Cognition and Operant Conditioning
... James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers ...
... James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers ...
PSYCHOLOGY Unit 3: Learning“Operant Conditioning”
... does not actually offer any information about more appropriate or desired behaviors. While subjects might be learning to not perform certain actions, they are not really learning anything about what they should be doing. Another thing to consider about punishment is that it can have unintended and u ...
... does not actually offer any information about more appropriate or desired behaviors. While subjects might be learning to not perform certain actions, they are not really learning anything about what they should be doing. Another thing to consider about punishment is that it can have unintended and u ...
Answers To Test Yourself Questions
... Some behaviours are highly related to the genetic makeup of the organism (e.g., species-specific behaviours). These behaviours are referred to as prepared and are emitted without applying learning contingencies (e.g., cats lick themselves after eating without being taught to do so; humans may easily ...
... Some behaviours are highly related to the genetic makeup of the organism (e.g., species-specific behaviours). These behaviours are referred to as prepared and are emitted without applying learning contingencies (e.g., cats lick themselves after eating without being taught to do so; humans may easily ...
File - Learning! Outside of Class!
... Big Bang Theory: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mt4N9GSBoMI ...
... Big Bang Theory: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mt4N9GSBoMI ...
What Is Psychology?
... responses, will, mental images) Believe that mind functions by creatively combining the elements of experience ...
... responses, will, mental images) Believe that mind functions by creatively combining the elements of experience ...
Operant Conditioning A type of learning in which behavior is
... emotions (via conditioning), rather than the rational, thoughtful part of the mind because they are more effective in influencing our behavior. Since they work (reinforced), politicians and their strategists will use them. Until we stop being influenced by them, politicians will use them less. • Pro ...
... emotions (via conditioning), rather than the rational, thoughtful part of the mind because they are more effective in influencing our behavior. Since they work (reinforced), politicians and their strategists will use them. Until we stop being influenced by them, politicians will use them less. • Pro ...
File
... If you decide the situation is an example of operant conditioning, you should decide which of the following principles most applies: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, positive punishment, or negative punishment. ...
... If you decide the situation is an example of operant conditioning, you should decide which of the following principles most applies: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, positive punishment, or negative punishment. ...
Theories of Human Behavior Objectives
... memory cognitive activity, motivated to perform (or not) iii. Reciprocal Determinism: interaction of individual and their environment; behavior is influenced by environment and can impact the environment iv. Behavior not just result of past reinforcement but due to anticipated future reinforcement ...
... memory cognitive activity, motivated to perform (or not) iii. Reciprocal Determinism: interaction of individual and their environment; behavior is influenced by environment and can impact the environment iv. Behavior not just result of past reinforcement but due to anticipated future reinforcement ...
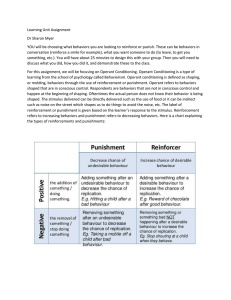
Learning Unit Assignment Dr Sharon Myer YOU will be choosing
... YOU will be choosing what behaviors you are looking to reinforce or punish. These can be behaviors in conversation (reinforce a smile for example), what you want someone to do (to leave, to get you something, etc.). You will have about 25 minutes to design this with your group. Then you will need to ...
... YOU will be choosing what behaviors you are looking to reinforce or punish. These can be behaviors in conversation (reinforce a smile for example), what you want someone to do (to leave, to get you something, etc.). You will have about 25 minutes to design this with your group. Then you will need to ...
The Science of Psychology - Texas Christian University
... Theory stated that we are motivated by unconscious instincts and urges that are not available to the rational, conscious part of our mind. Sigmund Freud-- physician who was convinced that many ailments were psychological rather than physiological in nature. He was trying to explain the psycholog ...
... Theory stated that we are motivated by unconscious instincts and urges that are not available to the rational, conscious part of our mind. Sigmund Freud-- physician who was convinced that many ailments were psychological rather than physiological in nature. He was trying to explain the psycholog ...
Chapter 8 pt. 2: Operant Conditioning and Social Learning
... cognitive map) that is not apparent until there is an incentive to justify it. Ex: rats that were not reinforced while in a maze could navigate it just as fast when there was a reward put at the end. ...
... cognitive map) that is not apparent until there is an incentive to justify it. Ex: rats that were not reinforced while in a maze could navigate it just as fast when there was a reward put at the end. ...
Learning? What`s that?
... Pavlov says process is stimulus substitution. Cognitive psychologists believe there must be an expectancy created by the CS/UCS pair. ...
