Structure of Flower
... All plants have a life cycle in which a diploid sporophyte generation alternates with a haploid gametophyte generation. Gametophyte plants produce male and female gametes—sperm and eggs. When the gametes join, they form a zygote that begins the next sporophyte generation. In some plants, the two sta ...
... All plants have a life cycle in which a diploid sporophyte generation alternates with a haploid gametophyte generation. Gametophyte plants produce male and female gametes—sperm and eggs. When the gametes join, they form a zygote that begins the next sporophyte generation. In some plants, the two sta ...
pub3250downymildewofwheat
... severely dwarfed, with many tillers growing only a few inches tall. Other plants have thickened leaves that are yellow striped, fleshy, twisted, curled and stiff. These plants rarely produce heads, and those heads that are produced are distorted and abnormally large. The stem below the affected head ...
... severely dwarfed, with many tillers growing only a few inches tall. Other plants have thickened leaves that are yellow striped, fleshy, twisted, curled and stiff. These plants rarely produce heads, and those heads that are produced are distorted and abnormally large. The stem below the affected head ...
Lesson 3 | Plant Reproduction
... Some seeds have outer coats that are hard, abrasive, or heavily barbed with hooks on the end of sharp spines. These seeds readily snag onto a passing animal’s fur or person’s clothing. Animals often become irritated when there are too many burrs stuck to them. When you see deer rubbing against trees ...
... Some seeds have outer coats that are hard, abrasive, or heavily barbed with hooks on the end of sharp spines. These seeds readily snag onto a passing animal’s fur or person’s clothing. Animals often become irritated when there are too many burrs stuck to them. When you see deer rubbing against trees ...
üreme 2 - benanbiology
... Microspres undergo mitosis and forme pollen with 2 nuclei. (vegetative and generative nucleus) Vegetative nucleus forms pollen tube when it lands on stigma during pollination. Generative nucleus divides by mitosis and form 3 sperm cells. ...
... Microspres undergo mitosis and forme pollen with 2 nuclei. (vegetative and generative nucleus) Vegetative nucleus forms pollen tube when it lands on stigma during pollination. Generative nucleus divides by mitosis and form 3 sperm cells. ...
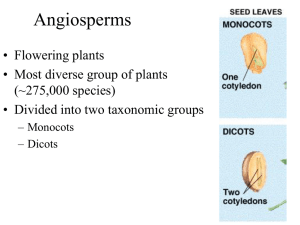
Comparing a Monocot to a Dicot Seed
... Both monocot and dicot seeds develop in similar ways and have the same parts. There are a few minor differences: monocots start out with one seed leaf, while dicots have two. The technical word for seed leaf is cotyledon: you can find it on the coloring sheet; it is the first leaf to emerge from a d ...
... Both monocot and dicot seeds develop in similar ways and have the same parts. There are a few minor differences: monocots start out with one seed leaf, while dicots have two. The technical word for seed leaf is cotyledon: you can find it on the coloring sheet; it is the first leaf to emerge from a d ...
Definitions of Food Groups
... be represented by the entire plant including the seedhead, or by a single leaf or group of leaves Hard mast: includes nuts from walnut, hickory, oak, beech, pecan, almond, and common hazel; may be shown with or without the husk Insects and spiders: small invertebrate (without a backbone) animals; sp ...
... be represented by the entire plant including the seedhead, or by a single leaf or group of leaves Hard mast: includes nuts from walnut, hickory, oak, beech, pecan, almond, and common hazel; may be shown with or without the husk Insects and spiders: small invertebrate (without a backbone) animals; sp ...
Growing Plants Using a Hydroponic Germinator
... On a Lunar or Mars base, it will be essential to grow plants through various means. We can not take all of the food that we need on a trip to the moon or Mars for all of the astronauts. Most of the food will be grown on the moon or Mars in greenhouses. There are two possible ways to grow plants for ...
... On a Lunar or Mars base, it will be essential to grow plants through various means. We can not take all of the food that we need on a trip to the moon or Mars for all of the astronauts. Most of the food will be grown on the moon or Mars in greenhouses. There are two possible ways to grow plants for ...
(Chastain) for Organismal saved on 25feb09
... For lack of a better name, this group is referred by botanists as the seedless vascular plants. Not highly related to each other, except by evolutionary status, these plants legitimately can be thought of as the first true land plants. In there hey-day, they formed a vast and luxuriant green landsca ...
