Introduction to Plants
... Let’s recall some basic facts about plants: • All plants are multicellular, eukaryotic, autotrophic organisms • All plant cells contain cell walls composed of cellulose • All plants are photosynthetic, and contain cellular components with pigments to capitalize on that process • All plants take up w ...
... Let’s recall some basic facts about plants: • All plants are multicellular, eukaryotic, autotrophic organisms • All plant cells contain cell walls composed of cellulose • All plants are photosynthetic, and contain cellular components with pigments to capitalize on that process • All plants take up w ...
Different groups of plants
... major root--like the one the beet plant has--is called a taproot. A taproot grows down and forms many small secondary roots. Plants with taproot systems use their roots to store food. You can see these plants and roots in many gardens and grocery stores--carrots, beets, radishes, and turnips. Some t ...
... major root--like the one the beet plant has--is called a taproot. A taproot grows down and forms many small secondary roots. Plants with taproot systems use their roots to store food. You can see these plants and roots in many gardens and grocery stores--carrots, beets, radishes, and turnips. Some t ...
Care of Lithops - Desert Botanical Garden
... LIGHT: In Arizona, Lithops should be grown in bright light but not direct sun. At higher elevations, they may require full sun in order to receive adequate light. Plants receiving too much water or not enough light will often grow way out of the soil. Healthy plants are at the level of the soil with ...
... LIGHT: In Arizona, Lithops should be grown in bright light but not direct sun. At higher elevations, they may require full sun in order to receive adequate light. Plants receiving too much water or not enough light will often grow way out of the soil. Healthy plants are at the level of the soil with ...
Four years ago I began working at a greenhouse. When I first
... arrangements are pretty much the same as any other cut flower. If the flowers are going into a vase arrangement the vases must be clean and free of bacteria, and water should be replaced every 3 or 4 days. This will help keep the water free of bacteria that could grow and cause the stems to clog, wh ...
... arrangements are pretty much the same as any other cut flower. If the flowers are going into a vase arrangement the vases must be clean and free of bacteria, and water should be replaced every 3 or 4 days. This will help keep the water free of bacteria that could grow and cause the stems to clog, wh ...
Unit 2 Plant notes File
... Heart shaped reproductive structure in ferns that contains both the male portion (Antheridium) and female portion ...
... Heart shaped reproductive structure in ferns that contains both the male portion (Antheridium) and female portion ...
NVCplant labF2016 - Napa Valley College
... • They are multicellular, having various specialized tissues. • They photosynthesize, using a cell organelle called a chloroplast. • They have adaptations to living on land and have evolved as terrestrial organisms. • Their leaves and other above-ground parts have a cuticle of wax that protects them ...
... • They are multicellular, having various specialized tissues. • They photosynthesize, using a cell organelle called a chloroplast. • They have adaptations to living on land and have evolved as terrestrial organisms. • Their leaves and other above-ground parts have a cuticle of wax that protects them ...
Parasitic Higher Plants - Missouri State University
... Attach, Produce Appressorium that Surrounds Root ...
... Attach, Produce Appressorium that Surrounds Root ...
Living organisms: plants
... When plants carry out photosynthesis, they also absorb some carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. 1 Find out how carbon dioxide can damage the environment. 2 Find out how much carbon dioxide an average-sized tree can absorb. 3 Are there any other ways to absorb the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere? ...
... When plants carry out photosynthesis, they also absorb some carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. 1 Find out how carbon dioxide can damage the environment. 2 Find out how much carbon dioxide an average-sized tree can absorb. 3 Are there any other ways to absorb the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere? ...
plant identification - Arizona Section, Society for Range Management
... A. Is individual wearing glasses B. Individual is not wearing glasses B. Individual is wearing short pants ...
... A. Is individual wearing glasses B. Individual is not wearing glasses B. Individual is wearing short pants ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... – Development of vascular tissue – Development of seeds – Development of flowers ...
... – Development of vascular tissue – Development of seeds – Development of flowers ...
secondary growth
... – End wall is perforated forming sieve plate – Lose most of their internal components – only has plasma membrane, few mitochondria and some endoplasmic reticulum ...
... – End wall is perforated forming sieve plate – Lose most of their internal components – only has plasma membrane, few mitochondria and some endoplasmic reticulum ...
1) Check off which of the following things that soil does: __X __ Acts
... 42) What are factors that are threatening bumble bees and other pollinators? A. Pesticide exposure B. habitat loss and climate change, C. competition from non-native bees, introduced diseases. D. All of the above 43) Bumble bees need… A. High-quality habitat for nesting B. Plentiful food and water r ...
... 42) What are factors that are threatening bumble bees and other pollinators? A. Pesticide exposure B. habitat loss and climate change, C. competition from non-native bees, introduced diseases. D. All of the above 43) Bumble bees need… A. High-quality habitat for nesting B. Plentiful food and water r ...
Plant Adaptions
... conditions allow for germination. • Seeds have adaptations that allow them to be dispersed and also to have enough food for the plant until it begins to make its own food. ...
... conditions allow for germination. • Seeds have adaptations that allow them to be dispersed and also to have enough food for the plant until it begins to make its own food. ...
Miterwort Information
... Miterwort Plants With Buds As people observe plants, they see shapes that remind them of other objects, beliefs, or experiences in their lives. The Greek word mitra means little cap. The flower and seed capsule of the Miterwort look like a little cap. The flower is sometimes also known as Bishop’s C ...
