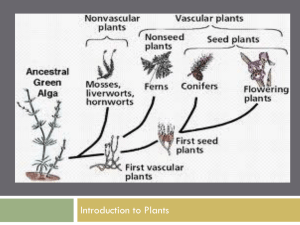
Plant Diversity II
... Male cones are smaller and delicate, disintegrating after releasing clouds of pollen grains Female cones are large w/ woody scales Each scale has two 1N female gametophytes, each producing eggs ...
... Male cones are smaller and delicate, disintegrating after releasing clouds of pollen grains Female cones are large w/ woody scales Each scale has two 1N female gametophytes, each producing eggs ...
Plant Questions | Classification of Plants
... a. What is/are the function(s) of seeds? 9 Nourish the embryo (food) 9 Protect the embryo b. What is dormancy and how is this beneficial for the adaptation of seed plants? 9 No growth…waiting for right conditions to grow Cone bearing plants and flowering plants 6. Seed plants can be classified into ...
... a. What is/are the function(s) of seeds? 9 Nourish the embryo (food) 9 Protect the embryo b. What is dormancy and how is this beneficial for the adaptation of seed plants? 9 No growth…waiting for right conditions to grow Cone bearing plants and flowering plants 6. Seed plants can be classified into ...
Flowering Plants - Science with Ms. C
... from threats that could potentially kill the plant. • Examples of natural defenses that plants have developed over time may be: ▫ Thorns that defend the plant from being eaten by some animals ▫ Fruits and leaves with poisons so that they are not eaten by animals ▫ The ability to close its leaves whe ...
... from threats that could potentially kill the plant. • Examples of natural defenses that plants have developed over time may be: ▫ Thorns that defend the plant from being eaten by some animals ▫ Fruits and leaves with poisons so that they are not eaten by animals ▫ The ability to close its leaves whe ...
Systems in Plants
... • Specialized structures for sexual reproduction • The male reproductive structures produce pollen grains • the female structures produce eggs • After fertilization, the female parts form seeds, What are ways of pollination? which are often protected PLEASE NOTE by fruits. ...
... • Specialized structures for sexual reproduction • The male reproductive structures produce pollen grains • the female structures produce eggs • After fertilization, the female parts form seeds, What are ways of pollination? which are often protected PLEASE NOTE by fruits. ...
2. No vascular tissue
... adaptations that allow sperm to meet egg without water (e.g. spores that have waterproof coverings, seeds) ...
... adaptations that allow sperm to meet egg without water (e.g. spores that have waterproof coverings, seeds) ...
seed
... Zygote becomes an EMBRYO (Diploid sporophyte) COTYLEDONS – Seed leaf of embryo SEED COAT – Protects embryo ...
... Zygote becomes an EMBRYO (Diploid sporophyte) COTYLEDONS – Seed leaf of embryo SEED COAT – Protects embryo ...
Kingdom Plantae
... • The sporophytes of lycophytes consist of true roots, stems and leaves. • Sporophylls are specialized leaves that bear sporangia and are organized into a structure called the strobilus (pl. strobili). • Some Selaginella are heterosporous; Lycopodium is homosporous. ...
... • The sporophytes of lycophytes consist of true roots, stems and leaves. • Sporophylls are specialized leaves that bear sporangia and are organized into a structure called the strobilus (pl. strobili). • Some Selaginella are heterosporous; Lycopodium is homosporous. ...
Sporophyte Stage - St. Ambrose School
... Sexual Reproduction – Water or wind can bring the gametes together, insects such as bees can also bring them together ...
... Sexual Reproduction – Water or wind can bring the gametes together, insects such as bees can also bring them together ...
Chapter 25: Plants
... make adaptations for obtaining water and to prevent its loss. Water was also required to provide a medium for the fertilization of eggs by flagellated sperm. In addition, once plants emerged from the protective cover of water, genetic material was more susceptible to damage by UV radiation. The foll ...
... make adaptations for obtaining water and to prevent its loss. Water was also required to provide a medium for the fertilization of eggs by flagellated sperm. In addition, once plants emerged from the protective cover of water, genetic material was more susceptible to damage by UV radiation. The foll ...
notes
... The objective of this indicator is to summarize each of the processes in the life cycle of flowering plants; therefore, the primary focus of assessment should be to generalize the major points about the life cycle of seed plants (including germination, plant development, fertilization, and seed prod ...
... The objective of this indicator is to summarize each of the processes in the life cycle of flowering plants; therefore, the primary focus of assessment should be to generalize the major points about the life cycle of seed plants (including germination, plant development, fertilization, and seed prod ...
