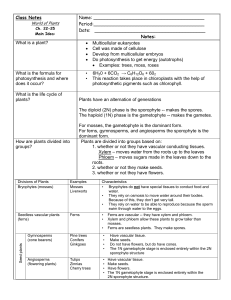
File
... beaches, mangroves, and other wetlands across the United States. Herons are usually gray, though a white subspecies can be found in Florida. They have long wings and legs, and a long bill that tapers to a point. Usually hunting while standing in the water, they spot prey by sight, feeding on such di ...
... beaches, mangroves, and other wetlands across the United States. Herons are usually gray, though a white subspecies can be found in Florida. They have long wings and legs, and a long bill that tapers to a point. Usually hunting while standing in the water, they spot prey by sight, feeding on such di ...
Botany Final Exam Study Guide - Merrillville Community School
... Describe the structure of plants cells, identify cell parts, contrast with animal cells ...
... Describe the structure of plants cells, identify cell parts, contrast with animal cells ...
Biology Content Standard #10 Plants
... (And Chapter 22 & 24) ***Create a foldable drawing using Figure 22-7 & Title it “Overview of the Plant Kingdom” Be sure to draw, color and label just as you see the diagram in the book. ...
... (And Chapter 22 & 24) ***Create a foldable drawing using Figure 22-7 & Title it “Overview of the Plant Kingdom” Be sure to draw, color and label just as you see the diagram in the book. ...
PASS Review—Plants Name: All living organisms share the
... shoots from roots; leaves—houseplants like African violets can produce new plants from leaves placed on top of soil All plants perform certain processes that are necessary for their survival. Photosynthesis: process by which plants make their own food, a simple sugar, for survival; chloroplasts, fou ...
... shoots from roots; leaves—houseplants like African violets can produce new plants from leaves placed on top of soil All plants perform certain processes that are necessary for their survival. Photosynthesis: process by which plants make their own food, a simple sugar, for survival; chloroplasts, fou ...
Roberta`s Growing Guide
... Trim back in late winter. Stems will root into the ground where they touch, and any new plants that form can be easily moved in spring or fall. Also easily divided. WINTER DORMANCY These are evergreen and stay green year-round in mild climates and cold climates. It forms dense mats of foliage 4 to 6 ...
... Trim back in late winter. Stems will root into the ground where they touch, and any new plants that form can be easily moved in spring or fall. Also easily divided. WINTER DORMANCY These are evergreen and stay green year-round in mild climates and cold climates. It forms dense mats of foliage 4 to 6 ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... 9. The openings in leaves that allow plants to respire are called a. stomata. c. xylem. b. cambium. d. phloem. 10.Which is one advantage of sexual reproduction? a. More offspring are produced. b. More offspring survive to maturity. c. The offspring have more genetic variation. d. The offspring and t ...
... 9. The openings in leaves that allow plants to respire are called a. stomata. c. xylem. b. cambium. d. phloem. 10.Which is one advantage of sexual reproduction? a. More offspring are produced. b. More offspring survive to maturity. c. The offspring have more genetic variation. d. The offspring and t ...
topic: living things – plants - Lancashire Grid for Learning
... 2a. Ask questions and decide how they might find the answers to them. ...
... 2a. Ask questions and decide how they might find the answers to them. ...
Ouch! What was that? I look down and I have a goat head stuck in
... pesky things? Well to start with let us help you understand what the plant actually is and about its infamous tri-pointed seeds known as goat heads. We will explain how to identify and help eliminate them from your gardens, yards and driveways. Puncturevine or Tribulus terrestris is a plant that ori ...
... pesky things? Well to start with let us help you understand what the plant actually is and about its infamous tri-pointed seeds known as goat heads. We will explain how to identify and help eliminate them from your gardens, yards and driveways. Puncturevine or Tribulus terrestris is a plant that ori ...
Specialized Tissues In Plants
... in trees and other woody plants • Epidermis – the outermost tissue layer • Cuticle – waxy, waterproof coating secreted by epidermal cells • Stomata – (singular - stoma) the pores on plant surfaces that function in gas exchange • Vascular tissue – the plant tissue composed of conducting tubes of xyle ...
... in trees and other woody plants • Epidermis – the outermost tissue layer • Cuticle – waxy, waterproof coating secreted by epidermal cells • Stomata – (singular - stoma) the pores on plant surfaces that function in gas exchange • Vascular tissue – the plant tissue composed of conducting tubes of xyle ...
Plant Science
... and amino acids from their source (usually leaves or storage areas) to the ‘sink’ (fruits, seeds, roots). • The source is where food is produced, this would be the leaves. They produce glucose which is then converted to sucrose which enter the phloem. This makes the water potential more negative mak ...
... and amino acids from their source (usually leaves or storage areas) to the ‘sink’ (fruits, seeds, roots). • The source is where food is produced, this would be the leaves. They produce glucose which is then converted to sucrose which enter the phloem. This makes the water potential more negative mak ...
