secondary growth
... • Pits allow water and minerals to flow between vessel element and tracheid • Vessel element die after development and add support to the plant ...
... • Pits allow water and minerals to flow between vessel element and tracheid • Vessel element die after development and add support to the plant ...
our observations, we conclude that carotenoids and MAA, that both
... Drought is one of the primary constraints of crop productivity. Improving the efficiency of water usage and the tolerance for growth under conditions of sub-optimal water have a profound impact on rice production. Therefore the aim of this work is to understand how drought affects the growth of the ...
... Drought is one of the primary constraints of crop productivity. Improving the efficiency of water usage and the tolerance for growth under conditions of sub-optimal water have a profound impact on rice production. Therefore the aim of this work is to understand how drought affects the growth of the ...
PLANTS - SharpSchool
... interact to perform the functions of transport in plants? 2. How do the root and shoot systems interact to perform the functions of reproduction in plants? 3. How do the root and shoot systems interact to perform the functions of response in plants? ...
... interact to perform the functions of transport in plants? 2. How do the root and shoot systems interact to perform the functions of reproduction in plants? 3. How do the root and shoot systems interact to perform the functions of response in plants? ...
Flowers
... • If the ovary has more than one carpel you usually see more than one locule (chamber containing seeds) • You can sometimes tell how many carpels are in a flower by looking at the tip of the style. Number of style tips = number of carpels • Carpels are leaves that have rolled up to enclose the ovule ...
... • If the ovary has more than one carpel you usually see more than one locule (chamber containing seeds) • You can sometimes tell how many carpels are in a flower by looking at the tip of the style. Number of style tips = number of carpels • Carpels are leaves that have rolled up to enclose the ovule ...
Document
... Taxonomy -- the naming of groups (taxa, singular taxon) Systematics -- a method (or system) for classifying organisms into groups ...
... Taxonomy -- the naming of groups (taxa, singular taxon) Systematics -- a method (or system) for classifying organisms into groups ...
The role of boron in flowering and fruit, nut and seed formation
... symptoms of B deficiency. This suggests that flowering and fruit set may have a greater demand for B than does vegetative growth. Foliar sprays of Solubor® at the pre-bloom or bloom stages of fruit and nut crops supplies available B at the critical periods of pollen formation, germination and fertil ...
... symptoms of B deficiency. This suggests that flowering and fruit set may have a greater demand for B than does vegetative growth. Foliar sprays of Solubor® at the pre-bloom or bloom stages of fruit and nut crops supplies available B at the critical periods of pollen formation, germination and fertil ...
giant hyssop - Prairie Originals
... CULTURE In the garden Giant Hyssop grows very well in full sun or part shade. It tolerates a wide range of soils. Medium to moist soil is best however the plant is quite drought tolerant once established. It self seeds somewhat but not to the point of being a problem. Groups of hyssop can be used in ...
... CULTURE In the garden Giant Hyssop grows very well in full sun or part shade. It tolerates a wide range of soils. Medium to moist soil is best however the plant is quite drought tolerant once established. It self seeds somewhat but not to the point of being a problem. Groups of hyssop can be used in ...
Forms of Inflorescence: panicle, raceme, spike
... does the plant belong? This is based on how the plant reproduces. – Spores – Lichen, Mosses & Liverworts, Ferns, (Bryophyta, Pteridophyta) – Naked seeds, ie conifers (Gymnospermophyta) – Seeds enclosed in an ovary – flowering plants (Angiospermophyta) ...
... does the plant belong? This is based on how the plant reproduces. – Spores – Lichen, Mosses & Liverworts, Ferns, (Bryophyta, Pteridophyta) – Naked seeds, ie conifers (Gymnospermophyta) – Seeds enclosed in an ovary – flowering plants (Angiospermophyta) ...
Plants
... Why is water, air, light and soil important to plants Water- Plants need water. Water is essential to all life on earth. No known organism can exist without water. Plants use water to carry moisture and nutrients from the roots to he leaves and food from the leaves back down to the roots. Air- Pl ...
... Why is water, air, light and soil important to plants Water- Plants need water. Water is essential to all life on earth. No known organism can exist without water. Plants use water to carry moisture and nutrients from the roots to he leaves and food from the leaves back down to the roots. Air- Pl ...
Unit 6 - root,stems, leaves
... 20. explain what a plant tropism is and give an example of both a positive and a negative tropism for a stem. For a root. 21. explain the role of auxin in making a plant grow toward a light source. ...
