Heuchera hybrids, CORAL BELLS - Tree of Life Nursery California
... been located on the historic Rancho Mission Viejo in San Juan Capistrano for over 20 years. Largely a wholesale nursery, the Roundhouse Plant Store is open to the public Fridays year-round and Saturdays in fall and spring. For those interested in learning more, we offer a large selection of books on ...
... been located on the historic Rancho Mission Viejo in San Juan Capistrano for over 20 years. Largely a wholesale nursery, the Roundhouse Plant Store is open to the public Fridays year-round and Saturdays in fall and spring. For those interested in learning more, we offer a large selection of books on ...
Airplane Plant
... This perennial does best in full sun to partial shade. It prefers dry to average moisture levels with very well-drained soil, and will often die in standing water. It is considered to be drought-tolerant, and thus makes an ideal choice for a low-water garden or xeriscape application. It is not parti ...
... This perennial does best in full sun to partial shade. It prefers dry to average moisture levels with very well-drained soil, and will often die in standing water. It is considered to be drought-tolerant, and thus makes an ideal choice for a low-water garden or xeriscape application. It is not parti ...
Indian Hawthorn `Majestic Beauty`
... Pests and diseases: Scales, leaf spots, fire blight, and nematode problems affect this plant. Leaf spot problems are more severe by excessive watering with over-head sprinkler irrigation. Entomosporium leaf spot is one of the most common fungal diseases of this plant. Morning sun is helpful in disco ...
... Pests and diseases: Scales, leaf spots, fire blight, and nematode problems affect this plant. Leaf spot problems are more severe by excessive watering with over-head sprinkler irrigation. Entomosporium leaf spot is one of the most common fungal diseases of this plant. Morning sun is helpful in disco ...
Sage Brush - Herbalpedia
... (Norwegian); Sieversi puju (Estonian) Cultivation: Easily grown in a well-drained circumneutral or slightly alkaline loamy soil, preferring a warm sunny dry position. Established plants are drought tolerant. Plants are longer lived, more hardy and more aromatic when they are grown in a poor dry soil ...
... (Norwegian); Sieversi puju (Estonian) Cultivation: Easily grown in a well-drained circumneutral or slightly alkaline loamy soil, preferring a warm sunny dry position. Established plants are drought tolerant. Plants are longer lived, more hardy and more aromatic when they are grown in a poor dry soil ...
Chapter 29
... The Lycophyta and Pterophyta represent the modern lineages of seedless vascular plants that formed forests during the Carboniferous period about 290-363 million years ago. The coal beds, oil fields and natural gas deposits that are mined in modern times are derived from these ancient forests. From t ...
... The Lycophyta and Pterophyta represent the modern lineages of seedless vascular plants that formed forests during the Carboniferous period about 290-363 million years ago. The coal beds, oil fields and natural gas deposits that are mined in modern times are derived from these ancient forests. From t ...
Plant Anatomy and Physiology
... stroma – chemical soup, contain their own DNA, can replicate inside a plant cell 4. pigments: chlorophyll a– main light trapping pigment (b, c); other accessory pigments trap light of different wavelengths ...
... stroma – chemical soup, contain their own DNA, can replicate inside a plant cell 4. pigments: chlorophyll a– main light trapping pigment (b, c); other accessory pigments trap light of different wavelengths ...
From Seed to Plant
... Green leaves grow up from the shoot toward the sun As the plant grows bigger, the leaves make food for the plant from the water and minerals in the soil, the sunlight, and the air all around the plant ...
... Green leaves grow up from the shoot toward the sun As the plant grows bigger, the leaves make food for the plant from the water and minerals in the soil, the sunlight, and the air all around the plant ...
Most Unwanted List
... simple and one parted. The flowers are fragrant, bright yellow and pea shaped. In addition to its invasive nature, Spanish broom is a potential fire hazard and all parts of the plant are poisonous. Seeds can remain viable for over 80 years. ...
... simple and one parted. The flowers are fragrant, bright yellow and pea shaped. In addition to its invasive nature, Spanish broom is a potential fire hazard and all parts of the plant are poisonous. Seeds can remain viable for over 80 years. ...
