17 Surface and Interface Physics
... Reconstruction and Relaxation The surface of a crystalline solid in vacuum is generally defined as the few, approximately three, outermost atomic layers of the solid that differ significantly from the bulk. The surface may be entirely clean or it may have foreign atoms deposited on it or incorporate ...
... Reconstruction and Relaxation The surface of a crystalline solid in vacuum is generally defined as the few, approximately three, outermost atomic layers of the solid that differ significantly from the bulk. The surface may be entirely clean or it may have foreign atoms deposited on it or incorporate ...
Specific adsorption of carbonate ions at the zinc oxide/electrolyte
... Practical application is the most important aspect for experimental study of properties of the electrical double layer. Zeta potential measurements give important information concerning the properties of the diffuse part of the edl. Measurements include surface charge, ion adsorption, and zeta poten ...
... Practical application is the most important aspect for experimental study of properties of the electrical double layer. Zeta potential measurements give important information concerning the properties of the diffuse part of the edl. Measurements include surface charge, ion adsorption, and zeta poten ...
Surface Tension Measurements
... levels in excess of its bulk values. The reverse is true if this quantity is negative. ...
... levels in excess of its bulk values. The reverse is true if this quantity is negative. ...
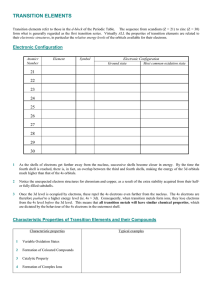
TRANSITION ELEMENTS
... Formation of Coloured Compounds Most of the compounds and complexes of transition elements are coloured. The colour of these compounds can often be related to incompletely filled d-orbitals in the transition metal ion. The outer electronic orbitals of transition metal ions have only small energy dif ...
... Formation of Coloured Compounds Most of the compounds and complexes of transition elements are coloured. The colour of these compounds can often be related to incompletely filled d-orbitals in the transition metal ion. The outer electronic orbitals of transition metal ions have only small energy dif ...
How many molecules?
... contains many different ions/elements – sometimes they get into the mineral • Ease with which they do this: – Solid solution: ions which substitute easily form a series of minerals with varying compositions ...
... contains many different ions/elements – sometimes they get into the mineral • Ease with which they do this: – Solid solution: ions which substitute easily form a series of minerals with varying compositions ...
cREO Whitepaper - Translucent Inc.
... coefficient 3.9x10-‐6 K-‐1). In combination with very strong crystallographic coupling between silicon substrate and the oxide layer, the mismatch in thermal coefficient results stronger thermal expansion ...
... coefficient 3.9x10-‐6 K-‐1). In combination with very strong crystallographic coupling between silicon substrate and the oxide layer, the mismatch in thermal coefficient results stronger thermal expansion ...
Inorganic Chemistry Basics
... Chelation refers to coordination of two or more donor atoms from a single ligand to a central metal ion The resulting complex is characterized by an unusual thermodynamic stability The gain in stability upon chelation is usually ascribed to a significant gain in entropy (however: this is not always ...
... Chelation refers to coordination of two or more donor atoms from a single ligand to a central metal ion The resulting complex is characterized by an unusual thermodynamic stability The gain in stability upon chelation is usually ascribed to a significant gain in entropy (however: this is not always ...
Squaring the Interface: "Surface-Assisted" Coordination Chemistry
... At lower Fe concentrations the connectivity of the molecular network is achieved in part by additional hydrogen bonds between the aromatic H atoms of the phenyl ring and the oxygen atoms of the carboxylate groups. At higher Fe concentrations the formation of the dimeric Fe2-based structures predomin ...
... At lower Fe concentrations the connectivity of the molecular network is achieved in part by additional hydrogen bonds between the aromatic H atoms of the phenyl ring and the oxygen atoms of the carboxylate groups. At higher Fe concentrations the formation of the dimeric Fe2-based structures predomin ...
Decomposition Reaction
... considered active metals and they will react with very hot water or steam to form the oxide and hydrogen gas. 4. The oxides of all of these first metals resist reduction by H2 . 5. The next six metals (iron - lead) replace hydrogen from HCl and dil. sulfuric and nitric acids. Their oxides undergo re ...
... considered active metals and they will react with very hot water or steam to form the oxide and hydrogen gas. 4. The oxides of all of these first metals resist reduction by H2 . 5. The next six metals (iron - lead) replace hydrogen from HCl and dil. sulfuric and nitric acids. Their oxides undergo re ...
Reaction types summary
... collision of the copper and the hydroxide ions within the solution forms the insoluble substance, the remaining ions are simply spectators and named as such. To collect the sodium sulphate it would be necessary to remove the water ...
... collision of the copper and the hydroxide ions within the solution forms the insoluble substance, the remaining ions are simply spectators and named as such. To collect the sodium sulphate it would be necessary to remove the water ...