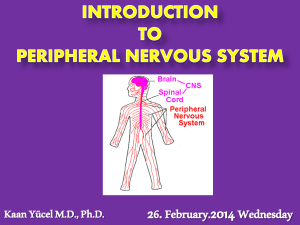
1. 2. a) Explain the compositions of white matter and gray matter
... while the right hemisphere is essentially mute. Furthermore, his work showed that while only the left hemisphere is able to verbalize the information carried by visual stimuli, both hemispheres are able to process and comprehend the information. In what are now known as the split brain experiments, ...
... while the right hemisphere is essentially mute. Furthermore, his work showed that while only the left hemisphere is able to verbalize the information carried by visual stimuli, both hemispheres are able to process and comprehend the information. In what are now known as the split brain experiments, ...
Biological Bases
... The brain’s ability to quickly regrow damaged neurons The surface texture and appearance cause by the layer known as the cerebral cortex The brain’s versatility caused by the millions of different neural connections Our adaptability to different problems ranging from survival needs to abstract reaso ...
... The brain’s ability to quickly regrow damaged neurons The surface texture and appearance cause by the layer known as the cerebral cortex The brain’s versatility caused by the millions of different neural connections Our adaptability to different problems ranging from survival needs to abstract reaso ...
1 2 The Advent of Modern Neuroscience
... in a patient who could speak clearly. The brains of people who suffered from Wernicke’s aphasia revealed a lesion in an area now referred to as Wernicke’s area. In patients suffering from Wernicke’s aphasia, speech is fluent, but does not make any sense. He used his findings with those of Broca, Frits ...
... in a patient who could speak clearly. The brains of people who suffered from Wernicke’s aphasia revealed a lesion in an area now referred to as Wernicke’s area. In patients suffering from Wernicke’s aphasia, speech is fluent, but does not make any sense. He used his findings with those of Broca, Frits ...
Study Shows Practice May Have Potential to Change Brain`s
... ScienceDaily (July 14, 2011) — Two years ago, researchers at UCLA found that specific regions in the brains of long-term meditators were larger and had more gray matter than the brains of individuals in a control group. This suggested that meditation may indeed be good for all of us since, alas, our ...
... ScienceDaily (July 14, 2011) — Two years ago, researchers at UCLA found that specific regions in the brains of long-term meditators were larger and had more gray matter than the brains of individuals in a control group. This suggested that meditation may indeed be good for all of us since, alas, our ...
The Brain
... o Asymmetrical cell division: Progenitor cell and Brain cell (radial glial cells- support migration, and neurons)-> create brain tissue o Longer a/symmetrical division stages= larger brains o After 5 months: Apoptosis- suicide signal for progenitor cells (tells cells to stop) o Ventricles produc ...
... o Asymmetrical cell division: Progenitor cell and Brain cell (radial glial cells- support migration, and neurons)-> create brain tissue o Longer a/symmetrical division stages= larger brains o After 5 months: Apoptosis- suicide signal for progenitor cells (tells cells to stop) o Ventricles produc ...
The Brain - Gordon State College
... The Brain Can Alter Its Neural Connections – Plasticity: the flexibility of the brain to alter its neural connections following injury – Hemispherectomy: a radical surgical procedure in which one of the cerebral hemispheres is removed to control life-threatening epileptic seizures. The remaining he ...
... The Brain Can Alter Its Neural Connections – Plasticity: the flexibility of the brain to alter its neural connections following injury – Hemispherectomy: a radical surgical procedure in which one of the cerebral hemispheres is removed to control life-threatening epileptic seizures. The remaining he ...
Biosocial Development - Austin Community College District
... • Proceeds most rapidly from age 4 and continues through adolescence, allowing children to gain increasing neurological control over their motor functions and sensory abilities and facilitates their intellectual functioning as well. ...
... • Proceeds most rapidly from age 4 and continues through adolescence, allowing children to gain increasing neurological control over their motor functions and sensory abilities and facilitates their intellectual functioning as well. ...
Exam 1 Review - Central Connecticut State University
... • 1. The division of the nervous system that is made up of neurons that control the heart, intestines, and other organs is the ...
... • 1. The division of the nervous system that is made up of neurons that control the heart, intestines, and other organs is the ...
Frontal Lobe - Washington School Counselor Association
... Addiction occurs when repeated use of drugs changes how a person ...
... Addiction occurs when repeated use of drugs changes how a person ...
STUDY GUIDE: UNIT III – BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR AP
... 12-1: What are the functions served by the various cerebral cortex regions? Brain parts & regions Motor cortex & sensory cortex Phineas Gage & association areas 12-2: To what extent can a damaged brain reorganize itself? Brain plasticity neurogenesis ...
... 12-1: What are the functions served by the various cerebral cortex regions? Brain parts & regions Motor cortex & sensory cortex Phineas Gage & association areas 12-2: To what extent can a damaged brain reorganize itself? Brain plasticity neurogenesis ...
Hippocampus - Solon City Schools
... Areas of the Cerebral Cortex • Divided into eight lobes, four in each hemisphere (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal). • Any area not dealing with our senses or muscle movements are called association areas. ...
