Name Date ______ Hour_______ Table ____ Wonderful World of
... ______________________ are leaves that surround a flower’s bud. ...
... ______________________ are leaves that surround a flower’s bud. ...
REPRODUCTION IN FLOWERING PLANTS (Flowering Seed Plants
... 5. Flowering plants use the _________, _____________, ____________, ____________ and ________________ to transfer pollen from the male (stamen) part of the flower to the female (pistil) part of the flower. 6. A flower is pollinated when a pollen grain lands on its ________. 7. In fertilization, pol ...
... 5. Flowering plants use the _________, _____________, ____________, ____________ and ________________ to transfer pollen from the male (stamen) part of the flower to the female (pistil) part of the flower. 6. A flower is pollinated when a pollen grain lands on its ________. 7. In fertilization, pol ...
All gymnosperms produce naked seeds. Many gymnosperms have
... The male cone produces pollen grains, which contains cells that will mature into sperm cells. ...
... The male cone produces pollen grains, which contains cells that will mature into sperm cells. ...
Flower Structure and Function
... Take in CO2, make glucose, release O2. Waxy coat to prevent water loss. 4. Flowers - Contain angiosperms reproductive parts. ...
... Take in CO2, make glucose, release O2. Waxy coat to prevent water loss. 4. Flowers - Contain angiosperms reproductive parts. ...
Botany Review Sheet
... 6. Describe the difference between the following: a. xylem and phloem b. taproots and fibrous roots c. woody stems and herbaceous stems d. photosynthesis and respiration 7. What is the equation of photosynthesis? (Label the reactants and the products.) ...
... 6. Describe the difference between the following: a. xylem and phloem b. taproots and fibrous roots c. woody stems and herbaceous stems d. photosynthesis and respiration 7. What is the equation of photosynthesis? (Label the reactants and the products.) ...
Angiosperms
... Root development -• In most dicots (and in most seed plants) the root develops from the lower end of the embryo, from a region known as the radicle. • The radicle gives rise to an apical meristem which continues to produce root tissue for much of the plant's life. • By contrast, the radicle aborts ...
... Root development -• In most dicots (and in most seed plants) the root develops from the lower end of the embryo, from a region known as the radicle. • The radicle gives rise to an apical meristem which continues to produce root tissue for much of the plant's life. • By contrast, the radicle aborts ...
Seed Plants
... haploid stage in the life cycle of plants. Sporophyte: Sporophyte: The diploid form of a plant that produces , haploid, asexual spores through the process of meiosis – reduction division. ...
... haploid stage in the life cycle of plants. Sporophyte: Sporophyte: The diploid form of a plant that produces , haploid, asexual spores through the process of meiosis – reduction division. ...
Chapter 21 and 22 Notes - Plants
... sporophyte, which has diploid cells. The cells of the sporophyte undergo meiosis to create haploid cells which develop into gametophytes, thereby starting a new phase in the alternation of generations and bringing the organism completely through the alternation of generations, from gametophyte to sp ...
... sporophyte, which has diploid cells. The cells of the sporophyte undergo meiosis to create haploid cells which develop into gametophytes, thereby starting a new phase in the alternation of generations and bringing the organism completely through the alternation of generations, from gametophyte to sp ...
Meiosis in Flowering Plants
... through the micropyle near the base of the ovule. The generative nucleus in the pollen grain divides by mitosis. The two nuclei move into the embryo sac where one fertilizes the polar nucleus to produce a triploid endosperm nucleus and the other fertilizes the egg nucleus to form a zygote. ...
... through the micropyle near the base of the ovule. The generative nucleus in the pollen grain divides by mitosis. The two nuclei move into the embryo sac where one fertilizes the polar nucleus to produce a triploid endosperm nucleus and the other fertilizes the egg nucleus to form a zygote. ...
Cymbidium devonianum
... Habitat: High altitude 1500 to 2000 meters, The plants grow on trees rocks and steep banks in seasonally wet forest. Description: A medium sized plant with 50cm leaves and up to 20 flowers on a pendulous spike. It can flower from both old and new psuedobulbs and makes an excellent specimen plant. Cu ...
... Habitat: High altitude 1500 to 2000 meters, The plants grow on trees rocks and steep banks in seasonally wet forest. Description: A medium sized plant with 50cm leaves and up to 20 flowers on a pendulous spike. It can flower from both old and new psuedobulbs and makes an excellent specimen plant. Cu ...
KINGDOMS OF ORGANISMS
... resources, asexual reproduction is faster than sexual reproduction and produces offspring that are well adapted to the existing environment ...
... resources, asexual reproduction is faster than sexual reproduction and produces offspring that are well adapted to the existing environment ...