... Miterwort Plants With Buds As people observe plants, they see shapes that remind them of other objects, beliefs, or experiences in their lives. The Greek word mitra means little cap. The flower and seed capsule of the Miterwort look like a little cap. The flower is sometimes also known as Bishop’s C ...
Diversity of Plants - Dublin City University
... • Evolution is driven by the need to absorb, transport and retain water, and the need to reduce the requirement of water for fertilisation. ...
... • Evolution is driven by the need to absorb, transport and retain water, and the need to reduce the requirement of water for fertilisation. ...
Name - cloudfront.net
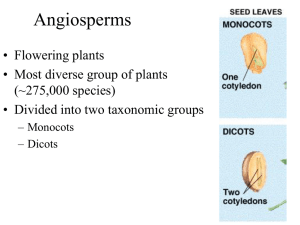
... Veins in leaves are parallel. Veins in leaves are netlike. Flower parts are usually in multiples of 3. Flower parts are usually in multiples of 4 or 5. Vascular bundles in stem are scattered. Vascular bundles in stem form a ring. Wood and bark are not common. Wood and bark are common. ...
... Veins in leaves are parallel. Veins in leaves are netlike. Flower parts are usually in multiples of 3. Flower parts are usually in multiples of 4 or 5. Vascular bundles in stem are scattered. Vascular bundles in stem form a ring. Wood and bark are not common. Wood and bark are common. ...
Structures of a seed
... Dormant– the ability of a seed or plant to become inactive, but when conditions are right, the seed or plant will become active. ...
... Dormant– the ability of a seed or plant to become inactive, but when conditions are right, the seed or plant will become active. ...
Reproduction with Cones and Flowers
... Stem is partially buried in soil Usually use rooting powders to stimulate root growth ...
... Stem is partially buried in soil Usually use rooting powders to stimulate root growth ...
tość wynosi obecnie około 70 mld dolarów
... to the discovery of the signalling role of microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). The compounds responsible for the flower’s scent all have small molecular weight and a low boiling point, they belong to various chemical groups. Their main role is attracting pollinating insects but b ...
... to the discovery of the signalling role of microRNAs (miRNAs) and small interfering RNAs (siRNAs). The compounds responsible for the flower’s scent all have small molecular weight and a low boiling point, they belong to various chemical groups. Their main role is attracting pollinating insects but b ...
What makes a Plant a Plant?
... several years before they grow; the timing will depend on the needs of the plant. When the time is right, a seed absorbs water and expands. This breaks the seed coat, and the embryo begins to grow. ...
... several years before they grow; the timing will depend on the needs of the plant. When the time is right, a seed absorbs water and expands. This breaks the seed coat, and the embryo begins to grow. ...
Aquatic Plants PowerPoint
... They are food for the fish and other tiny animals. They provide shelter for fish to hide from predators. Some add beauty with their bright colors and unusual shapes. They help provide oxygen for the animals in the water. ...
... They are food for the fish and other tiny animals. They provide shelter for fish to hide from predators. Some add beauty with their bright colors and unusual shapes. They help provide oxygen for the animals in the water. ...
Seed Plants
... Seed Plants • Seed plants are divided into 2 groups: – Gymnosperms • Cones – sporophyte structure where gametophytes grow & mature • Seeds exposed directly on the surfaces of cones ...
... Seed Plants • Seed plants are divided into 2 groups: – Gymnosperms • Cones – sporophyte structure where gametophytes grow & mature • Seeds exposed directly on the surfaces of cones ...
Botany

Botany, also called plant science(s) or plant biology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specializes in this field of study. The term ""botany"" comes from the Ancient Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) meaning ""pasture"", ""grass"", or ""fodder""; βοτάνη is in turn derived from βόσκειν (boskein), ""to feed"" or ""to graze"". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists study approximately 400,000 species of living organisms of which some 260,000 species are vascular plants and about 248,000 are flowering plants.Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, medicinal and poisonous plants, making it one of the oldest branches of science. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to monasteries, contained plants of medical importance. They were forerunners of the first botanical gardens attached to universities, founded from the 1540s onwards. One of the earliest was the Padua botanical garden. These gardens facilitated the academic study of plants. Efforts to catalogue and describe their collections were the beginnings of plant taxonomy, and led in 1753 to the binomial system of Carl Linnaeus that remains in use to this day.In the 19th and 20th centuries, new techniques were developed for the study of plants, including methods of optical microscopy and live cell imaging, electron microscopy, analysis of chromosome number, plant chemistry and the structure and function of enzymes and other proteins. In the last two decades of the 20th century, botanists exploited the techniques of molecular genetic analysis, including genomics and proteomics and DNA sequences to classify plants more accurately.Modern botany is a broad, multidisciplinary subject with inputs from most other areas of science and technology. Research topics include the study of plant structure, growth and differentiation, reproduction, biochemistry and primary metabolism, chemical products, development, diseases, evolutionary relationships, systematics, and plant taxonomy. Dominant themes in 21st century plant science are molecular genetics and epigenetics, which are the mechanisms and control of gene expression during differentiation of plant cells and tissues. Botanical research has diverse applications in providing staple foods and textiles, in modern horticulture, agriculture and forestry, plant propagation, breeding and genetic modification, in the synthesis of chemicals and raw materials for construction and energy production, in environmental management, and the maintenance of biodiversity.