Slide 1
... months before they actually bloom. The trigger is the length of the light-dark cycle. In order to get poinsettias to bloom in December, florists change the length of the light-dark cycle in September. Given the information and clues above, which of the following is FALSE? a. Poinsettias are short da ...
... months before they actually bloom. The trigger is the length of the light-dark cycle. In order to get poinsettias to bloom in December, florists change the length of the light-dark cycle in September. Given the information and clues above, which of the following is FALSE? a. Poinsettias are short da ...
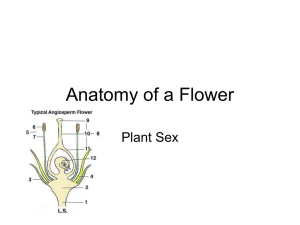
flower_parts_(p._20_IO)
... Flowers Their main job for the plant is: •Develop into seeds & fruits = Sexual reproduction •Reproduce the plant. ...
... Flowers Their main job for the plant is: •Develop into seeds & fruits = Sexual reproduction •Reproduce the plant. ...
Catchweed Bedstraw
... Can be a serious weed in cultivated fields but the main problem isn't competition with crops but difficulty in harvesting when bedstraw becomes tangled with the crop or equipment ...
... Can be a serious weed in cultivated fields but the main problem isn't competition with crops but difficulty in harvesting when bedstraw becomes tangled with the crop or equipment ...
Slide 1
... Plants with seeds that are not enclosed within a fruit, derive their name from the Greek words gymnos (naked) and sperma (seed). In this plant group, the seeds are produced on the open surface of a scale. Unlike flowering plants, the gymnosperms do not form true flowers or fruits. There are four div ...
... Plants with seeds that are not enclosed within a fruit, derive their name from the Greek words gymnos (naked) and sperma (seed). In this plant group, the seeds are produced on the open surface of a scale. Unlike flowering plants, the gymnosperms do not form true flowers or fruits. There are four div ...
Plants can be classified based on how they absorb and circulate
... 4. _Xylem_____ transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. 5. _Phloem____ transport food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. 6. Examples include trees and many shrubs with _woody___ stems that grow very tall and grasses, dandelions, and tomato plants with _soft__ herb ...
... 4. _Xylem_____ transport water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. 5. _Phloem____ transport food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. 6. Examples include trees and many shrubs with _woody___ stems that grow very tall and grasses, dandelions, and tomato plants with _soft__ herb ...
Plant Life Essay, Research Paper The kingdom Plantae
... gymnosperms (conifers) and angiosperms (flowering plants). The male gametes of gymnosperms and angiosperms are carried by pollen; each of these types of plants also produce seeds, which protect the embryos inside from drying out in a terrestrial environment. Angiosperms, with their flowers and fruit ...
... gymnosperms (conifers) and angiosperms (flowering plants). The male gametes of gymnosperms and angiosperms are carried by pollen; each of these types of plants also produce seeds, which protect the embryos inside from drying out in a terrestrial environment. Angiosperms, with their flowers and fruit ...
5th and 6th grade Ch 4 test Notes:
... 1) Stomata – holes in the epidermis that allows water and gasses pass 2) Guard Cells – open and close Stomata 3) Transpiration – water loss through Stomata 4) Cuticle – Waxy layer – slows water loss D) Photosynthesis 1) Process in which plants make glucose and releases oxygen 2) Takes place in the m ...
... 1) Stomata – holes in the epidermis that allows water and gasses pass 2) Guard Cells – open and close Stomata 3) Transpiration – water loss through Stomata 4) Cuticle – Waxy layer – slows water loss D) Photosynthesis 1) Process in which plants make glucose and releases oxygen 2) Takes place in the m ...
24-2 Reading Guide
... underlined word or words to make the statement true. 13. In most monocots, the cotyledon remains underground. ...
... underlined word or words to make the statement true. 13. In most monocots, the cotyledon remains underground. ...
Natural Selection acts on phenotypic variations in populations.
... environment, but occur through random changes in the DNA and through new gene combinations Some phenotypic variations significantly increase or decrease fitness of the organism and the and the ...
... environment, but occur through random changes in the DNA and through new gene combinations Some phenotypic variations significantly increase or decrease fitness of the organism and the and the ...
Ch. 20 Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants
... Vascular seed plants producing a flower. Most diverse and widespread ...
... Vascular seed plants producing a flower. Most diverse and widespread ...
Flowering plant

The flowering plants (angiosperms), also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within the seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. Etymologically, angiosperm means a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure, in other words, a fruiting plant.The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 160 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 120 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.