Ch 6 Learning Notes
... – We know that the response is still there, just not active, because of spontaneous recovery • Spontaneous Recovery: an extinguished response reappears after a period of non-pairing. • Stimulus Generalization: occurs when conditioning generalizes to additional stimuli that are similar to the CS; – f ...
... – We know that the response is still there, just not active, because of spontaneous recovery • Spontaneous Recovery: an extinguished response reappears after a period of non-pairing. • Stimulus Generalization: occurs when conditioning generalizes to additional stimuli that are similar to the CS; – f ...
Unit 6 Practice Test
... 9. Monica's psychotherapist reminds her so much of her own father that she has many of the same mixed emotional reactions to him that she has to her own dad. Her reactions to her therapist best illustrate the importance of: A) habituation. B) latent learning. C) generalization. D) delayed reinforcem ...
... 9. Monica's psychotherapist reminds her so much of her own father that she has many of the same mixed emotional reactions to him that she has to her own dad. Her reactions to her therapist best illustrate the importance of: A) habituation. B) latent learning. C) generalization. D) delayed reinforcem ...
Chapter 8 Practice Test
... 9. Monica's psychotherapist reminds her so much of her own father that she has many of the same mixed emotional reactions to him that she has to her own dad. Her reactions to her therapist best illustrate the importance of: A) habituation. B) latent learning. C) generalization. D) delayed reinforcem ...
... 9. Monica's psychotherapist reminds her so much of her own father that she has many of the same mixed emotional reactions to him that she has to her own dad. Her reactions to her therapist best illustrate the importance of: A) habituation. B) latent learning. C) generalization. D) delayed reinforcem ...
Chapter 5: Learning and Behavior A. Learning
... 2. Extinction can be slowed by having less frequent reinforcements this is called intermittent (partial) reinforcement in which not every response is followed by a reinforcer 3. Reacquisition after extinction is generally more rapid than original acquisition 4. Reacquisition and spontaneous recovery ...
... 2. Extinction can be slowed by having less frequent reinforcements this is called intermittent (partial) reinforcement in which not every response is followed by a reinforcer 3. Reacquisition after extinction is generally more rapid than original acquisition 4. Reacquisition and spontaneous recovery ...
Learning Psychology
... Ex: A child whines and gags while being forced to eat meat loaf because she doesn’t like it and the parent removes the meatloaf (escape) If the child whines as soon as it comes out of the oven and is not served meatloaf (avoidance) ...
... Ex: A child whines and gags while being forced to eat meat loaf because she doesn’t like it and the parent removes the meatloaf (escape) If the child whines as soon as it comes out of the oven and is not served meatloaf (avoidance) ...
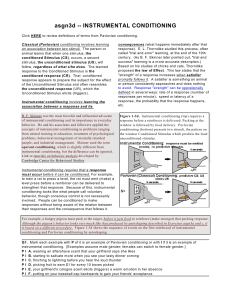
asgn3d -- INSTRUMENTAL CONDITIONING
... Prem ack proposed a Response Strength theory. It states that a weaker response will get stronger when doing it provides access to doing a stronger one. Prem ack m easured the operant level of pairs of responses and showed that the weaker response (the one with the lower operant level) can be strengt ...
... Prem ack proposed a Response Strength theory. It states that a weaker response will get stronger when doing it provides access to doing a stronger one. Prem ack m easured the operant level of pairs of responses and showed that the weaker response (the one with the lower operant level) can be strengt ...
Learning
... This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or part, of any images; any r ...
... This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following are prohibited by law: any public performance or display, including transmission of any image over a network; preparation of any derivative work, including the extraction, in whole or part, of any images; any r ...
Edwin Ray Guthrie (1886
... was difficult, so avoiding stimuli that cause undesirable habits was to sidetrack them. Undesirable behavioral patterns (like smoking) in one environment can be sidetracked by going to a completely new environment (where cigarettes/tobacco is not available). ...
... was difficult, so avoiding stimuli that cause undesirable habits was to sidetrack them. Undesirable behavioral patterns (like smoking) in one environment can be sidetracked by going to a completely new environment (where cigarettes/tobacco is not available). ...
What is learned?
... better starting from that 11th day...but instead: Tolman found running was slow for 11 days, then was suddenly fast from 12th day on ...
... better starting from that 11th day...but instead: Tolman found running was slow for 11 days, then was suddenly fast from 12th day on ...
Handout - ADE Special Education
... behaviors is by watching others. They watch you – how you handle your anger, etc. They watch other students – and what behaviors get reinforced and punished. When you model a procedure in order to teach them how to do it – they learn by watching you demonstrate. Much learning happens this way. ...
... behaviors is by watching others. They watch you – how you handle your anger, etc. They watch other students – and what behaviors get reinforced and punished. When you model a procedure in order to teach them how to do it – they learn by watching you demonstrate. Much learning happens this way. ...
Chapter 5 Classical and Operant Conditioning
... • The law of effect...responses followed by a “satisfying state of affairs” are strengthened, and are more likely to occur again in the same situation, whereas responses followed by an “unsatisfying or unpleasant state of affairs” are weakened and are less likely to occur again. • B.F. Skinner belie ...