Section 22–5 Angiosperms—Flowering Plants (pages
... reproduction, growth, and development; TEKS SUPPORT: 8A Classify organisms ...
... reproduction, growth, and development; TEKS SUPPORT: 8A Classify organisms ...
flowering plants
... Gymnosperms – seed plants • conifers (pine, fir, cedar, ginko) • ‘naked seeds’ – not protected or enclosed in an ovary. •seeds are plant embryos packaged in a protective coat along with a food supply. ...
... Gymnosperms – seed plants • conifers (pine, fir, cedar, ginko) • ‘naked seeds’ – not protected or enclosed in an ovary. •seeds are plant embryos packaged in a protective coat along with a food supply. ...
Plants topics 1-3 Wrap-up
... ____________________ occurs when pollen has been transferred from the anther to the stigma. When the pollen grain germinates on the stigma it creates a burrow called the ____________________ ____________________ as it travels toward the ovary. ...
... ____________________ occurs when pollen has been transferred from the anther to the stigma. When the pollen grain germinates on the stigma it creates a burrow called the ____________________ ____________________ as it travels toward the ovary. ...
21 - Deepwater.org
... a. They are all multicellular b. They are all photosynthetic. c. They are all marine. d. They are all nonparasitic e. They are all eukaryotic. ...
... a. They are all multicellular b. They are all photosynthetic. c. They are all marine. d. They are all nonparasitic e. They are all eukaryotic. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - The Genetic Basis of Growth and
... Plants are made up of • cells • tissues • organs ...
... Plants are made up of • cells • tissues • organs ...
General Biology II Lecture Plants Land Plants – monophyletic group
... Vascular cambium – provides secondary xylem toward inside of stem and phloem toward outside of stem ...
... Vascular cambium – provides secondary xylem toward inside of stem and phloem toward outside of stem ...
Plant Reproduction and Development
... • Disadvantages – An unstable enviroment • New pathogens • Varied offspring means some can survive. ...
... • Disadvantages – An unstable enviroment • New pathogens • Varied offspring means some can survive. ...
Plant Reproduction and Development
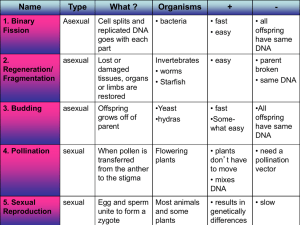
... Egg and sperm Most animals unite to form a and some zygote plants ...
... Egg and sperm Most animals unite to form a and some zygote plants ...
Plants Study Guide
... transport the water, nutrients and food leaves: where photosynthesis takes place (food factory for the plant) flower: attracts pollinators and makes it possible for seeds to be produced Explain the process of photosynthesis and label a diagram showing the process. (Make sure you know the four ...
... transport the water, nutrients and food leaves: where photosynthesis takes place (food factory for the plant) flower: attracts pollinators and makes it possible for seeds to be produced Explain the process of photosynthesis and label a diagram showing the process. (Make sure you know the four ...
Science Study Guide: Chapter 2 1. All plants have cells. 2. All plants
... 1. All plants have cells. 2. All plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to live. 3. Know where the chloroplast is located in a plant cell. 4. A pine needle and a tulip leaf are both kinds of leaves. 5. Stems carry materials and support the plant. 6. Daisy’s have a flexible stem because they ...
... 1. All plants have cells. 2. All plants need sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to live. 3. Know where the chloroplast is located in a plant cell. 4. A pine needle and a tulip leaf are both kinds of leaves. 5. Stems carry materials and support the plant. 6. Daisy’s have a flexible stem because they ...
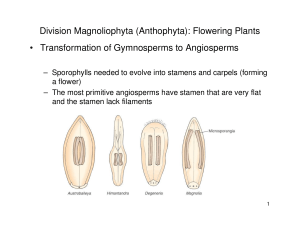
Flowering Plants • Transformation of Gymnosperms to Angiosperms
... – Evolution of double fertilization and the formation of endosperm ...
... – Evolution of double fertilization and the formation of endosperm ...
Plant Kingdom PPT
... Adaptations for living on land • Plants get water and nutrients from the soil • Plants lose water through transpiration • Plants have a cuticle to keep them from drying out. • Some plants use a system of tubelike structures called Vascular Tissue to move materials. • Vascular tissue also supports s ...
... Adaptations for living on land • Plants get water and nutrients from the soil • Plants lose water through transpiration • Plants have a cuticle to keep them from drying out. • Some plants use a system of tubelike structures called Vascular Tissue to move materials. • Vascular tissue also supports s ...
Flowering plant

The flowering plants (angiosperms), also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within the seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. Etymologically, angiosperm means a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure, in other words, a fruiting plant.The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 160 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 120 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.