Biol 203 Lab Week 10 Nervous System Histology
... Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between successive Schwann cells along the length of the axon ...
... Nodes of Ranvier Gaps between successive Schwann cells along the length of the axon ...
Exam - McLoon Lab
... C. in the synaptic cleft for degradation of neurotransmitter. D. in the dendrite for response to activation of excitatory neurotransmitter receptors. E. in the soma for synthesis of neurotransmitter. 29. Cocaine can function by blocking … A. action potentials. B. neurotransmitter release. ...
... C. in the synaptic cleft for degradation of neurotransmitter. D. in the dendrite for response to activation of excitatory neurotransmitter receptors. E. in the soma for synthesis of neurotransmitter. 29. Cocaine can function by blocking … A. action potentials. B. neurotransmitter release. ...
first ten slides
... stick out from the cell body Dendrites receive impulses or messages from other neurons and send them to the cell body ...
... stick out from the cell body Dendrites receive impulses or messages from other neurons and send them to the cell body ...
The Nervous System - chemistrywithmrsmorton
... Cell body – contains nucleus; metabolic center Dendrite – fiber that conveys messages toward cell body Axon – conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body Axon terminals – end of axon; contain neurotransmitters & release them Synaptic cleft/synapse – gap between neurons ...
... Cell body – contains nucleus; metabolic center Dendrite – fiber that conveys messages toward cell body Axon – conduct nerve impulses away from the cell body Axon terminals – end of axon; contain neurotransmitters & release them Synaptic cleft/synapse – gap between neurons ...
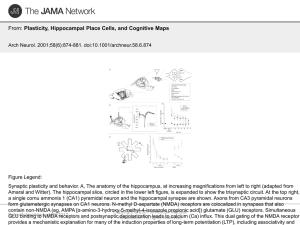
Plasticity, Hippocampal Place Cells, and Cognitive Maps
... (Ca) influx. This dual gating of the NMDA receptor All rights reserved. provides a mechanistic explanation for many of the induction properties of long-term potentiation (LTP), including associativity and ...
... (Ca) influx. This dual gating of the NMDA receptor All rights reserved. provides a mechanistic explanation for many of the induction properties of long-term potentiation (LTP), including associativity and ...
FINAL LECTURE EXAM – HUMAN ANATOMY
... 3. Which of the following about gray rami is FALSE? a. They carry preganglionic neurons from the anterior rami to trunk ganglia. b. They contain only sympathetic nerve fibers. c. They carry impulses from sympathetic trunk ganglia to spinal nerves. d. They are located at all levels of the vertebral c ...
... 3. Which of the following about gray rami is FALSE? a. They carry preganglionic neurons from the anterior rami to trunk ganglia. b. They contain only sympathetic nerve fibers. c. They carry impulses from sympathetic trunk ganglia to spinal nerves. d. They are located at all levels of the vertebral c ...
The Nervous System
... • Center: Collection of neurons with a shared function • Nucleus: A center with a discrete anatomical boundary • Neural cortex – gray matter covering of brain portions • White matter - Bundles of axons (tracts) that share origins, destinations, and functions, tracts in the spinal cord form larger gr ...
... • Center: Collection of neurons with a shared function • Nucleus: A center with a discrete anatomical boundary • Neural cortex – gray matter covering of brain portions • White matter - Bundles of axons (tracts) that share origins, destinations, and functions, tracts in the spinal cord form larger gr ...
Nervous System
... serotonin, dopamine, and gammaaminobutyric acid (GABA). Most are exciteatory in some places and inhibitory in others. ...
... serotonin, dopamine, and gammaaminobutyric acid (GABA). Most are exciteatory in some places and inhibitory in others. ...
Nervous System - Academic Computer Center
... There are two main types of neurotransmitter receptors: channel-linked receptors mediate direct transmitter action and result in brief, localized changes; and G proteinlinked receptors mediate indirect transmitter action resulting in slow, persistent, and often diffuse changes. ...
... There are two main types of neurotransmitter receptors: channel-linked receptors mediate direct transmitter action and result in brief, localized changes; and G proteinlinked receptors mediate indirect transmitter action resulting in slow, persistent, and often diffuse changes. ...
nerve slide show
... • Glia cells DO NOT carry nerve impulses (without glia, the neurons would not work) • Function; 1) clean up brain "debris"; 2) transport nutrients to neurons; 3) hold neurons in place; 4) digest parts of dead neurons; 5) regulate content of extracellular space 6) insulate and support neurons ...
... • Glia cells DO NOT carry nerve impulses (without glia, the neurons would not work) • Function; 1) clean up brain "debris"; 2) transport nutrients to neurons; 3) hold neurons in place; 4) digest parts of dead neurons; 5) regulate content of extracellular space 6) insulate and support neurons ...
General design of the nervous system
... among others. The ANS is divided into two systems – the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Sympathetic nervous system: Fight or flight – will prepare for an emergency, such as being chased by a lion. Heart beats faster, contraction of arteries, increase in blood pressure. Parasympathet ...
