File
... • Process in which pollen is spread • Plants can be self-pollinated or cross-pollinated – Wind, insects, & animals can all help pollinate ...
... • Process in which pollen is spread • Plants can be self-pollinated or cross-pollinated – Wind, insects, & animals can all help pollinate ...
Kingdom Plantae The Diversity of Plants - Biology102-104
... Conserve water (vessels that transport water and nutrients to all parts of the plant) Dispersal of gametes and zygotes independent of water ...
... Conserve water (vessels that transport water and nutrients to all parts of the plant) Dispersal of gametes and zygotes independent of water ...
Kingdom Plantae : “Plants”... - nonmotile eukaryotic, multicellular
... when pollen is made in the spring, some grains land next to an archegonium...it makes a pollen tube into it, sperm cells use this tube to reach the ovum. Seeds are formed after this fertilization. Male cones disintegrate, female cones stay on the tree...maturing a season or two. ...
... when pollen is made in the spring, some grains land next to an archegonium...it makes a pollen tube into it, sperm cells use this tube to reach the ovum. Seeds are formed after this fertilization. Male cones disintegrate, female cones stay on the tree...maturing a season or two. ...
sexual reproduction in flowering plants
... Sexual reproduction in flowering plants What you must be able to do: You need to be able to name all the parts of a flower (find different pictures of flowers on the internet to practice). You need to be able to label all the parts of a seed / bean What develops from the ovule, ovary and egg cell ...
... Sexual reproduction in flowering plants What you must be able to do: You need to be able to name all the parts of a flower (find different pictures of flowers on the internet to practice). You need to be able to label all the parts of a seed / bean What develops from the ovule, ovary and egg cell ...
21 - Deepwater.org
... 29. In what ways are all protists alike? a. They are all multicellular b. They are all photosynthetic. c. They are all marine. d. They are all nonparasitic e. They are all eukaryotic. ...
... 29. In what ways are all protists alike? a. They are all multicellular b. They are all photosynthetic. c. They are all marine. d. They are all nonparasitic e. They are all eukaryotic. ...
Sexual Asexual Reproduction
... • An insect or the wind carries pollen grains from the anther of another flower. • The pollen grains land on the stigma and a pollen tube grows down through the style to the ovary. • The nucleus of the pollen grain passes down the tube. It fertilizes the egg cell inside the ovule. • The fertilized e ...
... • An insect or the wind carries pollen grains from the anther of another flower. • The pollen grains land on the stigma and a pollen tube grows down through the style to the ovary. • The nucleus of the pollen grain passes down the tube. It fertilizes the egg cell inside the ovule. • The fertilized e ...
PLANTS - MrsRyan
... Must keep gametes from drying out. Gametangia – jacket surrounding moist ...
... Must keep gametes from drying out. Gametangia – jacket surrounding moist ...
22-4 Seed Plants
... Reproduction Free From Water Seed plants have life cycles that alternate between a gametophyte stage and a sporophyte stage. They do not need water for fertilization of gametes. Adaptations that allow seeds plants to reproduce without water include: 1.________________________________________________ ...
... Reproduction Free From Water Seed plants have life cycles that alternate between a gametophyte stage and a sporophyte stage. They do not need water for fertilization of gametes. Adaptations that allow seeds plants to reproduce without water include: 1.________________________________________________ ...
Worksheet for grade 12 biology REPRODUCTION IN ORGANISMS
... 6. Juvenile Phase: It is the period of growth before maturity when sex organs are not functional. 7. Meiocytes: These are specialized cells of diploid organisms which undergo meiosis. 8. Pericarp: It is the protective covering of fruit, may be divided into epicarp, mesocarp and endocarp. Parthenogen ...
... 6. Juvenile Phase: It is the period of growth before maturity when sex organs are not functional. 7. Meiocytes: These are specialized cells of diploid organisms which undergo meiosis. 8. Pericarp: It is the protective covering of fruit, may be divided into epicarp, mesocarp and endocarp. Parthenogen ...
Colorado AgriScience Plant Science
... • Known as plant cloning • Leaves, stem, or roots may be used to grow a new plant • Occurs naturally and artificially • Produces a genetically identical plant ...
... • Known as plant cloning • Leaves, stem, or roots may be used to grow a new plant • Occurs naturally and artificially • Produces a genetically identical plant ...
Types of Reproduction sexual reproduction involve two parents
... asexual reproduction involves one parent who produces a diploid gamete which will develop into an adult (an exact copy) ...
... asexual reproduction involves one parent who produces a diploid gamete which will develop into an adult (an exact copy) ...
Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants Study Guide List five
... Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants Study Guide ...
... Plant Diversity II: The Evolution of Seed Plants Study Guide ...
Plant Diversity
... Charophytes are the green algae most closely related to land plants 4 main groups of land plants : ...
... Charophytes are the green algae most closely related to land plants 4 main groups of land plants : ...
Quiz 8.doc
... 1. Examples of non-vascular plants are a. ferns b. conifers c. flowering plants d. mosses and liverworts e. none of the above 2. Plant adaptations to life on land include all of these, except: a. chlorophyl b. cuticle , cork and bark c. stomata d. lignin e. xylem and phloem 3. The green, leaflike st ...
