
Document
... • To identify and explain the 3 different structures of neurons. • To compare and contrast sensory, motor, and interneurons and explain a general pathway. • To determine the functions of the 5 types of neuroglia. ...
... • To identify and explain the 3 different structures of neurons. • To compare and contrast sensory, motor, and interneurons and explain a general pathway. • To determine the functions of the 5 types of neuroglia. ...
Nervous System and Senses - Avon Community School Corporation
... When an action potential reaches the end of an axon, Ca channels in the neuron open Ca rushes in and cause the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the cell membrane and release the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft After binding, neurotransmitters will either be destroyed in the synaptic cle ...
... When an action potential reaches the end of an axon, Ca channels in the neuron open Ca rushes in and cause the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the cell membrane and release the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft After binding, neurotransmitters will either be destroyed in the synaptic cle ...
nerve net
... • The fatty insulation covering produced by the Schwann cells. • Nodes of Ranvier – Area of no myelin ...
... • The fatty insulation covering produced by the Schwann cells. • Nodes of Ranvier – Area of no myelin ...
Central Nervous System
... Columns of gray running the length of the spinal cord Posterior (dorsal) horns (cell bodies of interneurons) Anterior (ventral) horns (cell bodies of motor neurons) Lateral horns in thoracic and superior lumbar cord ...
... Columns of gray running the length of the spinal cord Posterior (dorsal) horns (cell bodies of interneurons) Anterior (ventral) horns (cell bodies of motor neurons) Lateral horns in thoracic and superior lumbar cord ...
Textbook PowerPoint
... Relative Refractory Period Neuron would only respond to very strong impulse ...
... Relative Refractory Period Neuron would only respond to very strong impulse ...
013368718X_CH31_483-498.indd
... Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system collects information about the body’s internal and external environment, processes that information, and responds to it. The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves and supporting cells. It collects information about the body’s internal and ext ...
... Functions of the Nervous System The nervous system collects information about the body’s internal and external environment, processes that information, and responds to it. The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves and supporting cells. It collects information about the body’s internal and ext ...
Central nervous system
... Efferent neurons convey information from the central nervous system out to effector cells (particularly muscle or gland cells or other neurons). ...
... Efferent neurons convey information from the central nervous system out to effector cells (particularly muscle or gland cells or other neurons). ...
Axons break in animals lacking β-spectrin
... vertebrate peripheral nervous system, axons are exposed to strains generated by length changes during movement (Phillips et al., 2004). Strain has also been proposed to assist in wiring the central nervous system (Van Essen, 1997) and to underlie axon extension in response to growth cone migration ( ...
... vertebrate peripheral nervous system, axons are exposed to strains generated by length changes during movement (Phillips et al., 2004). Strain has also been proposed to assist in wiring the central nervous system (Van Essen, 1997) and to underlie axon extension in response to growth cone migration ( ...
The Central Nervous System CNS
... called nodes of Ranvier. • Collectively, the Schwann cells make up the myelin sheath (numbers of which side-by-side form white ...
... called nodes of Ranvier. • Collectively, the Schwann cells make up the myelin sheath (numbers of which side-by-side form white ...
14-Taste & Smell
... ciliated, nerve cells. They are not present all over the nasal mucosa , but present only in a small , 5 cm2 , yellowish-pigmented part of it called olfactory epithelium ( or olfactory mucous membrane ) This olfactory epithelium is located at the roof of the nasal cavity near the septum . Sniffing , ...
... ciliated, nerve cells. They are not present all over the nasal mucosa , but present only in a small , 5 cm2 , yellowish-pigmented part of it called olfactory epithelium ( or olfactory mucous membrane ) This olfactory epithelium is located at the roof of the nasal cavity near the septum . Sniffing , ...
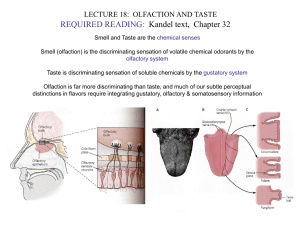
LECTURE18.Olfaction&Taste
... CHANGING ODORANT RECEPTOR EXPRESSED IN A NEURON CHANGES ITS PROJECTION ...
... CHANGING ODORANT RECEPTOR EXPRESSED IN A NEURON CHANGES ITS PROJECTION ...
Nervous System
... longer able to respond to the stimulus. C) The responding cell runs out of potassium and is no longer able to respond to the stimulus. D) The chemically gated ion channels of the receiving cell's membrane can only transport for a short period of time before they close. E) The neurotransmitter is bro ...
... longer able to respond to the stimulus. C) The responding cell runs out of potassium and is no longer able to respond to the stimulus. D) The chemically gated ion channels of the receiving cell's membrane can only transport for a short period of time before they close. E) The neurotransmitter is bro ...
Nervous System
... longer able to respond to the stimulus. C) The responding cell runs out of potassium and is no longer able to respond to the stimulus. D) The chemically gated ion channels of the receiving cell's membrane can only transport for a short period of time before they close. E) The neurotransmitter is bro ...
