Lesson 1
... whenever an electrical current is present there is an accompanying magnetic field, MEG detects neural activity too brief to be detected by PET or MRI. This technique has been used to locate seizure-producing regions in epileptic patients. C. PRONG--parallel recording of neural groups Electrodes that ...
... whenever an electrical current is present there is an accompanying magnetic field, MEG detects neural activity too brief to be detected by PET or MRI. This technique has been used to locate seizure-producing regions in epileptic patients. C. PRONG--parallel recording of neural groups Electrodes that ...
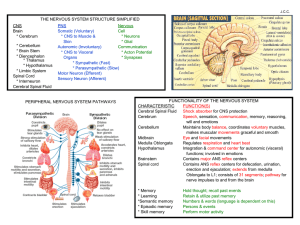
CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
... Oblongata to L1; consists of 31 segments; pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain * Memory * Learning *Semantic memory * Episodic memory * Skill memory ...
... Oblongata to L1; consists of 31 segments; pathway for nerve impulses to and from the brain * Memory * Learning *Semantic memory * Episodic memory * Skill memory ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
... 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
Neuron Note #3 - WordPress.com
... that their son forgot his dinosaur today. When he looks puzzled, she holds up the child’s lunchbox & repeats, “You know, his dinosaur.” This man’s predicament is most like which of the following disorders? Wernicke’s aphasia b) Broca’s aphasia c) Apraxia d) Spatial neglect a) ...
... that their son forgot his dinosaur today. When he looks puzzled, she holds up the child’s lunchbox & repeats, “You know, his dinosaur.” This man’s predicament is most like which of the following disorders? Wernicke’s aphasia b) Broca’s aphasia c) Apraxia d) Spatial neglect a) ...
Additional Nervous System Notes
... • Contain rhodopsin – visual pigment made up of protein (opsin) and retinal (made from vitamin A) – Light falling on rhodopsin causes reversible change in shape – called bleaching – This generates an action potential that is carried to visual cortex of brain via optic nerve • Groups of rods may pass ...
... • Contain rhodopsin – visual pigment made up of protein (opsin) and retinal (made from vitamin A) – Light falling on rhodopsin causes reversible change in shape – called bleaching – This generates an action potential that is carried to visual cortex of brain via optic nerve • Groups of rods may pass ...
Nervous System
... • Bilaterally symmetrical – anterior and posterior end and a right and left side • Cephalization - sense organs are concentrated at the anterior end • Brain – a complex integrating center made up of clusters of ganglia • Ganglia – groupings of neuronal cell bodies • Nuclei – groupings or neuronal ce ...
... • Bilaterally symmetrical – anterior and posterior end and a right and left side • Cephalization - sense organs are concentrated at the anterior end • Brain – a complex integrating center made up of clusters of ganglia • Ganglia – groupings of neuronal cell bodies • Nuclei – groupings or neuronal ce ...
Lecture 7A
... directly controls an animal’s internal perception of sweet and bitter taste and drives behavioral actions. • Essentially, it does not matter what sensory receptors are reporting. You perceive only the cortical neurons activity. ...
... directly controls an animal’s internal perception of sweet and bitter taste and drives behavioral actions. • Essentially, it does not matter what sensory receptors are reporting. You perceive only the cortical neurons activity. ...
chapter 15 sensory, motor, and integrative systems
... 21. What part of the brain receives information about planned activity, compares this with actual movements, and supplies corrective feedback signals to other parts of the brain? a. cerebral cortex b. thalamus c. cerebellum d. medulla oblongata 22. Sensations of pain and temperature are conveyed fr ...
... 21. What part of the brain receives information about planned activity, compares this with actual movements, and supplies corrective feedback signals to other parts of the brain? a. cerebral cortex b. thalamus c. cerebellum d. medulla oblongata 22. Sensations of pain and temperature are conveyed fr ...
