Behavior Solutions: How Dogs Learn
... than is necessary to achieve the correct response from your dog. Unconditioned punishment is something your dog instinctively dislikes as related to survival (pain, loud noises, loss of necessities). An example of an unconditioned punishment for some dogs would be thunder. Conditioned punishment is ...
... than is necessary to achieve the correct response from your dog. Unconditioned punishment is something your dog instinctively dislikes as related to survival (pain, loud noises, loss of necessities). An example of an unconditioned punishment for some dogs would be thunder. Conditioned punishment is ...
Lumbert, Samantha P. "Conformity and Group Mentality: Why We
... entire lives, young people who are seeking to define themselves are generally most influenced by the attitudes of their peers. Adolescents often encourage friends to do or try things that they themselves are doing in order to fit into to a group. The encouragement can be positive (studying hard to g ...
... entire lives, young people who are seeking to define themselves are generally most influenced by the attitudes of their peers. Adolescents often encourage friends to do or try things that they themselves are doing in order to fit into to a group. The encouragement can be positive (studying hard to g ...
Behavior Therapy
... or feelings come a client’s way, they are encouraged to first notice them and then accept them instead of trying to change or control them. Clients are encouraged to take note of their thoughts as if they were not their own and view them as an outsider. Putting a different perspective on their thoug ...
... or feelings come a client’s way, they are encouraged to first notice them and then accept them instead of trying to change or control them. Clients are encouraged to take note of their thoughts as if they were not their own and view them as an outsider. Putting a different perspective on their thoug ...
chapter 6 review with answers
... taught by observing. Sometimes we observe someone taking part in operant conditioning and we mimic their actions 1. Attention - To learn through observation you must pay attention 2. Retention - Must store mental representation of what you’ve witnessed in your memory 3. Reproduction - Enacting a mod ...
... taught by observing. Sometimes we observe someone taking part in operant conditioning and we mimic their actions 1. Attention - To learn through observation you must pay attention 2. Retention - Must store mental representation of what you’ve witnessed in your memory 3. Reproduction - Enacting a mod ...
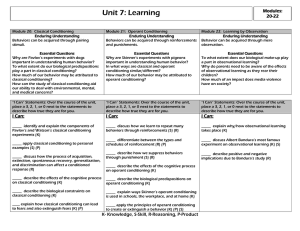
Modules 20-22
... Why are Skinner’s experiments with pigeons important in understanding human behavior? In what ways are classical and operant conditioning similar/different? How much of our behavior may be attributed to operant conditioning? ...
... Why are Skinner’s experiments with pigeons important in understanding human behavior? In what ways are classical and operant conditioning similar/different? How much of our behavior may be attributed to operant conditioning? ...
Learning
... The tendency to respond differently to two or more similar stimuli. In classical conditioning, it occurs when a stimulus similar to the condition stimulus (CS) fails to evoke a conditioned response ...
... The tendency to respond differently to two or more similar stimuli. In classical conditioning, it occurs when a stimulus similar to the condition stimulus (CS) fails to evoke a conditioned response ...
1. Stimulus-intrinsic theories
... -children that had high baseline preference for pinball increased the amount of candy they ate -then, reversed the contingency: children now had to play pinball a certain amount of time to receive candy -now, children that had a high baseline preference for eating candy increased their pinball-playi ...
... -children that had high baseline preference for pinball increased the amount of candy they ate -then, reversed the contingency: children now had to play pinball a certain amount of time to receive candy -now, children that had a high baseline preference for eating candy increased their pinball-playi ...
Memory - Peoria Public Schools
... Evidence of cognitive processes during operant learning comes from rats during a maze exploration in which they navigate the maze without an obvious reward. Rats seem to develop cognitive maps, or mental representations, of the layout of the maze ...
... Evidence of cognitive processes during operant learning comes from rats during a maze exploration in which they navigate the maze without an obvious reward. Rats seem to develop cognitive maps, or mental representations, of the layout of the maze ...
Second-order conditioning
... when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur; those which are accompanied or closely followed by discomfort to the animal will, other things being equal, have their connections to the situation weakened, so that, when it recurs, they will be less likely to occur. ...
... when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur; those which are accompanied or closely followed by discomfort to the animal will, other things being equal, have their connections to the situation weakened, so that, when it recurs, they will be less likely to occur. ...
learning - Wofford
... • is the shorthand for a collection of procedures, techniques and outcomes that produce a change in an organisms behavior Learning involves some relatively permanent change in the state of the learner ...
... • is the shorthand for a collection of procedures, techniques and outcomes that produce a change in an organisms behavior Learning involves some relatively permanent change in the state of the learner ...
Week 9
... This is why second order conditioning is weaker, because the original US is absent in second order conditioning. ...
... This is why second order conditioning is weaker, because the original US is absent in second order conditioning. ...
Foundations of Individual Behavior
... by Gary Larson © 1993 Far Works, Inc. All rights reserved. Used with ...
... by Gary Larson © 1993 Far Works, Inc. All rights reserved. Used with ...
