* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproduction with Cones and Flowers
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
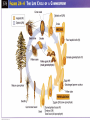
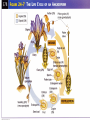
Reproduction with Cones and Flowers Chapter 22 Alternation of Generations All plants have a diploid sporophyte generation and a haploid gametophyte generation Gametophyte plants produce sperm and eggs Fertilization begins the sporophyte generation Generations cont. Actual plant is the diploid sporophyte generation Gametophytes are found in cones or flowers Pollen cones and seed cones Pollen cones (male) produce male gametophytes or pollen grains – One haploid nuclei will develop into 2 sperm Seed cones (female) produce female gametophytes contained in the ovules – Each ovule contains a few eggs for fertilization Pollination Gymnosperm life cycle takes 2 years for completion Male cones release pollen which is carried by wind to female cones Fertilization and development Pollen grains stuck to female cones will develop a pollen tube containing the 2 sperm One sperm disintegrates, the other fertilizes the egg to make a diploid zygote Zygote grows into an embryo which is enclosed in a seed Flower structure Flowers are reproductive structures Have four parts – – – – Sepals Petals Stamens Carpels (pistils) Sepals and petals Sepals – Outermost circle of parts (green) – Protect the bud before it opens Petals – Usually brightly colored – Found inside the sepals – Attract pollinators Stamens and carpels Stamen – Filament-long, thin stalk that supports anther – Anther-sac at end of filament that contains pollen grains Carpel (pistils) – Ovary-broad base containing one or more ovules – Style-narrow stalk extending from top of ovary – Stigma-sticky section on top of style that collects pollen Complete and incomplete flowers Complete flowers – Contain all flower parts: sepals, petals, stamen, carpel Incomplete flowers – Missing one or more flower parts – Often seen in plants that produce separate male and female plants – Or in plants that have separate male and female flowers (on same plant) Angiosperm life cycle Flowers are produced Meiosis occurs in the anther to produce pollen grains Meiosis occurs in the ovary to produce the embryo sac which contains the egg and endosperm nuclei Pollination Pollen picked up by pollinator and carried to stigma Some wind pollinated More efficient pollination by insects or animals Fertilization Once pollen reaches a stigma, pollen tube develops and grows into the ovule 2 sperm nuclei develop Double fertilization occurs – One sperm fertilizes the egg to make the zygote – One sperm fertilizes the endosperm to make a triploid cell or endosperm (food for the embryo) Seed development After fertilization, nutrients flow into flower tissue to support development of embryo and seed Ovary walls thicken to make fruit to protect the seeds Ovule toughens to become seed coat FRUIT-is any seed enclosed within the embryo wall; includes common fruits, vegetables, nuts Seed dispersal Animals – Seeds usually found in fleshy fruits; can pass through digestive tracts unharmed – Deposited in new areas with animal feces Wind and water – Usually light weight seeds – Can float on air currents or in water – Carried to far places or remote places (islands) Seed dormancy Embryo is alive but not growing Length of dormancy varies in each plant Allows for long-distance dispersal Environmental factors cause seeds to end dormancy and germinate Seed germination Early growth stage of embryo Seeds must absorb water to crack seed coat Root emerges first Shoots emerge next – Can be protected by a sheath (monocots) – Can be protected by the cotyledons or a “shoot arch” (dicots) Vegetative reproduction Asexual form of reproduction Produce many plants from horizontal stems (stolons), plantlets, or underground roots No pollination or seeds New plants are genetically identical to parent plant Plant propagation Use cuttings or grafting or budding from original plant to produce offspring from seedless plants Avoids genetic variation Preserves wanted characteristics Cuttings Pieces of stem with buds containing meristematic tissue Stem is partially buried in soil Usually use rooting powders to stimulate root growth Grafting and budding Grafting – Plants with poor roots grown on plants with strong roots – Stem is cut (scion) and attached to another plant (stock) – Words bests when plants are dormant – Vascular tissues of scion / stock must connect Budding – Using buds for scions instead of stems Plant hormones and responses Hormone- chemical messenger that stimulates or suppresses activity of cells in another area – Released in response to environmental ques – Released in response to internal changes of the plant as part of the life cycle Gibberellins Hormones that produce dramatic increase in size End seed dormancy Start germination Promote rapid growth of the seedling Increase the size of fruits Elongate stems/stalks Ethylene Hormone that causes ripening Naturally produced by fruits Cytokinins Hormones that stimulate cytokinesis (final part of cell division) Produced in growing roots and developing seeds and fruits Involved in the “width” growth or lateral growth of stems and branches Slows the aging process of plant organs Auxins Hormones involved in lengthening plant cells of the apical meristem Stimulate growth of primary stem Prevents growth of new branches Prevent root growth Phototropism Tendency of a plant to grow toward light Thigmotropism Response to touch – Coiling around trellises or other stems when in contact – Curling up when touched by other organisms Gravitropism Positive - is growing down toward gravity (roots, stimulated by low levels of auxins) Negative – growing up away from gravity (stems stimulated by high levels of auxins) Photoperiodism Plant responses to changing lengths of day/night Longer days trigger flowering Shorter days trigger change in leaf colors and dropping of leaves in deciduous plants