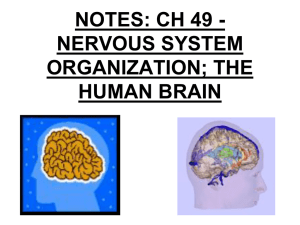
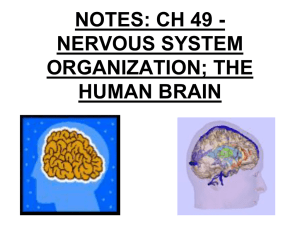
BRAIN
... Connects fore and hind brains. Mainly responsible for movements such as head and eyes focussing on an object. ...
... Connects fore and hind brains. Mainly responsible for movements such as head and eyes focussing on an object. ...
Brain Jokes (Questions)
... 9. What kind of fish performs brain operations? 10. What do you get when you cross a thought with a light bulb? 11. Why do neurons like e-mail? 12. Which cranial nerve would be right at home in a well-known city in Nevada? 13. Where do brains go for vacation in Massachusetts? 14. What did the Hollyw ...
... 9. What kind of fish performs brain operations? 10. What do you get when you cross a thought with a light bulb? 11. Why do neurons like e-mail? 12. Which cranial nerve would be right at home in a well-known city in Nevada? 13. Where do brains go for vacation in Massachusetts? 14. What did the Hollyw ...
In your journal, take notes by writing the name of
... brain stem, which is close to the center of the brain. The human thalamus can be divided into two pear-shaped halves. The thalamus is often referred to as the "relay station" of the brain. This is because the thalamus has a primary function of relaying information to other parts of the body. The tha ...
... brain stem, which is close to the center of the brain. The human thalamus can be divided into two pear-shaped halves. The thalamus is often referred to as the "relay station" of the brain. This is because the thalamus has a primary function of relaying information to other parts of the body. The tha ...
Adolescents Brain Development
... • Use it or lose it • Adolescence and young adulthood is a time of great potential for change and development ...
... • Use it or lose it • Adolescence and young adulthood is a time of great potential for change and development ...
What Our Brains Can Teach Us
... since the height of the space race.” He mentioned mapping the human brain, but it’s more likely that scientists will start with smaller brains and central nervous systems — like those of worms, fruit flies, zebra fish and small mammals — before they move on to primates. No firm budget exists yet, bu ...
... since the height of the space race.” He mentioned mapping the human brain, but it’s more likely that scientists will start with smaller brains and central nervous systems — like those of worms, fruit flies, zebra fish and small mammals — before they move on to primates. No firm budget exists yet, bu ...
The Brain
... can be identified by the text being underlined and a different color (usually purple). – Unit subsections hyperlinks: Immediately after the unit title slide, a page (slide #3) can be found listing all of the unit’s subsections. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of these hyperlinks will take ...
... can be identified by the text being underlined and a different color (usually purple). – Unit subsections hyperlinks: Immediately after the unit title slide, a page (slide #3) can be found listing all of the unit’s subsections. While in slide show mode, clicking on any of these hyperlinks will take ...
Nervous System - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... sensory information to and from cerebrum; ● incoming information from all the senses is sorted here and sent on to the appropriate higher brain center; ● involved in regulating emotion & arousal (wakefulness) ...
... sensory information to and from cerebrum; ● incoming information from all the senses is sorted here and sent on to the appropriate higher brain center; ● involved in regulating emotion & arousal (wakefulness) ...
Ch 48: Nervous System – part 2 THE HUMAN BRAIN
... sensory information to and from cerebrum; ● incoming information from all the senses is sorted here and sent on to the appropriate higher brain center; ● involved in regulating emotion & arousal (wakefulness) ...
... sensory information to and from cerebrum; ● incoming information from all the senses is sorted here and sent on to the appropriate higher brain center; ● involved in regulating emotion & arousal (wakefulness) ...
Nervous System - Holy Trinity Diocesan High School
... Relay information between the brain and the body Information is electrical and chemical Receptors: specialized structures that pick up information Negative feedback to the body Stimulus-Response: much faster change but a short lasting effect compared to hormones Structures: 1. Neuron: Nerve cell; ...
... Relay information between the brain and the body Information is electrical and chemical Receptors: specialized structures that pick up information Negative feedback to the body Stimulus-Response: much faster change but a short lasting effect compared to hormones Structures: 1. Neuron: Nerve cell; ...
to Psychology 3
... - "researchers assess hereditary influence by examining blood relatives to see how much they resemble one another on a specific trait" - traits with genetic roots should also show greater correlation between family members with greater gene correlations (ex. brothers:50%, parents: 50%, grandparents: ...
... - "researchers assess hereditary influence by examining blood relatives to see how much they resemble one another on a specific trait" - traits with genetic roots should also show greater correlation between family members with greater gene correlations (ex. brothers:50%, parents: 50%, grandparents: ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... What are: 1)Sensory (messages from sensory receptors to CNS), 2)Motor (messages from CNS to muscles and glands) ...
... What are: 1)Sensory (messages from sensory receptors to CNS), 2)Motor (messages from CNS to muscles and glands) ...
SPHS 4050, Neurological bases, PP 03a
... gyrus) is part of the LIMBIC SYSTEM which includes the hippocampus and amygdala, interconneted with parts of the diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus) and olfactory (smell) system. The limbic system is strongly associated with memory and emotion ...
... gyrus) is part of the LIMBIC SYSTEM which includes the hippocampus and amygdala, interconneted with parts of the diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus) and olfactory (smell) system. The limbic system is strongly associated with memory and emotion ...
