral ventric ...
... reelin- and parvalbuminexpressing neurons in PFC; reduced DA levels and D1 receptors in PFC; increased TH expression in striatum; reduced density of cerebellar Purkinje cells; delayed myelination of hippocampus; reduced parvalbuminexpressing neurons in the hippocampus; enlargement of lateral ventric ...
Glossary of Neuroanatomical Terms and Eponyms
... functions at the base of each cerebral hemisphere. Cortex. L. bark. Outer layer of gray matter of the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum. Crus. L. leg. Crus cerebri is the ventral part of the cerebral peduncle of the midbrain on each side, separated from the dorsal part by the substantia nigra. Als ...
... functions at the base of each cerebral hemisphere. Cortex. L. bark. Outer layer of gray matter of the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum. Crus. L. leg. Crus cerebri is the ventral part of the cerebral peduncle of the midbrain on each side, separated from the dorsal part by the substantia nigra. Als ...
UNIT-5 - Search
... 1. A correct answer for each example or instance is available. 2. Learning is done from known sample input and output. Unsupervised learning It is a learning pattern is which correct answers are not given for the input. It is mainly used in probabilistic learning system. Reinforcement learning Here ...
... 1. A correct answer for each example or instance is available. 2. Learning is done from known sample input and output. Unsupervised learning It is a learning pattern is which correct answers are not given for the input. It is mainly used in probabilistic learning system. Reinforcement learning Here ...
ANPS 019 Black 11-30
... CN IX, X, XI & XII exit at medulla Since upper motor neurons innervate the cranial nerve nuclei bilaterally, the other side provides backup innervation; therefore, damage doesn’t result in clinical deficit (the exception is the facial nucleus) The Action Comes from: THE EXTRAPYRAMIDAL SYSTEM Brainst ...
... CN IX, X, XI & XII exit at medulla Since upper motor neurons innervate the cranial nerve nuclei bilaterally, the other side provides backup innervation; therefore, damage doesn’t result in clinical deficit (the exception is the facial nucleus) The Action Comes from: THE EXTRAPYRAMIDAL SYSTEM Brainst ...
Name________________________ Midterm #1 Biology 3330, Fall
... The main organ of taste is the tongue on which the tip is sensitive to _________, the back is sensitive to __________, and the sides are sensitive to _______. On the tongue surface, there are small projections called _________, and each have hundreds of ______________ with several (50-150) _________ ...
... The main organ of taste is the tongue on which the tip is sensitive to _________, the back is sensitive to __________, and the sides are sensitive to _______. On the tongue surface, there are small projections called _________, and each have hundreds of ______________ with several (50-150) _________ ...
Otxl and Otx2 Define Layers and Regions in Developing Cerebral
... the EGL is restricted to the production of granule neurons (Hallonet et al., 1990; Gao et al., 199 l), the developmental potential of these precursors has only recently been explored through transplantation experiments (Gao and Hatten, 1994). The two populations of cerebellar precursors, one residin ...
... the EGL is restricted to the production of granule neurons (Hallonet et al., 1990; Gao et al., 199 l), the developmental potential of these precursors has only recently been explored through transplantation experiments (Gao and Hatten, 1994). The two populations of cerebellar precursors, one residin ...
Your Amazing Brain:
... When Things Go Wrong: Stroke • Cause: blood clot (embolus) or ruptured blood vessel (aneurysm) • Symptoms: weakness, trouble speaking, paralysis, severe headache, vision problems • Treatment: TPA to bust clot (must be within 3 hrs), surgery if aneurysm, therapy to minimize deficits • Prevention: co ...
... When Things Go Wrong: Stroke • Cause: blood clot (embolus) or ruptured blood vessel (aneurysm) • Symptoms: weakness, trouble speaking, paralysis, severe headache, vision problems • Treatment: TPA to bust clot (must be within 3 hrs), surgery if aneurysm, therapy to minimize deficits • Prevention: co ...
Conditioning and Learning
... much tequila may learn a profound dislike of the taste and odor of tequila—a phenomenon called taste aversion conditioning. The fact that flavors can be associated with so many consequences of eating is important for animals (including rats and humans) that often need to learn about new foods. And i ...
... much tequila may learn a profound dislike of the taste and odor of tequila—a phenomenon called taste aversion conditioning. The fact that flavors can be associated with so many consequences of eating is important for animals (including rats and humans) that often need to learn about new foods. And i ...
Chapter 7 - Bakersfield College
... • Axons from gustatory nucleus synapse in the ventral posterior medial (VPM) nucleus of the thalamus – Projects to the gustatory cortex in the parietal lobe for identification of primary taste qualities – Projects to the orbitofrontal cortex in the frontal lobe for combination with olfaction and vis ...
... • Axons from gustatory nucleus synapse in the ventral posterior medial (VPM) nucleus of the thalamus – Projects to the gustatory cortex in the parietal lobe for identification of primary taste qualities – Projects to the orbitofrontal cortex in the frontal lobe for combination with olfaction and vis ...