... 20. explain what a plant tropism is and give an example of both a positive and a negative tropism for a stem. For a root. 21. explain the role of auxin in making a plant grow toward a light source. ...
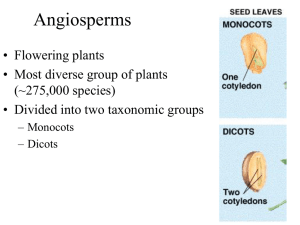
ch 31_lecture
... 1. Describe two main kinds of flowering plants and how they differ in number of seed leaves and in structures such as stems, roots, leaves, and flowers 2. Name the three tissue systems that make up the plant body and the functions of each 3. Describe the structure and function of five types of cells ...
... 1. Describe two main kinds of flowering plants and how they differ in number of seed leaves and in structures such as stems, roots, leaves, and flowers 2. Name the three tissue systems that make up the plant body and the functions of each 3. Describe the structure and function of five types of cells ...
Unit 7
... hyphae not divided into cells by cross wall. They are called coenocytes, which results from repeated division of nuclei without cytoplasmic division. Distinguish among fungi and list some common examples of each. Describe asexual and sexual reproduction in Zygomycota, Ascomycota, and Basidiomycota, ...
... hyphae not divided into cells by cross wall. They are called coenocytes, which results from repeated division of nuclei without cytoplasmic division. Distinguish among fungi and list some common examples of each. Describe asexual and sexual reproduction in Zygomycota, Ascomycota, and Basidiomycota, ...
Parts of a Flower - New Jersey Agricultural Society
... Ovule: small parts inside the ovary that when fertilized with pollen become seeds. Stamen: the male parts of the flower that surround the pistil Anthers: the top of the stamen stalk that is filled with pollen. When the pollen is ready to be spread, the anthers open up to release pollen. Filament: th ...
... Ovule: small parts inside the ovary that when fertilized with pollen become seeds. Stamen: the male parts of the flower that surround the pistil Anthers: the top of the stamen stalk that is filled with pollen. When the pollen is ready to be spread, the anthers open up to release pollen. Filament: th ...
Jr Sr Plant Part Study Guide
... plant. Broccoli is another type of flower that we eat.” The flower has many parts that all work together to produce a seed. The flower stem is called a peduncle. The base of the flower is a receptacle. The sepals are the outermost circle of leaf-like structures. Sepals protect the developing flower ...
... plant. Broccoli is another type of flower that we eat.” The flower has many parts that all work together to produce a seed. The flower stem is called a peduncle. The base of the flower is a receptacle. The sepals are the outermost circle of leaf-like structures. Sepals protect the developing flower ...
video slide - Course
... • Angiosperms are seed plants with reproductive structures called flowers and fruits. • They are the most widespread and diverse of all plants. • All angiosperms are classified in a single phylum: Anthophyta. • The name comes from the Greek anthos, flower. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., p ...
... • Angiosperms are seed plants with reproductive structures called flowers and fruits. • They are the most widespread and diverse of all plants. • All angiosperms are classified in a single phylum: Anthophyta. • The name comes from the Greek anthos, flower. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., p ...
Jr Sr Plant Part Study Guide - Yankton County 4-H
... plant. Broccoli is another type of flower that we eat.” The flower has many parts that all work together to produce a seed. The flower stem is called a peduncle. The base of the flower is a receptacle. The sepals are the outermost circle of leaf-like structures. Sepals protect the developing flower ...
... plant. Broccoli is another type of flower that we eat.” The flower has many parts that all work together to produce a seed. The flower stem is called a peduncle. The base of the flower is a receptacle. The sepals are the outermost circle of leaf-like structures. Sepals protect the developing flower ...
Tropism
... Life Spans of Angiosperms • Angiosperms are classified as annuals, biennials, and perennials. • Flowering plants that complete a life cycle in one growing season are called annuals. • Biennials will complete their life cycle in two years. In the first year, they germinate and grow roots, with very ...
... Life Spans of Angiosperms • Angiosperms are classified as annuals, biennials, and perennials. • Flowering plants that complete a life cycle in one growing season are called annuals. • Biennials will complete their life cycle in two years. In the first year, they germinate and grow roots, with very ...
Plant Reproduction and Development 621
... and discharges its two sperm nuclei into the embryo sac. One sperm unites with the egg to form the zygote. The other sperm combines with the two polar nuclei to form a 3N nucleus in the large central cell of the embryo sac. = This central cell will give rise to the endosperm which is a food storing ...
