Here
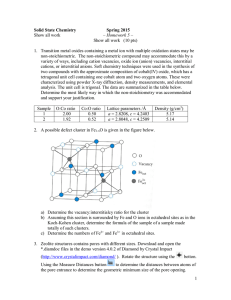
... 5. Do the charges add up to zero? F. Crystal Lattice 1. A 3-D arrangement so that each (+) charged ion is surrounded by (-) ion and vice versa 2. Lattice energy – the energy required to separate 1 mol of ions from an ionic compound – the greater the E, the greater the force of attraction, the hard t ...
... 5. Do the charges add up to zero? F. Crystal Lattice 1. A 3-D arrangement so that each (+) charged ion is surrounded by (-) ion and vice versa 2. Lattice energy – the energy required to separate 1 mol of ions from an ionic compound – the greater the E, the greater the force of attraction, the hard t ...
Chemical Bonding
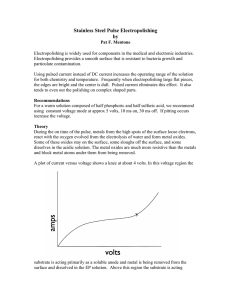
... Metals usually want to give electrons (electron doners) » Becomes positively charged ion (cation) Non-Metals usually want to take electrons (electron receivers) » Becomes negatively charged ion (anion) » Changes name suffix to –ide (e.g.ChlorineChloride) The metal will donate the electron to the n ...
... Metals usually want to give electrons (electron doners) » Becomes positively charged ion (cation) Non-Metals usually want to take electrons (electron receivers) » Becomes negatively charged ion (anion) » Changes name suffix to –ide (e.g.ChlorineChloride) The metal will donate the electron to the n ...
Actinides (actinoids)
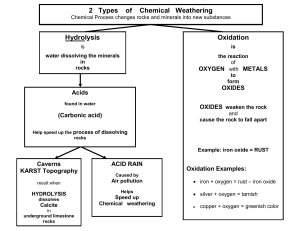
... Properties of metals are quite similar to those of lanthanides: - Silver white, reactive (tarnish in air moisture) - Tolerate acids better than expected (alkalis too). Concentrated HNO3 passivates (adding F- dissolves) - React with most non-metals if heated - In boiling water H2 is liberated - Meta ...
... Properties of metals are quite similar to those of lanthanides: - Silver white, reactive (tarnish in air moisture) - Tolerate acids better than expected (alkalis too). Concentrated HNO3 passivates (adding F- dissolves) - React with most non-metals if heated - In boiling water H2 is liberated - Meta ...