Neuroscience 1: Cerebral hemispheres/Telencephalon
... d On the left side, the pars opercularis and pars triangularis are considered to be BA 44&45 (respectively) i They are important areas for motor aspect of speech ii Lesion at these areas brings about expressive aphasia AKA non-fluent aphasia/motor aphasia The inability/difficulty to speak Fron ...
... d On the left side, the pars opercularis and pars triangularis are considered to be BA 44&45 (respectively) i They are important areas for motor aspect of speech ii Lesion at these areas brings about expressive aphasia AKA non-fluent aphasia/motor aphasia The inability/difficulty to speak Fron ...
operant conditioning
... likelihood of a behaviour being repeated and punishment is intended to decrease the likelihood of behaviour being repeated. ...
... likelihood of a behaviour being repeated and punishment is intended to decrease the likelihood of behaviour being repeated. ...
Learning - SchoolRack
... Stimulus generalization involves giving a conditioned response to stimuli that are similar to the CS Stimulus discrimination involves responding to one stimulus but not to stimuli that are similar Confusing stimuli may cause experimental neurosis Copyright © Allyn & Bacon 2007 ...
... Stimulus generalization involves giving a conditioned response to stimuli that are similar to the CS Stimulus discrimination involves responding to one stimulus but not to stimuli that are similar Confusing stimuli may cause experimental neurosis Copyright © Allyn & Bacon 2007 ...
UNIT-5 - Search
... 1. A correct answer for each example or instance is available. 2. Learning is done from known sample input and output. Unsupervised learning It is a learning pattern is which correct answers are not given for the input. It is mainly used in probabilistic learning system. Reinforcement learning Here ...
... 1. A correct answer for each example or instance is available. 2. Learning is done from known sample input and output. Unsupervised learning It is a learning pattern is which correct answers are not given for the input. It is mainly used in probabilistic learning system. Reinforcement learning Here ...
07.11 - UCSD Cognitive Science
... The cerebellum and basal ganglia are critically involved in voluntary motor control, contributing to the programming, initiation, and execution of limb and eye movements (Brooks and Thach, 1981; DeL ong and Georgopoulos, 1981). Dysf unction of these subcortical nuclei can result in profound motor di ...
... The cerebellum and basal ganglia are critically involved in voluntary motor control, contributing to the programming, initiation, and execution of limb and eye movements (Brooks and Thach, 1981; DeL ong and Georgopoulos, 1981). Dysf unction of these subcortical nuclei can result in profound motor di ...
Lower motor neuron
... monosynaptically by projections from the cortex • In humans most of the efferent fibers emerging from the red nucleus terminate in the inferior olive • Ends on interneurons that, in turn, project to the dorsal aspect of ventral (motor) horn cells • Facilitates flexor motor neurons and inhibit exte ...
... monosynaptically by projections from the cortex • In humans most of the efferent fibers emerging from the red nucleus terminate in the inferior olive • Ends on interneurons that, in turn, project to the dorsal aspect of ventral (motor) horn cells • Facilitates flexor motor neurons and inhibit exte ...
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... • Parkinson’s disease results from deterioration of dopaminesecreting neurons of the substantia nigra, and leads to a loss in coordination of movement and a persistent tremor • Huntington’s disease is a fatal hereditary disorder that results from deterioration of the basal nuclei and cerebral cortex ...
... • Parkinson’s disease results from deterioration of dopaminesecreting neurons of the substantia nigra, and leads to a loss in coordination of movement and a persistent tremor • Huntington’s disease is a fatal hereditary disorder that results from deterioration of the basal nuclei and cerebral cortex ...
lecture CNS
... modifies motor commands that have originated from the cerebral cortex comprised of several nuclei including the: ...
... modifies motor commands that have originated from the cerebral cortex comprised of several nuclei including the: ...
Temporal Dependent Plasticity: An Information Theoretic Approach
... Hebbian plasticity, the major learning paradigm in neuroscience, was until recently interpreted as learning by correlated neuronal It has recently received novel interpretation showing that changes in synaptic eÆcacies highly depend on the relative timing of the pre and postsynaptic spikes: The eÆca ...
... Hebbian plasticity, the major learning paradigm in neuroscience, was until recently interpreted as learning by correlated neuronal It has recently received novel interpretation showing that changes in synaptic eÆcacies highly depend on the relative timing of the pre and postsynaptic spikes: The eÆca ...
Brain Storm - School of Rehabilitation Therapy
... During brain development the rostral end of the neural tube ends at the lamina terminalis of the diencephalon. The lateral ventricles then expand along with the accompanying cerebral hemispheres (telencephalon) with its axis centered about the insula (L. island). A number of C-shaped brain structure ...
... During brain development the rostral end of the neural tube ends at the lamina terminalis of the diencephalon. The lateral ventricles then expand along with the accompanying cerebral hemispheres (telencephalon) with its axis centered about the insula (L. island). A number of C-shaped brain structure ...
Dopamine and Reward - University College London
... More elaborate behavioral phenomena (Neural data) ...
... More elaborate behavioral phenomena (Neural data) ...