... 1. Examples of non-vascular plants are a. ferns b. conifers c. flowering plants d. mosses and liverworts e. none of the above 2. Plant adaptations to life on land include all of these, except: a. chlorophyl b. cuticle , cork and bark c. stomata d. lignin e. xylem and phloem 3. The green, leaflike st ...
chapter 25-2 - mshernandezscience
... c. Once together they form a sporophyte, which can then continue its life cycle. ...
... c. Once together they form a sporophyte, which can then continue its life cycle. ...
No Slide Title
... Seeds • Double Fertilization creates the zygote and the endosperm • The zygote divides to form an embryo • The endosperm divides and grows, storing nutrients for the embryo (oils, proteins, ...
... Seeds • Double Fertilization creates the zygote and the endosperm • The zygote divides to form an embryo • The endosperm divides and grows, storing nutrients for the embryo (oils, proteins, ...
Ch. 38 Plant reproduction and development
... Floral organs: sepals, petals, stamens (male ), carpels (female) •complete: all 4 floral organs •incomplete: lacking 1 or more floral organs •perfect: both stamens and carpels on 1 flower •imperfect: lacking either a stamen or carpel •monoecious: staminate and carpellate flowers on 1 plant) •dioecio ...
... Floral organs: sepals, petals, stamens (male ), carpels (female) •complete: all 4 floral organs •incomplete: lacking 1 or more floral organs •perfect: both stamens and carpels on 1 flower •imperfect: lacking either a stamen or carpel •monoecious: staminate and carpellate flowers on 1 plant) •dioecio ...
Plant Reproduction and Development
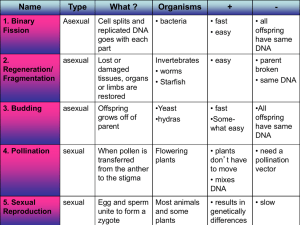
... Lost or Invertebrates damaged • worms tissues, organs • Starfish or limbs are restored ...
... Lost or Invertebrates damaged • worms tissues, organs • Starfish or limbs are restored ...
Kingdom Plantae Introduction Questions
... 1. What is the cell wall of plants made of? (pg 551) 2. A spore producing plant is known as a _____________ (pg 552). 3. Name three examples of a bryophyte (pg 556). 4. Bryophytes lack true roots. Instead, they have _______, which are long a thin and help anchor them to the ground (pg 557). 5. Which ...
... 1. What is the cell wall of plants made of? (pg 551) 2. A spore producing plant is known as a _____________ (pg 552). 3. Name three examples of a bryophyte (pg 556). 4. Bryophytes lack true roots. Instead, they have _______, which are long a thin and help anchor them to the ground (pg 557). 5. Which ...
Reproduction of Seed Plants - Science Class: Mrs. Boulougouras
... ovule of a flowering plant • If fertilized, a zygote will form and grow into a new sporophyte plant ...
... ovule of a flowering plant • If fertilized, a zygote will form and grow into a new sporophyte plant ...
BIOLOGY –Practice Test Plants MR. SECHRENGOST MATCHING
... 21. Cross pollination requires one plant to occur. 22. A vegetable is defined as a mature ovary 23. Dogs may help in pollination as they feed on nectar. 24. Ovules are located at the top of filaments. 25. Ferns contain seeds that are enclosed in sori. 26. Asexual reproduction gives genetically diffe ...
... 21. Cross pollination requires one plant to occur. 22. A vegetable is defined as a mature ovary 23. Dogs may help in pollination as they feed on nectar. 24. Ovules are located at the top of filaments. 25. Ferns contain seeds that are enclosed in sori. 26. Asexual reproduction gives genetically diffe ...
Asexual Reproduction
... Spore able to survive for weeks (even years) through drought, heat, even radiation ...
... Spore able to survive for weeks (even years) through drought, heat, even radiation ...
Flowering Plants (Angiosperms)
... Plants have both a haploid and diploid phase of reproduction, which are both multi-cellular. In the life cycle of a plant, they go back and forth between these two phases. This is called alternation of generations. The two phases of reproduction are called the sporophyte and the gametophyte. • In no ...
... Plants have both a haploid and diploid phase of reproduction, which are both multi-cellular. In the life cycle of a plant, they go back and forth between these two phases. This is called alternation of generations. The two phases of reproduction are called the sporophyte and the gametophyte. • In no ...
10.4 Plant Reproduction
... 1st Year: The plant germinates and grows roots, short stems and leaves 2nd Year: The stems lengthen, new leaves grow, flowers and seeds are produced Ex: Parsley, Celery, and foxglove ...
... 1st Year: The plant germinates and grows roots, short stems and leaves 2nd Year: The stems lengthen, new leaves grow, flowers and seeds are produced Ex: Parsley, Celery, and foxglove ...
Plant reproduction

Plant reproduction is the production of new individuals or offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parents. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plants and each other, except when mutations occur. In seed plants, the offspring can be packaged in a protective seed, which is used as an agent of dispersal.