... longer able to respond to the stimulus. C) The responding cell runs out of potassium and is no longer able to respond to the stimulus. D) The chemically gated ion channels of the receiving cell's membrane can only transport for a short period of time before they close. E) The neurotransmitter is bro ...
4-Nervous system I: Structure and organization
... Harwood, P. 1963. Therapeutic dosage in small and large mammals . Science 139: 684-685. ...
... Harwood, P. 1963. Therapeutic dosage in small and large mammals . Science 139: 684-685. ...
Physiology 1B
... The point of contact at which impulses are passed from one cell to another are known as Synapse ...
... The point of contact at which impulses are passed from one cell to another are known as Synapse ...
Chapter 9 Senses - msubillings.edu
... these neurons extend up through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone, these axons help to form the olfactory nerve, and synapse with interneurons in the olfactory bulb which sends action potentials down the olfactory tract to the olfactory cortex located in the temporal and frontal lobes of the ...
... these neurons extend up through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone, these axons help to form the olfactory nerve, and synapse with interneurons in the olfactory bulb which sends action potentials down the olfactory tract to the olfactory cortex located in the temporal and frontal lobes of the ...
Understanding Perceptual Motor Function Building Better Robots
... • The visual cortex of babies is also partially developed. • These 3 drawings of neurons at different stages of development show that the dendritic trees and interconnections of neurons become increasingly complex over the first 6 months of life. ...
... • The visual cortex of babies is also partially developed. • These 3 drawings of neurons at different stages of development show that the dendritic trees and interconnections of neurons become increasingly complex over the first 6 months of life. ...
Modification of brain circuits as a result of experience
... increased. • Correlated activity between presynaptic and postsynaptic cells strengthens synaptic connections between them. • Cells that fire together, wire together. Also used in learning and memory, called long term potentiation (LTP). ...
... increased. • Correlated activity between presynaptic and postsynaptic cells strengthens synaptic connections between them. • Cells that fire together, wire together. Also used in learning and memory, called long term potentiation (LTP). ...
Lecture 12
... i. type Ia sensory fiber - in center ii. type II sensory fiber - at ends iii. gamma motor neurons - from ventral horn b. extrafusal fibers - outer muscle fibers i. alpha motor neurons - form ventral horn 3. Golgi (tendon) organs a. at junction of tendon and muscle 4. Joint Kinesthetic receptors a. w ...
... i. type Ia sensory fiber - in center ii. type II sensory fiber - at ends iii. gamma motor neurons - from ventral horn b. extrafusal fibers - outer muscle fibers i. alpha motor neurons - form ventral horn 3. Golgi (tendon) organs a. at junction of tendon and muscle 4. Joint Kinesthetic receptors a. w ...
File - Mr. Downing Biology 30
... Caption: Wearable computing. Male researcher using the prototype fingernail touch sensor he has developed. This affective computer detects each touch of the finger by the change it causes in the colour of the blood capillaries below the nail. Such a system could be used for buttonless controls, for ...
... Caption: Wearable computing. Male researcher using the prototype fingernail touch sensor he has developed. This affective computer detects each touch of the finger by the change it causes in the colour of the blood capillaries below the nail. Such a system could be used for buttonless controls, for ...
SBI4U Nervous System
... carries impulses towards the cell body • Axon: extension of the cytoplasm that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body • Myelin Sheath: insulated covering over the axon • Axon Terminal: contains synapses, specialized structures where neurotransmitter chemicals are released in order to communi ...
... carries impulses towards the cell body • Axon: extension of the cytoplasm that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body • Myelin Sheath: insulated covering over the axon • Axon Terminal: contains synapses, specialized structures where neurotransmitter chemicals are released in order to communi ...
Central Nervous System Control of Energy and Glucose
... The central nervous system (CNS) neuronal circuits integrate peripheral and central signals to appropriately regulate energy and glucose homeostasis. Serotonin 2C receptors (5-HT2CRs) expressed by the anorexigenic (appetite-suppressing) proopiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate ...
... The central nervous system (CNS) neuronal circuits integrate peripheral and central signals to appropriately regulate energy and glucose homeostasis. Serotonin 2C receptors (5-HT2CRs) expressed by the anorexigenic (appetite-suppressing) proopiomelanocortin (POMC) neurons in the hypothalamic arcuate ...
PDF
... Novel neuronal migration mode branches out Many migrating neurons and growing axons reach their correct targets during brain development by adjusting the growth of their leading process in response to guidance cues. Now, though, Martini and co-workers propose that the dynamic regulation of leading p ...
... Novel neuronal migration mode branches out Many migrating neurons and growing axons reach their correct targets during brain development by adjusting the growth of their leading process in response to guidance cues. Now, though, Martini and co-workers propose that the dynamic regulation of leading p ...














![Welcome [www.sciencea2z.com]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008568661_1-062fb6959798aae5bb439e7880889016-300x300.png)