L1.b
... This is not meant to be printed off and given as a test…this document is to give you ideas of how this standard might be assessed. Please use these as an example when you are developing your own formative assessments. Remember formative assessment is to be given throughout the teaching of a standard ...
... This is not meant to be printed off and given as a test…this document is to give you ideas of how this standard might be assessed. Please use these as an example when you are developing your own formative assessments. Remember formative assessment is to be given throughout the teaching of a standard ...
Parrotfeather - Whatcom County
... State, it is no longer legal to purchase this plant. The first record of an escaped population of parrotfeather in Whatcom County was recorded in 2004. DESCRIPTION: Parrotfeather is an aquatic perennial. It grows best when rooted in shallow water, but can also grow as a floating plant in deeper wate ...
... State, it is no longer legal to purchase this plant. The first record of an escaped population of parrotfeather in Whatcom County was recorded in 2004. DESCRIPTION: Parrotfeather is an aquatic perennial. It grows best when rooted in shallow water, but can also grow as a floating plant in deeper wate ...
Anthurium Plant - Green Thumbs Plant Care
... is insufficient light, flower production slows down and leaves stretch toward the light. Water Water an Anthurium well and then allow the top two or three inches of soil to dry out before watering again. Over-watering causes yellow leaf tips, under- watering causes brown leaf tips. Fertilizer Use a ...
... is insufficient light, flower production slows down and leaves stretch toward the light. Water Water an Anthurium well and then allow the top two or three inches of soil to dry out before watering again. Over-watering causes yellow leaf tips, under- watering causes brown leaf tips. Fertilizer Use a ...
poisonous plants - Humber Nurseries Ltd.
... By this definition, the effects of poisonous plants can range from mild skin irritation to death. Contact with poison ivy, for example, may cause irritation while the ingestion of Ricin, the principal toxin in the Castor Bean, even in minute quantities, will cause death. There are many types of harm ...
... By this definition, the effects of poisonous plants can range from mild skin irritation to death. Contact with poison ivy, for example, may cause irritation while the ingestion of Ricin, the principal toxin in the Castor Bean, even in minute quantities, will cause death. There are many types of harm ...
Interiorscaping - Metropolitan Community College
... Swedish Ivy Plectranthus australis White or purple variegation type available 6-8 inches tall White flowers Mint family Native to Australia ...
... Swedish Ivy Plectranthus australis White or purple variegation type available 6-8 inches tall White flowers Mint family Native to Australia ...
Plants Review
... structures and functions, veins, cuticle p287 Photosynthesis (mesophyll) Stomata & gas exchange Compare monocot and dicot Transport in plants (see notes) Water transport- xylem, dead cells Capillarity- water climbs small tubes Transpiration-cohesion theory o -evaporation, photosynthesi ...
... structures and functions, veins, cuticle p287 Photosynthesis (mesophyll) Stomata & gas exchange Compare monocot and dicot Transport in plants (see notes) Water transport- xylem, dead cells Capillarity- water climbs small tubes Transpiration-cohesion theory o -evaporation, photosynthesi ...
An Introduction to Potentially Invasive
... arrangement. It produces a black berry that is readily consumed by birds. The seed passes through their digestive system, resulting in the plants establishing almost anywhere, and crowding out more desirable native plantings or disrupting the natural ecosystem. ...
... arrangement. It produces a black berry that is readily consumed by birds. The seed passes through their digestive system, resulting in the plants establishing almost anywhere, and crowding out more desirable native plantings or disrupting the natural ecosystem. ...
unit two: plants (2)
... plants can also build up chlorophyll in the light and so any leaves which develop in the dark are yellow and cannot produce carbohydrates. 4 Oxygen is released during photosynthesis and the process may be set out as follows: Carbon dioxide + water + energy NCO2 ...
... plants can also build up chlorophyll in the light and so any leaves which develop in the dark are yellow and cannot produce carbohydrates. 4 Oxygen is released during photosynthesis and the process may be set out as follows: Carbon dioxide + water + energy NCO2 ...
File
... Water in the plant carries food/nutrients directly from cell to cell. Because of this, they can’t grow tall. Since their small, they can absorb enough water to carry throughout the plants. ...
... Water in the plant carries food/nutrients directly from cell to cell. Because of this, they can’t grow tall. Since their small, they can absorb enough water to carry throughout the plants. ...
Study Sheet 4-A
... Could there be any affect on reduced genetic variability due to the use of genetically modified crops? Yes, much of the plant transformation technology is linked to proprietary ownership be a few large chemical and Biotechnology companies. There is a general trend to have mono-genotypic crops where ...
... Could there be any affect on reduced genetic variability due to the use of genetically modified crops? Yes, much of the plant transformation technology is linked to proprietary ownership be a few large chemical and Biotechnology companies. There is a general trend to have mono-genotypic crops where ...