... For lack of a better name, this group is referred by botanists as the seedless vascular plants. Not highly related to each other, except by evolutionary status, these plants legitimately can be thought of as the first true land plants. In there hey-day, they formed a vast and luxuriant green landsca ...
Seeing the Invisible: Mutualism and Plant Reproduction
... cycle for any organism. When reproduction is disrupted, such as through the loss of bees or habitat, a species may struggle to survive, sometimes even becoming extinct. How It Works In angiosperms (the scientific name for flowering plants), the flower is the reproductive organ. All flowering plants ...
... cycle for any organism. When reproduction is disrupted, such as through the loss of bees or habitat, a species may struggle to survive, sometimes even becoming extinct. How It Works In angiosperms (the scientific name for flowering plants), the flower is the reproductive organ. All flowering plants ...
Section 4- Microscopes, Cells and Reproduction: Summary Sheets
... In Vegetative Propagation, the roots, stems, or leaves can grow a new plant. 5 kinds of natural vegetative propagation: 1. Bulbs: a short underground stem surrounded by colourless leaves that store food and protect the bulb. 2. Corms: contain a solid mass of stem tissue, rather than concentric rings ...
... In Vegetative Propagation, the roots, stems, or leaves can grow a new plant. 5 kinds of natural vegetative propagation: 1. Bulbs: a short underground stem surrounded by colourless leaves that store food and protect the bulb. 2. Corms: contain a solid mass of stem tissue, rather than concentric rings ...
Information Sheet Giant Hog Weed DESCRIPTION Stems: Flowering
... issues). If you have been exposed to this plant, if is often suggested that you wash affected area immediately, avoid direct exposure to sunlight and seek medical advice. HUMAN HEALTH ISSUES Giant hogweed can be a serious health hazard for humans. Its watery, clear sap contains photosensitizing comp ...
... issues). If you have been exposed to this plant, if is often suggested that you wash affected area immediately, avoid direct exposure to sunlight and seek medical advice. HUMAN HEALTH ISSUES Giant hogweed can be a serious health hazard for humans. Its watery, clear sap contains photosensitizing comp ...
Aquatic Weed Control - Identification
... specific weeds or groups of weeds with similar growth habits. Aquatic weeds are divided into two botanical groups; algae and flowering plants. Algae are usually structurally very simple with no apparent roots, leaves, or stems. However, some (for example, Chara) can resemble flowering plants. Flower ...
... specific weeds or groups of weeds with similar growth habits. Aquatic weeds are divided into two botanical groups; algae and flowering plants. Algae are usually structurally very simple with no apparent roots, leaves, or stems. However, some (for example, Chara) can resemble flowering plants. Flower ...
Biology Chapter 29
... 27. heartwood: (p 611) the darker wood in the center of a tree 28. node: (p 609) the end of the internode where one or more leaves are attached 29. pith: (p 610) the plant tissue located in the center of the stem 30. pressure-flow hypothesis: (p 613) an explanation of the movement of sugars in the p ...
... 27. heartwood: (p 611) the darker wood in the center of a tree 28. node: (p 609) the end of the internode where one or more leaves are attached 29. pith: (p 610) the plant tissue located in the center of the stem 30. pressure-flow hypothesis: (p 613) an explanation of the movement of sugars in the p ...
weevils - Biology Resources
... distributed species of grain weevil, Sitophilus. These are smaller and less conspicuous than Alcidodes but they do more damage because they lay their eggs in the fruits or seeds of beans, maize or rice as the crops are growing in the field. While the seeds or grains are in store, the larvae eat the ...
... distributed species of grain weevil, Sitophilus. These are smaller and less conspicuous than Alcidodes but they do more damage because they lay their eggs in the fruits or seeds of beans, maize or rice as the crops are growing in the field. While the seeds or grains are in store, the larvae eat the ...
method of reproduction
... • The oldest amphibian fossils Ichthyostega – found in the Devonian of eastern Greenland – streamlined bodies, long tails, and fins – four legs, a strong backbone, a rib cage, and pelvic and pectoral girdle ...
... • The oldest amphibian fossils Ichthyostega – found in the Devonian of eastern Greenland – streamlined bodies, long tails, and fins – four legs, a strong backbone, a rib cage, and pelvic and pectoral girdle ...