Organizational Behavior 11e
... by Gary Larson © 1993 Far Works, Inc. All rights reserved. Used with ...
... by Gary Larson © 1993 Far Works, Inc. All rights reserved. Used with ...
Learning
... Ideas of classical conditioning originate from old philosophical theories. However, it was the Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov who elucidated classical conditioning. His work provided a basis for later behaviorists like John Watson and B. F. Skinner. ...
... Ideas of classical conditioning originate from old philosophical theories. However, it was the Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov who elucidated classical conditioning. His work provided a basis for later behaviorists like John Watson and B. F. Skinner. ...
Sample summary
... found for positions of responsibility. However, when the “right” people are leaving the company, meaning non-performers, it can be positive because employers are able to replace the positions with better/higher skilled and motivated people, and it might create opportunities for promotions. However, ...
... found for positions of responsibility. However, when the “right” people are leaving the company, meaning non-performers, it can be positive because employers are able to replace the positions with better/higher skilled and motivated people, and it might create opportunities for promotions. However, ...
Learning
... Ideas of classical conditioning originate from old philosophical theories. However, it was the Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov who elucidated classical conditioning. His work provided a basis for later behaviorists like John Watson and B. F. Skinner. ...
... Ideas of classical conditioning originate from old philosophical theories. However, it was the Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov who elucidated classical conditioning. His work provided a basis for later behaviorists like John Watson and B. F. Skinner. ...
Seminar: Skinner`s Analysis of Verbal Behavior
... properties of such behavior • Likely that additional private stimulation occurs in connection with the public behavior • Verbal community sets up the reinforcing contingency based upon the external behavior but private stimulation also acquires control ...
... properties of such behavior • Likely that additional private stimulation occurs in connection with the public behavior • Verbal community sets up the reinforcing contingency based upon the external behavior but private stimulation also acquires control ...
Learning: Test Revision Section A – Multiple choice questions
... evening, when John arrives home from work, he takes his son aside and smacks him for his poor behaviour earlier that day. a. With reference to operant conditioning, give two reasons why Jackie and John’s punishment of their son is likely to be ineffective. 1._________________________________________ ...
... evening, when John arrives home from work, he takes his son aside and smacks him for his poor behaviour earlier that day. a. With reference to operant conditioning, give two reasons why Jackie and John’s punishment of their son is likely to be ineffective. 1._________________________________________ ...
Theories of Behavior Change
... • Intention has been shown to be the most important variable in predicting behavior change, suggesting that behaviors are often linked with one’s personal motivation.8 This suggests that it may be important to present information to help shape positive attitudes towards the behavior and stress subj ...
... • Intention has been shown to be the most important variable in predicting behavior change, suggesting that behaviors are often linked with one’s personal motivation.8 This suggests that it may be important to present information to help shape positive attitudes towards the behavior and stress subj ...
T10_Motivation_(2009-2)_web
... getting things done. Volunteer services are scarce and more people expect higher salaries because of greed. Unlike intrinsic motivation, which comes from inside, extrinsic motivation is created from external factors. ...
... getting things done. Volunteer services are scarce and more people expect higher salaries because of greed. Unlike intrinsic motivation, which comes from inside, extrinsic motivation is created from external factors. ...
learning - Christopher J. Holden, Ph.D.
... • Instinctive drift: tendency for an animal’s behavior to revert to genetically controlled patterns – Each animal comes into the world (and the laboratory) with certain genetically determined instinctive patterns of behavior already in place. – These instincts differ from species to species. – There ...
... • Instinctive drift: tendency for an animal’s behavior to revert to genetically controlled patterns – Each animal comes into the world (and the laboratory) with certain genetically determined instinctive patterns of behavior already in place. – These instincts differ from species to species. – There ...
FREE Sample Here
... b. a constant flow of behavior that can be directed in only one way c. a constant flow of behavior that can be directed in many different ways d. a state where one is either motivated or not motivated [c 3 factual] 2. The concept of motivation is used to describe forces acting on or within an organi ...
... b. a constant flow of behavior that can be directed in only one way c. a constant flow of behavior that can be directed in many different ways d. a state where one is either motivated or not motivated [c 3 factual] 2. The concept of motivation is used to describe forces acting on or within an organi ...
psyc - Course Catalog 2016-2017
... This course will survey major theories and empirical findings of cognitive development and the development of interpersonal relations across childhood. Prereq.: PSYC 6905. PSYC 6940 Personality Theory 2 s.h. The study of major personality theories and their implications for psychotherapy and mental ...
... This course will survey major theories and empirical findings of cognitive development and the development of interpersonal relations across childhood. Prereq.: PSYC 6905. PSYC 6940 Personality Theory 2 s.h. The study of major personality theories and their implications for psychotherapy and mental ...
Cognition and Operant Conditioning
... performing certain actions or when observing another doing so may enable imitation, language learning, and empathy ...
... performing certain actions or when observing another doing so may enable imitation, language learning, and empathy ...