Plant nutrition
.jpg?width=300)
Plant nutrition is the study of the chemical elements and compounds that are necessary for plant growth, and also of their external supply and internal metabolism. In 1972, E. Epstein defined two criteria for an element to be essential for plant growth: in its absence the plant is unable to complete a normal life cycle; or that the element is part of some essential plant constituent or metabolite.This is in accordance with Liebig's law of the minimum. There are 14 essential plant nutrients. Carbon and oxygen are absorbed from the air, while other nutrients including water are typically obtained from the soil (exceptions include some parasitic or carnivorous plants).Plants must obtain the following mineral nutrients from the growing media: the primary macronutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K) the three secondary macronutrients: calcium (Ca), sulfur (S), magnesium (Mg) the micronutrients/trace minerals: boron (B), chlorine (Cl), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), nickel (Ni)The macronutrients are consumed in larger quantities and are present in plant tissue in quantities from 0.2% to 4.0% (on a dry matter weight basis). Micro nutrients are present in plant tissue in quantities measured in parts per million, ranging from 5 to 200 ppm, or less than 0.02% dry weight.Most soil conditions across the world can provide plants with adequate nutrition and do not require fertilizer for a complete life cycle. However, humans can artificially modify soil through the addition of fertilizer to promote vigorous growth and increase yield. The plants are able to obtain their required nutrients from the fertilizer added to the soil. A colloidal carbonaceous residue, known as humus, can serve as a nutrient reservoir. Even with adequate water and sunshine, nutrient deficiency can limit growth.Nutrient uptake from the soil is achieved by cation exchange, where root hairs pump hydrogen ions (H+) into the soil through proton pumps. These hydrogen ions displace cations attached to negatively charged soil particles so that the cations are available for uptake by the root.Plant nutrition is a difficult subject to understand completely, partly because of the variation between different plants and even between different species or individuals of a given clone. An element present at a low level may cause deficiency symptoms, while the same element at a higher level may cause toxicity. Further, deficiency of one element may present as symptoms of toxicity from another element. An abundance of one nutrient may cause a deficiency of another nutrient. For example, lower availability of a given nutrient such as SO42− can affect the uptake of another nutrient, such as NO3−. As another example, K+ uptake can be influenced by the amount of NH4+ available.The root, especially the root hair, is the most essential organ for the uptake of nutrients. The structure and architecture of the root can alter the rate of nutrient uptake. Nutrient ions are transported to the center of the root, the stele in order for the nutrients to reach the conducting tissues, xylem and phloem. The Casparian strip, a cell wall outside the stele but within the root, prevents passive flow of water and nutrients, helping to regulate the uptake of nutrients and water. Xylem moves water and inorganic molecules within the plant and phloem accounts for organic molecule transportation. Water potential plays a key role in a plants nutrient uptake. If the water potential is more negative within the plant than the surrounding soils, the nutrients will move from the region of higher solute concentration—in the soil—to the area of lower solute concentration: in the plant.There are three fundamental ways plants uptake nutrients through the root: simple diffusion, occurs when a nonpolar molecule, such as O2, CO2, and NH3 follows a concentration gradient, moving passively through the cell lipid bilayer membrane without the use of transport proteins. facilitated diffusion, is the rapid movement of solutes or ions following a concentration gradient, facilitated by transport proteins. Active transport, is the uptake by cells of ions or molecules against a concentration gradient; this requires an energy source, usually ATP, to power molecular pumps that move the ions or molecules through the membrane. Nutrients are moved inside a plant to where they are most needed. For example, a plant will try to supply more nutrients to its younger leaves than to its older ones. When nutrients are mobile, symptoms of any deficiency become apparent first on the older leaves. However, not all nutrients are equally mobile. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are mobile nutrients, while the others have varying degrees of mobility. When a less mobile nutrient is deficient, the younger leaves suffer because the nutrient does not move up to them but stays in the older leaves. This phenomenon is helpful in determining which nutrients a plant may be lacking.Many plants engage in symbiosis with microorganisms. Two important types of these relationship are with bacteria such as rhizobia, that carry out biological nitrogen fixation, in which atmospheric nitrogen (N2) is converted into ammonium (NH4); and with mycorrhizal fungi, which through their association with the plant roots help to create a larger effective root surface area. Both of these mutualistic relationships enhance nutrient uptake. Though nitrogen is plentiful in the Earth's atmosphere, relatively few plants harbor nitrogen fixing bacteria, so most plants rely on nitrogen compounds present in the soil to support their growth. These can be supplied by mineralization of soil organic matter or added plant residues, nitrogen fixing bacteria, animal waste, or through the application of fertilizers.Hydroponics, is a method for growing plants in a water-nutrient solution without the use of nutrient-rich soil. It allows researchers and home gardeners to grow their plants in a controlled environment. The most common solution, is the Hoagland solution, developed by D. R. Hoagland in 1933, the solution consists of all the essential nutrients in the correct proportions necessary for most plant growth. An aerator is used to prevent an anoxic event or hypoxia. Hypoxia can affect nutrient uptake of a plant because without oxygen present, respiration becomes inhibited within the root cells. The Nutrient film technique is a variation of hydroponic technique. The roots are not fully submerged, which allows for adequate aeration of the roots, while a ""film"" thin layer of nutrient rich water is pumped through the system to provide nutrients and water to the plant.