... and discharges its two sperm nuclei into the embryo sac. One sperm unites with the egg to form the zygote. The other sperm combines with the two polar nuclei to form a 3N nucleus in the large central cell of the embryo sac. = This central cell will give rise to the endosperm which is a food storing ...
1 Topic 7 THE PLANT KINGDOM
... WELWITSCHIA (GNETAE) is found only in south-west Africa. It is a remarkable woody plant, the sole member of its family. It has only two leaves which appear to be many when the two leaves have been split by wind action. ANGIOSPERMS are vascular plants with flowers and fruits which enclose the develop ...
... WELWITSCHIA (GNETAE) is found only in south-west Africa. It is a remarkable woody plant, the sole member of its family. It has only two leaves which appear to be many when the two leaves have been split by wind action. ANGIOSPERMS are vascular plants with flowers and fruits which enclose the develop ...
talent-guide - WordPress.com
... 19.Metacentric chromosomes are v-shaped 20.Submetacentric chromoseomes are L-shaped 21.Telocentric and acrocentric chromosomes are Rod shaped 22.Root hairs are produced from the short cells called Trichoblasts. 23.Largest Herbarium is Herbarium of Royal Botanical Garden, kew, London, Englant (more t ...
... 19.Metacentric chromosomes are v-shaped 20.Submetacentric chromoseomes are L-shaped 21.Telocentric and acrocentric chromosomes are Rod shaped 22.Root hairs are produced from the short cells called Trichoblasts. 23.Largest Herbarium is Herbarium of Royal Botanical Garden, kew, London, Englant (more t ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • The life cycle of a pine illustrates the three key adaptations to terrestrial life in seed plants: • increasing dominance of the sporophyte • seeds as a resistant, dispersal stage • pollen as an airborne agent bringing gametes together. ...
... • The life cycle of a pine illustrates the three key adaptations to terrestrial life in seed plants: • increasing dominance of the sporophyte • seeds as a resistant, dispersal stage • pollen as an airborne agent bringing gametes together. ...
Organismal Biology/30B2
... • The life cycle of a pine illustrates the three key adaptations to terrestrial life in seed plants: • increasing dominance of the sporophyte • seeds as a resistant, dispersal stage • pollen as an airborne agent bringing gametes together. ...
... • The life cycle of a pine illustrates the three key adaptations to terrestrial life in seed plants: • increasing dominance of the sporophyte • seeds as a resistant, dispersal stage • pollen as an airborne agent bringing gametes together. ...
Ch.8 - Wikispaces
... – The Structure of a Root • The root cap protects the root from injury from rocks as the root grows through the soil • Root hairs grow out of the root’s surface; these tiny hairs can enter the spaces between soil particles, where they absorb water and minerals (root hairs help the plant absorb large ...
... – The Structure of a Root • The root cap protects the root from injury from rocks as the root grows through the soil • Root hairs grow out of the root’s surface; these tiny hairs can enter the spaces between soil particles, where they absorb water and minerals (root hairs help the plant absorb large ...
Hardy Perennials Great for Area`s Hot Conditions
... winter and are favorite sources of nutty seeds for goldfinches and other small winter resident birds. Native plant enthusiasts obsess over yellow forms and kinds with scraggly pink ray flowers; endangered forms, including the Tennessee coneflower (Echinacea tennesseensis) which is a low growing moun ...
... winter and are favorite sources of nutty seeds for goldfinches and other small winter resident birds. Native plant enthusiasts obsess over yellow forms and kinds with scraggly pink ray flowers; endangered forms, including the Tennessee coneflower (Echinacea tennesseensis) which is a low growing moun ...
discov5_lecppt_Ch03
... The Evolution of Seeds Contributed to the Success of Gymnosperms • A seed is made up of a plant embryo and a short supply of food encased in a protective seed coat • Gymnosperms produce winged seeds that can drift far from the parent to increase the chance of survival ...
... The Evolution of Seeds Contributed to the Success of Gymnosperms • A seed is made up of a plant embryo and a short supply of food encased in a protective seed coat • Gymnosperms produce winged seeds that can drift far from the parent to increase the chance of survival ...
Flowering plant

The flowering plants (angiosperms), also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within the seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. Etymologically, angiosperm means a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure, in other words, a fruiting plant.The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 160 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 120 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.























