* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 22–5 Angiosperms—Flowering Plants (pages
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
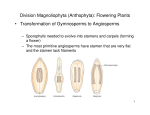
BIO_ALL IN1_StGd_tese_ch22 8/7/03 5:21 PM Page 397 Name______________________________ Class __________________ Date ______________ Section 22–5 Angiosperms—Flowering Plants (pages 569–572) TEKS FOCUS: 3D Careers; 13A Structural and physiological adaptations; 13B Methods of reproduction, growth, and development; TEKS SUPPORT: 8A Classify organisms This section identifies the characteristics of angiosperms. It also explains what monocots and dicots are and describes the three categories of plant life spans. Flowers and Fruits (page 569) 1. Angiosperms are members of the phylum Anthopyta . 2. Angiosperms have unique reproductive organs known as flowers 3. During which geologic period did flowering plants first appear? They first appeared . during the Cretaceous Period. ovary 4. In flowering plants, the seed is encased in a(an) . 5. What is a fruit? It is a wall of tissue surrounding the seed. 6. Why is using fruit to attract animals one of the reasons for the success of flowering plants? An animal eats the fruit, and by the time the seeds leave its digestive system the animal may have traveled many miles. By using fruit to attract animals, flowering plants increase the ranges they inhabit. Diversity of Angiosperms (pages 570–572) 7. The seed leaves of plant embryos are called cotyledons . 8. Complete the table about classes of angiosperms. © Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. CLASSES OF ANGIOSPERMS Class Common Name Number of Seed Leaves Examples Monocotyledonae Monocots One Corn, wheat, lilies, orchids, palms Dicotyledonae Dicots Two Roses, clover, tomatoes, oaks, daisies 9. Classify each of the following plants as either woody or herbaceous by writing the correct term on the line. Woody a. Rose shrubs b. Oaks c. Tomato plants d. Sunflowers e. Grape vines f. Dandelions Woody Herbaceous Herbaceous Woody Herbaceous Guided Reading and Study Workbook/Chapter 22 397 BIO_ALL IN1_StGd_tese_ch22 8/7/03 5:21 PM Page 398 Name______________________________ Class __________________ Date ______________ 10. Circle the letter of each plant feature that is characteristic of dicots. a. Parallel leaf veins b. Floral parts in multiples of 4 or 5 c. Roots include a taproot d. Vascular bundles scattered throughout stem 11. Woody plants are made primarily of what kind of cells? They are made primarily of cells with thick cell walls that support the plant body. 12. What characteristics do the stems of herbaceous plants have? Their plant stems are smooth and nonwoody. 13. Complete the table about plant life spans. PLANT LIFE SPANS Category Definition Examples Annuals Angiosperms that complete a life cycle within one growing season Marigolds, petunias, pansies, wheat, corn, cucumbers Biennials Angiosperms that complete a life cycle in two years Parsley, celery, foxgloves Perennials Angiosperms that live more than two years Peonies, asparagus, grasses, palm trees, sagebrush, oak trees, honeysuckle short stems, and sometimes leaves. 15. What happens to biennials once their flowers produce seeds? They die. 16. Is the following sentence true or false? Most perennials have herbaceous stems. false 398 Guided Reading and Study Workbook/Chapter 22 © Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 14. What structures do biennials produce in their first year of growth? They grow roots, very BIO_ALL IN1_StGd_tese_ch22 8/7/03 5:21 PM Page 399 Name______________________________ Class __________________ Date ______________ WordWise Use the clues below to identify vocabulary terms from Chapter 22. Write the terms on the lines, putting one letter in each blank. When you finish, the word enclosed in the diagonal will reveal an important term related to plants. Clues 1. Cluster of vascular tissue in a leaf 8. Spore-producing plant 2. Female reproductive structure in mosses 9. Bryophyte structure where sperm are produced 3. Supporting structure that connects roots and leaves 10. A long, thin cell that anchors a moss to the ground 4. Key cells in xylem 11. Flowering plant 5. A thick wall of tissue surrounding angiosperm seed 12. An embryo of a living plant that is encased in a protective covering 6. Process by which pollen is carried to the female gametophyte 13. A cluster of sporangia 14. Creeping or underground stem in ferns 7. Photosynthetic organ that contains vascular tissue Vocabulary Terms 1. v e i n 2. a r c h e s t e m a c h 5. f r 6. p o g o n e i d s u i t l l i n 7. l e a f 8. s p o 3. © Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 4. t 9. r a 10. 11. a n u m a t i o n r o p h y t i u m n t h e r i d r h i z o i d g i o s p e r m s e e d 12. 13. 14. i r h s o r u s i z o m e Guided Reading and Study Workbook/Chapter 22 e 399