Lecture 5 - Brain I - Linn
... Composed of distinctive cell groups: e.g. Caudate & lentiform Play a role in motor control, may be involved with attention and cognition. Disorders of the basal nuclei show up as too much or too little movement such as Huntington’s or Parkinson’s diseases. ...
... Composed of distinctive cell groups: e.g. Caudate & lentiform Play a role in motor control, may be involved with attention and cognition. Disorders of the basal nuclei show up as too much or too little movement such as Huntington’s or Parkinson’s diseases. ...
A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy
... The brain may be divided into many parts, but for the purpose of this unit, four main parts will be defined. They are referred to as the Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Cerebellum, and Brain Stem. Even though they are part of one organ, they function differently and work together to control body activities. ...
... The brain may be divided into many parts, but for the purpose of this unit, four main parts will be defined. They are referred to as the Cerebrum, Diencephalon, Cerebellum, and Brain Stem. Even though they are part of one organ, they function differently and work together to control body activities. ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY David Myers The Biology of Mind
... A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. Splitting the Brain A procedure in which the two hemispheres of the brain are isolated by cutting the connecting fibers (mainly ...
... A number of brain scan studies show normal individuals engage their right brain when completing a perceptual task and their left brain when carrying out a linguistic task. Splitting the Brain A procedure in which the two hemispheres of the brain are isolated by cutting the connecting fibers (mainly ...
Taken from the Body/brain BOOGIE VIDEO by Jeff Haebig
... brain, sends energy to the upper thinking cortex, and vice versa. This means that exercise involving the basal ganglia and cerebellum primes the executive frontal lobes involved with mental activity, making playground and gym time especially important. Downtime away from academics also strengthens t ...
... brain, sends energy to the upper thinking cortex, and vice versa. This means that exercise involving the basal ganglia and cerebellum primes the executive frontal lobes involved with mental activity, making playground and gym time especially important. Downtime away from academics also strengthens t ...
Taken from the Body/brain BOOGIE VIDEO by Jeff Haebig
... brain, sends energy to the upper thinking cortex, and vice versa. This means that exercise involving the basal ganglia and cerebellum primes the executive frontal lobes involved with mental activity, making playground and gym time especially important. Downtime away from academics also strengthens t ...
... brain, sends energy to the upper thinking cortex, and vice versa. This means that exercise involving the basal ganglia and cerebellum primes the executive frontal lobes involved with mental activity, making playground and gym time especially important. Downtime away from academics also strengthens t ...
Nervous System
... The brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some type of injury or illness. ...
... The brain is sculpted by our genes but also by our experiences. Plasticity refers to the brain’s ability to modify itself after some type of injury or illness. ...
Blue-Brain Technology
... • “YES", The IBM is now developing a virtual brain known as the BLUE BRAIN. • It would be the worlds first virtual brain. Within 30 years, we will be able to scan ourselves into the computers. ...
... • “YES", The IBM is now developing a virtual brain known as the BLUE BRAIN. • It would be the worlds first virtual brain. Within 30 years, we will be able to scan ourselves into the computers. ...
Introduction - Florida Atlantic University
... Humans evolved a number of characteristics that enabled them to fit into their environment and to successfully compete ...
... Humans evolved a number of characteristics that enabled them to fit into their environment and to successfully compete ...
Neuroscience
... Hippocampus: Involved in forming new memories. Neurogenesis takes place. Thalamus: Processes and distributes sensory and motor info to and from cerebral cortex. Regulates awareness, attention, and motivation Hypothalamus: Regulates both divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System. Amygdala: involved i ...
... Hippocampus: Involved in forming new memories. Neurogenesis takes place. Thalamus: Processes and distributes sensory and motor info to and from cerebral cortex. Regulates awareness, attention, and motivation Hypothalamus: Regulates both divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System. Amygdala: involved i ...