Nonvascular Plants: Moss
... 1) List the main types of plants 2) Define nonvascular. 3) Define moss and list 3 of the 5 main characteristics of mosses. 4) Why are mosses considered nonvascular if they appear to have a stem and a leaf? 5) List the two ways that moss species are classified. ...
... 1) List the main types of plants 2) Define nonvascular. 3) Define moss and list 3 of the 5 main characteristics of mosses. 4) Why are mosses considered nonvascular if they appear to have a stem and a leaf? 5) List the two ways that moss species are classified. ...
HAWKS CLASS HALF TERM OVERVIEW Spring Term II 2017
... Write a set of clear instructions including features learned ...
... Write a set of clear instructions including features learned ...
The Environment and Plant Responses
... the response of a plant to changes in the length of daylight (the reponses of a plant to changes in light intensity and length of days) It often determines whether or not a plant produces flowers. ...
... the response of a plant to changes in the length of daylight (the reponses of a plant to changes in light intensity and length of days) It often determines whether or not a plant produces flowers. ...
Plant Growth
... the response of a plant to changes in the length of daylight (the reponses of a plant to changes in light intensity and length of days) It often determines whether or not a plant produces flowers. ...
... the response of a plant to changes in the length of daylight (the reponses of a plant to changes in light intensity and length of days) It often determines whether or not a plant produces flowers. ...
209 Maintain the appearance of decorative amenity areas File
... The amount of nutrients a plant requires will of course vary during its life time. Seedlings require very little in the way of nutrients to germinate as the have a food supply in the seed. However once they begin to establish they will need increasing supplies of nutrients that are normally obtained ...
... The amount of nutrients a plant requires will of course vary during its life time. Seedlings require very little in the way of nutrients to germinate as the have a food supply in the seed. However once they begin to establish they will need increasing supplies of nutrients that are normally obtained ...
Description Picture Argintică Mountain avens Coada şoricelului
... SPAIN, ESTONIA, TURKEY, ROMANIA ...
... SPAIN, ESTONIA, TURKEY, ROMANIA ...
Hibiscus Southern Belle 0807
... ppm Nitrogen to maintain a media E.C. of 1.5 to 1.8 mmhos. Temperature and humidity: Hibiscus is a tropical plant and grows best between 68-85 °F/20-29 °C with high relative humidity. Plants may develop leaf chlorosis if grown cool at temperatures below 59 °F/15 °C. Growth retardants: B-9/Alar at 2, ...
... ppm Nitrogen to maintain a media E.C. of 1.5 to 1.8 mmhos. Temperature and humidity: Hibiscus is a tropical plant and grows best between 68-85 °F/20-29 °C with high relative humidity. Plants may develop leaf chlorosis if grown cool at temperatures below 59 °F/15 °C. Growth retardants: B-9/Alar at 2, ...
Snímek 1 - esf
... Food - cereals (wheat, corn), vegetables, spices, fruits, coffee, herbs etc. Nonfood – woods (for construction, furniture making), cotton (for clothing), medicines derived from plants (quinine, morphine) + drugs (nicotine, opium) Aesthetic uses – cut flowers, botanical gardens, indoors and outdoors ...
... Food - cereals (wheat, corn), vegetables, spices, fruits, coffee, herbs etc. Nonfood – woods (for construction, furniture making), cotton (for clothing), medicines derived from plants (quinine, morphine) + drugs (nicotine, opium) Aesthetic uses – cut flowers, botanical gardens, indoors and outdoors ...
secondary growth
... • Pits allow water and minerals to flow between vessel element and tracheid • Vessel element die after development and add support to the plant ...
... • Pits allow water and minerals to flow between vessel element and tracheid • Vessel element die after development and add support to the plant ...
Flowering plant

The flowering plants (angiosperms), also known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta, are the most diverse group of land plants. Angiosperms are seed-producing plants like the gymnosperms and can be distinguished from the gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within the seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. Etymologically, angiosperm means a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure, in other words, a fruiting plant.The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from gymnosperms around 245–202 million years ago, and the first flowering plants known to exist are from 160 million years ago. They diversified enormously during the Lower Cretaceous and became widespread around 120 million years ago, but replaced conifers as the dominant trees only around 60–100 million years ago.