... Areas of the Cerebral Cortex • Divided into eight lobes, four in each hemisphere (frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal). • Any area not dealing with our senses or muscle movements are called association areas. ...
Mod.73
... 1. Compare treated to those who are not on drug protocol [control group] 2. Placebo effect: simply taking a drug can affect behavior Drugs generally are more effective than the placebo effect Antipsychotics already covered!! Antianxiety [more clinical term is anxiolytic]: Xanax & Ativan also already ...
... 1. Compare treated to those who are not on drug protocol [control group] 2. Placebo effect: simply taking a drug can affect behavior Drugs generally are more effective than the placebo effect Antipsychotics already covered!! Antianxiety [more clinical term is anxiolytic]: Xanax & Ativan also already ...
(Early Period) - Connectionism
... either ‘firing’ electrochemical impulses down their lengthy projections (axons) towards junctions with other neurons (synapses) or are inactive. ● Hebb’s rule: Donald Hebb (1949) proposed that the connection between two biological neurons is strengthened when both neurons are simultaneously active. ...
... either ‘firing’ electrochemical impulses down their lengthy projections (axons) towards junctions with other neurons (synapses) or are inactive. ● Hebb’s rule: Donald Hebb (1949) proposed that the connection between two biological neurons is strengthened when both neurons are simultaneously active. ...
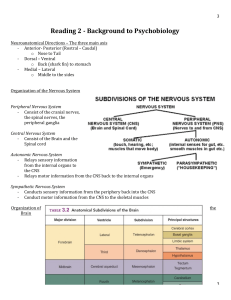
Reading 2 - Background to Psychobiology
... - Contains Primary motor cortex (area 4), premotor cortex (area 6), Broca’s area (area 44) and the prefrontal cortex. - Receives information from: 1. Thalamic nuclei 2. Hypothalamus 3. Limbic system 4. Other lobes - Functions 1. Working memory 2. Higher order cognitive behaviors – Pla ...
... - Contains Primary motor cortex (area 4), premotor cortex (area 6), Broca’s area (area 44) and the prefrontal cortex. - Receives information from: 1. Thalamic nuclei 2. Hypothalamus 3. Limbic system 4. Other lobes - Functions 1. Working memory 2. Higher order cognitive behaviors – Pla ...
Public Lecture - Indian Institute of Science Education and Research
... excellence. In a short span of 5 years she established a state-of-art institute in a rather remote location and created a new paradigm for research by integrating mathematical and computational science into the understanding complex biological systems. NBRC was granted deemed University status in Ma ...
... excellence. In a short span of 5 years she established a state-of-art institute in a rather remote location and created a new paradigm for research by integrating mathematical and computational science into the understanding complex biological systems. NBRC was granted deemed University status in Ma ...
Learning Styles PowerPoint
... behavior and often general attitude. Good at understanding self, focusing inwards on feelings and dreams, following instincts, pursuing goals and being original. Student needs to take time after class and pick out important information for notes. Notes need to be in their own words. Studying nee ...
... behavior and often general attitude. Good at understanding self, focusing inwards on feelings and dreams, following instincts, pursuing goals and being original. Student needs to take time after class and pick out important information for notes. Notes need to be in their own words. Studying nee ...
Reading the neural code in behaving animals, ~1000 neurons at a ,me
... The microscope also allows 3me-‐lapse imaging, for watching how individual cells' coding proper3es evolve over weeks. By using the integrated microscope to perform calcium-‐imaging in behaving mice as they rep ...
... The microscope also allows 3me-‐lapse imaging, for watching how individual cells' coding proper3es evolve over weeks. By using the integrated microscope to perform calcium-‐imaging in behaving mice as they rep ...
HW CH 5 PSY 2513 Submit your answers on canvas
... if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than language skills and are easier to recover after injury. d. the right and left hemispheres of the brain have become strongly lateralized. ...
... if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than language skills and are easier to recover after injury. d. the right and left hemispheres of the brain have become strongly lateralized. ...
Figure 3B.23 Testing the divided brain
... the motor cortex and the sensory cortex As you can see from this classic though inexact representation, the amount of cortex devoted to a body part is not proportional to that part’s size. Rather, the brain devotes more tissue to sensitive areas and to areas requiring precise control. Thus, the fing ...
... the motor cortex and the sensory cortex As you can see from this classic though inexact representation, the amount of cortex devoted to a body part is not proportional to that part’s size. Rather, the brain devotes more tissue to sensitive areas and to areas requiring precise control. Thus, the fing ...
Biology and Psychology - Austin Community College
... 4. Medulla (continuation of spine) regulates heartbeat, ...
... 4. Medulla (continuation of spine) regulates heartbeat, ...
DESIRED RESULTS (STAGE 1) - Anoka
... The Difference between the two hemispheres somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system The structure of the nervous system hormone limbic system How neurons communicate To understand, students will need to DO... REASONING ...
... The Difference between the two hemispheres somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system The structure of the nervous system hormone limbic system How neurons communicate To understand, students will need to DO... REASONING ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.