Chapter 4 Answers to Before You Go On Questions Describe how
... information from our bodies and sending it to our brains, as well as for enabling the brain to control body movement. So the spinal cord gathers information, which it passes along to the brain; the brain responds to that information and passes commands back down through the spinal cord to initiate m ...
... information from our bodies and sending it to our brains, as well as for enabling the brain to control body movement. So the spinal cord gathers information, which it passes along to the brain; the brain responds to that information and passes commands back down through the spinal cord to initiate m ...
Brain Connectivity Study Reveals Striking Differences Between Men
... cerebellum and cortex participate in bridging between perceptual experiences in the back of the brain, and action, in the front of the brain, according to the authors. The female connections likely facilitate integration of the analytic and sequential processing modes of the left hemisphere with the ...
... cerebellum and cortex participate in bridging between perceptual experiences in the back of the brain, and action, in the front of the brain, according to the authors. The female connections likely facilitate integration of the analytic and sequential processing modes of the left hemisphere with the ...
Analyzed by Symptoms and history Diagnosis 1. Walking down a
... while his eyes were closed. The impaired functioning of what part of Justin’s brain is responsible for these difficulties with motor coordination and balance? Which neurotransmitter is being stimulated? 5. Uncle Ed suffered a stroke which damaged a portion of his cortex. He shows some weakness and p ...
... while his eyes were closed. The impaired functioning of what part of Justin’s brain is responsible for these difficulties with motor coordination and balance? Which neurotransmitter is being stimulated? 5. Uncle Ed suffered a stroke which damaged a portion of his cortex. He shows some weakness and p ...
PSYCH 2 StudyGuide
... 10- What are the characteristics of insomnia, narcolepsy, sleep apnea, night terrors and sleepwalking: INSOMNIA is the inability to sleep or difficulty falling or staying asleep. NARCOLEPSY is a sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks that takes them directly into REM sleep. SLE ...
... 10- What are the characteristics of insomnia, narcolepsy, sleep apnea, night terrors and sleepwalking: INSOMNIA is the inability to sleep or difficulty falling or staying asleep. NARCOLEPSY is a sleep disorder characterized by uncontrollable sleep attacks that takes them directly into REM sleep. SLE ...
Neuroplasticity

Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, is an umbrella term that encompasses both synaptic plasticity and non-synaptic plasticity—it refers to changes in neural pathways and synapses due to changes in behavior, environment, neural processes, thinking, and emotions – as well as to changes resulting from bodily injury. The concept of neuroplasticity has replaced the formerly-held position that the brain is a physiologically static organ, and explores how – and in which ways – the brain changes in the course of a lifetime.Neuroplasticity occurs on a variety of levels, ranging from cellular changes (due to learning) to large-scale changes involved in cortical remapping in response to injury. The role of neuroplasticity is widely recognized in healthy development, learning, memory, and recovery from brain damage. During most of the 20th century, neuroscientists maintained a scientific consensus that brain structure was relatively immutable after a critical period during early childhood. This belief has been challenged by findings revealing that many aspects of the brain remain plastic even into adulthood.Hubel and Wiesel had demonstrated that ocular dominance columns in the lowest neocortical visual area, V1, remained largely immutable after the critical period in development. Researchers also studied critical periods with respect to language; the resulting data suggested that sensory pathways were fixed after the critical period. However, studies determined that environmental changes could alter behavior and cognition by modifying connections between existing neurons and via neurogenesis in the hippocampus and in other parts of the brain, including in the cerebellum.Decades of research have shown that substantial changes occur in the lowest neocortical processing areas, and that these changes can profoundly alter the pattern of neuronal activation in response to experience. Neuroscientific research indicates that experience can actually change both the brain's physical structure (anatomy) and functional organization (physiology). As of 2014 neuroscientists are engaged in a reconciliation of critical-period studies (demonstrating the immutability of the brain after development) with the more recent research showing how the brain can, and does, change in response to hitherto unsuspected stimuli.