... • The law of effect...responses followed by a “satisfying state of affairs” are strengthened, and are more likely to occur again in the same situation, whereas responses followed by an “unsatisfying or unpleasant state of affairs” are weakened and are less likely to occur again. • B.F. Skinner belie ...
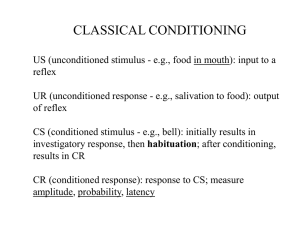
Classical Conditioning
... A mental representation of the layout of one’s environment Example: after exploring a maze, rats act as if they have learned a cognitive map of it ...
... A mental representation of the layout of one’s environment Example: after exploring a maze, rats act as if they have learned a cognitive map of it ...
Chapter Outline - Cengage Learning
... 19. Escape conditioning occurs when an organism learns that a particular response will terminate an aversive stimulus. (see Basic Components of Operant Conditioning) Example: Lydia has recently set up a computer at home and now does most of her work there. Her cat, Spooky, has begun to sit next to t ...
... 19. Escape conditioning occurs when an organism learns that a particular response will terminate an aversive stimulus. (see Basic Components of Operant Conditioning) Example: Lydia has recently set up a computer at home and now does most of her work there. Her cat, Spooky, has begun to sit next to t ...
operant conditioning
... Shaping is the procedure in which reinforcement is given for any response that successively approximates and ultimately leads to the final desired response, or target behaviour. (Also known as the method of successive ...
... Shaping is the procedure in which reinforcement is given for any response that successively approximates and ultimately leads to the final desired response, or target behaviour. (Also known as the method of successive ...
Ch. 6 Learning King 3rd Edition Updated 3-15
... • Watson on Albert – "Albert's life was normal: he was healthy from birth and one of the best developed youngsters ever brought to the hospital, weighing twenty-one pounds at nine months of age. He was on the whole solid and unemotional. His stability was one of the principal reasons for using him a ...
... • Watson on Albert – "Albert's life was normal: he was healthy from birth and one of the best developed youngsters ever brought to the hospital, weighing twenty-one pounds at nine months of age. He was on the whole solid and unemotional. His stability was one of the principal reasons for using him a ...
Classical, Instrumental and Operant Conditioning
... Escape conditioning: when an organism learns to make a response in order to end an aversive stimulus, or negative reinforcer. Avoidance conditioning: when an animal or person responds to a signal in a way that avoids exposure to an aversive stimulus. ...
... Escape conditioning: when an organism learns to make a response in order to end an aversive stimulus, or negative reinforcer. Avoidance conditioning: when an animal or person responds to a signal in a way that avoids exposure to an aversive stimulus. ...
Learning Theories - Dr. Howard Fine, Clinical Psychologist London UK
... people’s behavior Vicarious reinforcement or vicarious punishment affects the willingness of people to perform behaviors they learned by watching others ...
... people’s behavior Vicarious reinforcement or vicarious punishment affects the willingness of people to perform behaviors they learned by watching others ...
Learning Key Figures: Ivan Pavlov Theorist who
... becoming associated with the unconditioned stimulus, eventually comes to trigger a conditioned response. For example, suppose that the smell of food is an unconditioned stimulus and a feeling of hunger is the unconditioned response. Now, imagine that when you smelled your favorite food, you also ...
... becoming associated with the unconditioned stimulus, eventually comes to trigger a conditioned response. For example, suppose that the smell of food is an unconditioned stimulus and a feeling of hunger is the unconditioned response. Now, imagine that when you smelled your favorite food, you also ...
Psychological Perspectives on Behavior: From Purposeful to
... humans) followed certain fundamental laws. The most well-known of these is his law of effect, stating that behaviors that are followed by “satisfaction to the animal” will most likely recur, while actions followed by “discomfort to the animal” will be less likely to recur. Thorndike was the first ps ...
... humans) followed certain fundamental laws. The most well-known of these is his law of effect, stating that behaviors that are followed by “satisfaction to the animal” will most likely recur, while actions followed by “discomfort to the animal” will be less likely to recur. Thorndike was the first ps ...
Chapter 6 - ED-180
... Students are given unannounced quizzes, and sometimes the quizzes are returned the next day, and at other times they are returned a day or two ater. ...
... Students are given unannounced quizzes, and sometimes the quizzes are returned the next day, and at other times they are returned a day or two ater. ...
B.F. Skinner Skinner`s Life Reinforcement, Cont`d.
... • One of the first trained in our current model of clinical psychology ...
... • One of the first trained in our current model of clinical psychology ...
View Sample Pages - Plural Publishing
... not acceptable to a behaviorist to describe a behavior as an internal emotional event, such as joy. A behaviorist would instead describe and quantify behaviors that might indicate the person is joyful, such as smiling, laughing, jumping up and down, or making cheering noises. Empiricists also do not ...
... not acceptable to a behaviorist to describe a behavior as an internal emotional event, such as joy. A behaviorist would instead describe and quantify behaviors that might indicate the person is joyful, such as smiling, laughing, jumping up and down, or making cheering noises. Empiricists also do not ...