Vanda ustii - It`s all about Vandas
... GROWING MEDIA: Plants are usually grown in hanging pots or slatted wooden baskets filled with a very open, fast draining medium. Some are grown with only enough open chunky medium, such as charcoal, wine corks, or large cork chips, to anchor the plant until it becomes established. The roots should ...
... GROWING MEDIA: Plants are usually grown in hanging pots or slatted wooden baskets filled with a very open, fast draining medium. Some are grown with only enough open chunky medium, such as charcoal, wine corks, or large cork chips, to anchor the plant until it becomes established. The roots should ...
File
... Bark: outer part of woody stem; protective tissue consisting of phloem & cork tissue Sapwood: younger xylem, conducts water & minerals Heartwood: older xylem that fills with resins, oils and complex compounds - stems not woody and not very supportive - green and usually soft - do not survive winter ...
... Bark: outer part of woody stem; protective tissue consisting of phloem & cork tissue Sapwood: younger xylem, conducts water & minerals Heartwood: older xylem that fills with resins, oils and complex compounds - stems not woody and not very supportive - green and usually soft - do not survive winter ...
Senecio Mandraliscae: buy nursery plants online
... Water the plant only during dry summer weather. Blue finger is a drought-tolerant succulent that can survive long, dry periods. Watch for signs that the plant needs water, especially leaves that begin to look shrunken or wilted. Water the plant s site deeply, and then allow the soil to dry completel ...
... Water the plant only during dry summer weather. Blue finger is a drought-tolerant succulent that can survive long, dry periods. Watch for signs that the plant needs water, especially leaves that begin to look shrunken or wilted. Water the plant s site deeply, and then allow the soil to dry completel ...
plants - Miami Beach Senior High School
... Stoma (stomata) – small pores that act as a doorway for gases involved in photosynthesis (found mainly on the underside of leaves). Guard Cells – cells that regulate the opening of the stomata. Lower and upper epidermis – outer layer of a plant that serves for protection, like skin. ...
... Stoma (stomata) – small pores that act as a doorway for gases involved in photosynthesis (found mainly on the underside of leaves). Guard Cells – cells that regulate the opening of the stomata. Lower and upper epidermis – outer layer of a plant that serves for protection, like skin. ...
auxins - faculty lounge: non
... Starches within the cells of the stem sink downward in response to gravity, triggering the movement of auxin toward them. Auxin then stimulates faster growth in the regions where it occurs in higher concentration, causing the stem to bend upward. ...
... Starches within the cells of the stem sink downward in response to gravity, triggering the movement of auxin toward them. Auxin then stimulates faster growth in the regions where it occurs in higher concentration, causing the stem to bend upward. ...
Topic 13 - Southwest High School
... Rate of Transpiration Transpiration is the evaporation of water, so its rate is directly proportional to the intensity of sunlight and temperature. Dry air also causes a large increase in transpiration, as does wind. ...
... Rate of Transpiration Transpiration is the evaporation of water, so its rate is directly proportional to the intensity of sunlight and temperature. Dry air also causes a large increase in transpiration, as does wind. ...
Seedless Vascular Plants
... Seeds contain: Seed coat-protects the seed Embryo-small plant Endosperm (cotyledon)stored food Seeds can remain ...
... Seeds contain: Seed coat-protects the seed Embryo-small plant Endosperm (cotyledon)stored food Seeds can remain ...
The Plant Kingdom Plants In Too Much Water
... is added to water as it moves down stream or as it’s churned by waves or tides. Many man-made ponds or lakes keep water moving by turning on fountains that shoot water into the air. ...
... is added to water as it moves down stream or as it’s churned by waves or tides. Many man-made ponds or lakes keep water moving by turning on fountains that shoot water into the air. ...
Functional Analysis ofArabidopsisNHX Antiporters
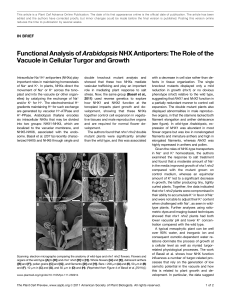
... suggesting that NHX1 and NHX2 function in a partially redundant manner to control cell expansion. The double mutant plants also displayed abnormalities in male reproductive organs, in that the stamens lacked both filament elongation and anther dehiscence (see figure). In wild-type Arabidopsis, expre ...