... Pavlov says process is stimulus substitution. Cognitive psychologists believe there must be an expectancy created by the CS/UCS pair. ...
skinner theory of operent conditioning and shaping
... in the experimental analysis of behaviour. Skinner proved this using a Bird in a Cage. Skinner says,” it is constructed by a continual process of differential reinforcement from undifferentiated behavior, just as the sculptor shapes his figure from a lump of clay” ...
... in the experimental analysis of behaviour. Skinner proved this using a Bird in a Cage. Skinner says,” it is constructed by a continual process of differential reinforcement from undifferentiated behavior, just as the sculptor shapes his figure from a lump of clay” ...
Learning? What`s that?
... Operant Conditioning? What’s that? Thorndike’s cats in boxes helps him establish the “Law of Effect”. Skinner continues the trend with rats in boxes. • What do we mean by a reinforcer? • Some reinforcers are primary? • Some reinforcers are secondary? Gold star • How are they different from a punish ...
... Operant Conditioning? What’s that? Thorndike’s cats in boxes helps him establish the “Law of Effect”. Skinner continues the trend with rats in boxes. • What do we mean by a reinforcer? • Some reinforcers are primary? • Some reinforcers are secondary? Gold star • How are they different from a punish ...
History of Neurology
... B-Susquehanna, Pennsylvania Hamilton College BA/Harvard PhD Psychology (1931) Influenced by Watson Research at Harvard till 1936 Then U Minn, U of Indiana & back to Harvard 1948-1970 Developed field of Radical Behaviorism – All actions have consequences of environmental reinforcement – Humans react ...
... B-Susquehanna, Pennsylvania Hamilton College BA/Harvard PhD Psychology (1931) Influenced by Watson Research at Harvard till 1936 Then U Minn, U of Indiana & back to Harvard 1948-1970 Developed field of Radical Behaviorism – All actions have consequences of environmental reinforcement – Humans react ...
- W.W. Norton
... The organism learns an association between a behavior and a punishment. The organism learns an association between a behavior and a consequence. E. None of the above ...
... The organism learns an association between a behavior and a punishment. The organism learns an association between a behavior and a consequence. E. None of the above ...
CHAPTER 2 FOUNDATIONS OF INDIVIDUAL BEHAVIOR
... will most likely engage in desired behaviors if they are positively reinforced for doing so. Rewards are most effective if they immediately follow the desired response. In addition, behavior that is not rewarded or is punished, is less likely to be repeated" (p. 42). ...
... will most likely engage in desired behaviors if they are positively reinforced for doing so. Rewards are most effective if they immediately follow the desired response. In addition, behavior that is not rewarded or is punished, is less likely to be repeated" (p. 42). ...
Katie Ross EDUF 7130 Dr. Jonathan Hilpert 5 September 2015
... “A New Goal for Psychology,” para.1). This view of psychology and human behavior is very simple in many ways, as it leaves out the concepts of free will and negotiation. For many years, operant conditioning has been used as a method of classroom management. Teachers and school administrators use the ...
... “A New Goal for Psychology,” para.1). This view of psychology and human behavior is very simple in many ways, as it leaves out the concepts of free will and negotiation. For many years, operant conditioning has been used as a method of classroom management. Teachers and school administrators use the ...
- OoCities
... retention, motor reproduction, and reinforcement processes. People learn from a model only when they recognize and pay attention to its critical features. We tend to be most influenced by models that are attractive, repeatedly available, important to us, or similar to us in our estimation. A model's ...
... retention, motor reproduction, and reinforcement processes. People learn from a model only when they recognize and pay attention to its critical features. We tend to be most influenced by models that are attractive, repeatedly available, important to us, or similar to us in our estimation. A model's ...
Behavior modification
... Change controlling variables or B Antecedents Consequences behavioral deficits Preparation, reminders Reinforcement behavioral excesses Punishment or extinction Reinforce competing responses ~ ...
... Change controlling variables or B Antecedents Consequences behavioral deficits Preparation, reminders Reinforcement behavioral excesses Punishment or extinction Reinforce competing responses ~ ...
eyes of the drug using parent
... How might it help people who work with drug endangered children to have a thorough understanding of how and why some people get addicted to drugs? Please explain your answer: _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ ______________________ ...
... How might it help people who work with drug endangered children to have a thorough understanding of how and why some people get addicted to drugs? Please explain your answer: _________________________________________________ _________________________________________________ ______________________ ...
Review Jeopardy
... As a child, you were playing in the yard one day when a neighbor’s cat wandered over. Your mother (who has a fear of cats) screamed and snatched you into her arms. Her behavior caused you to cry. You now have a fear of cats. What is the CR? What is the NS? ...
... As a child, you were playing in the yard one day when a neighbor’s cat wandered over. Your mother (who has a fear of cats) screamed and snatched you into her arms. Her behavior caused you to cry. You now have a fear of cats. What is the CR? What is the NS? ...