Tayler
... raise the charge inside of the cell from negative to positive Refractory period puts everything back to normal: Potassium returns inside, sodium returns outside ...
... raise the charge inside of the cell from negative to positive Refractory period puts everything back to normal: Potassium returns inside, sodium returns outside ...
Sheep Brain Dissection - Michigan State University
... to electrically stimulate this area in a sheep that was alive? The entire surface of the body is represented in the primary sensory cortex. Interestingly, some parts of the body have more cortical space that others. The figure below (right) is known as the homunculus and illustrates what the body wo ...
... to electrically stimulate this area in a sheep that was alive? The entire surface of the body is represented in the primary sensory cortex. Interestingly, some parts of the body have more cortical space that others. The figure below (right) is known as the homunculus and illustrates what the body wo ...
Page 1
... Make a prediction about the answer to each question. Put a star next to the answer that you think is correct for each question. Watch the video about the nervous system. Record the answer for each question on the line before the number as you watch the video. The Nervous System _________1. What are ...
... Make a prediction about the answer to each question. Put a star next to the answer that you think is correct for each question. Watch the video about the nervous system. Record the answer for each question on the line before the number as you watch the video. The Nervous System _________1. What are ...
Nervous System - Belle Vernon Area School District
... F. Cerebral palsy – general, defects in motor functions from several types of brain damage or birth related injury. G. Parkinsons – muscular rigidity, lack of movement H. Stroke I. Alzheimer’s disease – mental deterioration (dementia). J. Epilepsy – group of brain disorders that cause seizures K. He ...
... F. Cerebral palsy – general, defects in motor functions from several types of brain damage or birth related injury. G. Parkinsons – muscular rigidity, lack of movement H. Stroke I. Alzheimer’s disease – mental deterioration (dementia). J. Epilepsy – group of brain disorders that cause seizures K. He ...
Nervous Systems
... 4) Motor neuron: Activates effector 5) Effectors: Performs function (muscle / gland) ...
... 4) Motor neuron: Activates effector 5) Effectors: Performs function (muscle / gland) ...
Brain and Neuron Quiz Key
... Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the word bank. Some words may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. 1. The frontal lobes control motor function. ...
... Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the word bank. Some words may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. 1. The frontal lobes control motor function. ...
Press release - The Brain Prize
... The prizewinners, Stanislas Dehaene, Giacomo Rizzolatti and Trevor Robbins, from France, Italy and the UK respectively, were announced on Monday, 10 March 2014 in Copenhagen. The three scientists have provided extraordinary insights into reading skills, mathematical ability, motivations for behaviou ...
... The prizewinners, Stanislas Dehaene, Giacomo Rizzolatti and Trevor Robbins, from France, Italy and the UK respectively, were announced on Monday, 10 March 2014 in Copenhagen. The three scientists have provided extraordinary insights into reading skills, mathematical ability, motivations for behaviou ...
Nervous System Test Review
... Cerebrum Controls It regulates all your thoughts and actions. There are many sections of the cerebrum that control what you hear, smell, how you move, how you think, write, talk and express emotions. ...
... Cerebrum Controls It regulates all your thoughts and actions. There are many sections of the cerebrum that control what you hear, smell, how you move, how you think, write, talk and express emotions. ...
SENSATION - Ms. Kelly's AP Psychology Website
... is used to predict when a weak signal will be detected. A new theory that assumes there is no absolute threshold. Detection of a stimulus depends on a combination of actors: stimulus intensity, background noise, a person’s level of experience, motivation & physical condition. ...
... is used to predict when a weak signal will be detected. A new theory that assumes there is no absolute threshold. Detection of a stimulus depends on a combination of actors: stimulus intensity, background noise, a person’s level of experience, motivation & physical condition. ...
Nervous System Guided Notes
... A semi-conscious young woman is brought to the hospital by friends after falling from a roof. She did not lose consciousness immediately, and she was initially lucid. After a while, though, she became confused and then unresponsive. Questions What is a likely explanation for her condition? ...
... A semi-conscious young woman is brought to the hospital by friends after falling from a roof. She did not lose consciousness immediately, and she was initially lucid. After a while, though, she became confused and then unresponsive. Questions What is a likely explanation for her condition? ...
How Psychologists Study the Brain
... make detailed 3-dimensional pictures of organs, soft tissues, bone and most other internal body structures. Some MRI scans require a contrast medium to provide clearer images. Different tissues react differently to the magnetic current and this produces various images. No ionizing radiation is used ...
... make detailed 3-dimensional pictures of organs, soft tissues, bone and most other internal body structures. Some MRI scans require a contrast medium to provide clearer images. Different tissues react differently to the magnetic current and this produces various images. No ionizing radiation is used ...
Nervous System - teacherver.com
... Association cortex/Association areas comprises 75% of the cerebral cortex integrates information among the other cortex + a damage to a specific part does not result in specific loss of a function (except for the language areas eg: Broca’s area which is involved in speech production Wernicke’ ...
... Association cortex/Association areas comprises 75% of the cerebral cortex integrates information among the other cortex + a damage to a specific part does not result in specific loss of a function (except for the language areas eg: Broca’s area which is involved in speech production Wernicke’ ...
The Child’s Growth
... Brain Injury in Early Years of Life Young brain is not fully developed, hemispheric ...
... Brain Injury in Early Years of Life Young brain is not fully developed, hemispheric ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.