... suggesting that NHX1 and NHX2 function in a partially redundant manner to control cell expansion. The double mutant plants also displayed abnormalities in male reproductive organs, in that the stamens lacked both filament elongation and anther dehiscence (see figure). In wild-type Arabidopsis, expre ...
Unit 6 Homework
... 14. What is translocation in plants (not the translocation that occurs during translation)? Chapter 37 1. How do nutrients enter plants? 2. What is the difference between macronutrients and micronutrients? 3. Why is magnesium important to plants? 4. How do plants absorb cations from the soil? (i.e. ...
... 14. What is translocation in plants (not the translocation that occurs during translation)? Chapter 37 1. How do nutrients enter plants? 2. What is the difference between macronutrients and micronutrients? 3. Why is magnesium important to plants? 4. How do plants absorb cations from the soil? (i.e. ...
Name - Enseignons.be
... What we already know ... We planted watercress seeds in an egg with cotton and water. The same thing happen when we plant seeds in soil : ...
... What we already know ... We planted watercress seeds in an egg with cotton and water. The same thing happen when we plant seeds in soil : ...
HW 1: Growing Plants
... Copy and complete the following table by selecting two plants from the list and giving one different use for each plant. Plant ...
... Copy and complete the following table by selecting two plants from the list and giving one different use for each plant. Plant ...
Chapter 20
... This chapter begins by calling attention to differences between angiosperms and gymnosperms, and then discusses the theoretical origin of flowering plants. The exceptional diversity of form and habit of the flowering plants is reiterated before the chapter continues with a description of the paralle ...
... This chapter begins by calling attention to differences between angiosperms and gymnosperms, and then discusses the theoretical origin of flowering plants. The exceptional diversity of form and habit of the flowering plants is reiterated before the chapter continues with a description of the paralle ...
Plant Paper bush (Mitsumata) 23(05015) Primary essential
... Observe central part of stem below fork of 2year-old plants ...
... Observe central part of stem below fork of 2year-old plants ...
Botany

Botany, also called plant science(s) or plant biology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specializes in this field of study. The term ""botany"" comes from the Ancient Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) meaning ""pasture"", ""grass"", or ""fodder""; βοτάνη is in turn derived from βόσκειν (boskein), ""to feed"" or ""to graze"". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists study approximately 400,000 species of living organisms of which some 260,000 species are vascular plants and about 248,000 are flowering plants.Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, medicinal and poisonous plants, making it one of the oldest branches of science. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to monasteries, contained plants of medical importance. They were forerunners of the first botanical gardens attached to universities, founded from the 1540s onwards. One of the earliest was the Padua botanical garden. These gardens facilitated the academic study of plants. Efforts to catalogue and describe their collections were the beginnings of plant taxonomy, and led in 1753 to the binomial system of Carl Linnaeus that remains in use to this day.In the 19th and 20th centuries, new techniques were developed for the study of plants, including methods of optical microscopy and live cell imaging, electron microscopy, analysis of chromosome number, plant chemistry and the structure and function of enzymes and other proteins. In the last two decades of the 20th century, botanists exploited the techniques of molecular genetic analysis, including genomics and proteomics and DNA sequences to classify plants more accurately.Modern botany is a broad, multidisciplinary subject with inputs from most other areas of science and technology. Research topics include the study of plant structure, growth and differentiation, reproduction, biochemistry and primary metabolism, chemical products, development, diseases, evolutionary relationships, systematics, and plant taxonomy. Dominant themes in 21st century plant science are molecular genetics and epigenetics, which are the mechanisms and control of gene expression during differentiation of plant cells and tissues. Botanical research has diverse applications in providing staple foods and textiles, in modern horticulture, agriculture and forestry, plant propagation, breeding and genetic modification, in the synthesis of chemicals and raw materials for construction and energy production, in environmental management, and the maintenance of biodiversity.