... among others. The ANS is divided into two systems – the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Sympathetic nervous system: Fight or flight – will prepare for an emergency, such as being chased by a lion. Heart beats faster, contraction of arteries, increase in blood pressure. Parasympathet ...
Cell body
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons. • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...
... Schwann cells - supporting cells of the PNS that myelinate axons. • Myelin sheath – whitish lipoprotein that surrounds and insulates the axon (nerve fiber) • Neurilemma - external layer containing bulk of cytoplasm with nucleus and organelles Schwann cell ...
Nervous System Notes
... How a Nerve Impulse Travels • Nerve impulses can travels as fast as 120 meters per second! THAT’S FAST! • Messages travel from the Cell Body, down the axon, and to the axon tips! ...
... How a Nerve Impulse Travels • Nerve impulses can travels as fast as 120 meters per second! THAT’S FAST! • Messages travel from the Cell Body, down the axon, and to the axon tips! ...
Neuron and Neuroglial Review Worksheet
... provided in Column A. Place the correct term or letter response in the answer blanks. Column A 1. Releases neurotransmitters ____B_____ 2. Conducts electrical currents ___C_____ towards the cell body 3. Increases the speed of impulse ____D_____ transmission 4. Location of the nucleus _____E_______ 5 ...
... provided in Column A. Place the correct term or letter response in the answer blanks. Column A 1. Releases neurotransmitters ____B_____ 2. Conducts electrical currents ___C_____ towards the cell body 3. Increases the speed of impulse ____D_____ transmission 4. Location of the nucleus _____E_______ 5 ...
Auditory (Cochlear) System
... trapezoid body (both these centers contain 3rd order neurons). Unilateral lesions in the auditory nerve or cochlear nuclei ...
... trapezoid body (both these centers contain 3rd order neurons). Unilateral lesions in the auditory nerve or cochlear nuclei ...
Nociceptive sensation. Somatic sensory analyzer
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
... glucose and cuprum level in plasma, activation of hemostasis. • It considered to cause the majority of both visceral and biochemical reactions by excitation of sympathetic nervous system, which is presented by neurons of hypothalamus, hypophisis and cells in medullar substance of adrenal glands. ...
Somatosensory 2
... The sensation of pain is caused by activation of very small diameter nerve endings. When tissue is damaged, chemical substances are released that stimulate these fibers. Some stimuli that activate nociceptors: Thermal: high heat or extreme cold Mechanical: Intense mechanical stimuli Chemical: Irrita ...
... The sensation of pain is caused by activation of very small diameter nerve endings. When tissue is damaged, chemical substances are released that stimulate these fibers. Some stimuli that activate nociceptors: Thermal: high heat or extreme cold Mechanical: Intense mechanical stimuli Chemical: Irrita ...
PPT and questions for class today.
... • Action Potential – neuron fires down length of axon; called a neural impulse ...
... • Action Potential – neuron fires down length of axon; called a neural impulse ...
Review 3 ____ 1. The cells that provide structural support and
... 35. Imagine that a picture of a spoon is briefly flashed in the left visual field of an individual with a severed corpus callosum. At the same time, a picture of a cup is briefly flashed in the right visual field. Based on Roger Sperry's work with split-brain patients, you could predict that this in ...
... 35. Imagine that a picture of a spoon is briefly flashed in the left visual field of an individual with a severed corpus callosum. At the same time, a picture of a cup is briefly flashed in the right visual field. Based on Roger Sperry's work with split-brain patients, you could predict that this in ...
SCRIPT: Human Eye: Retina. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v
... colors, only rods are present around the periphery of the retina. Hence, rods are responsible for peripheral vision. Cones: cones are photoreceptors specialized for detecting different colors that is different wavelengths of light. However, they do not function under low-light conditions. Only cones ...
... colors, only rods are present around the periphery of the retina. Hence, rods are responsible for peripheral vision. Cones: cones are photoreceptors specialized for detecting different colors that is different wavelengths of light. However, they do not function under low-light conditions. Only cones ...
Chp3 Weiten - Napa Valley College
... seeing another monkey or person perform the same action. Mirror neurons appear to provide a new model for understanding complex social cognition at a neural level. New findings suggest mirror neurons may play a fundamental role in the acquisition of new motor skills ...
... seeing another monkey or person perform the same action. Mirror neurons appear to provide a new model for understanding complex social cognition at a neural level. New findings suggest mirror neurons may play a fundamental role in the acquisition of new motor skills ...
news release - Institut de recherches cliniques de Montréal
... many scientists around the world trying to unearth our nervous system’s countless mysteries. Dr. Artur Kania, Director of the IRCM’s Neural Circuit Development research unit, and a postdoctoral fellow in his laboratory, Dr. Tzu-Jen Kao, recently uncovered a new piece of the puzzle. Scientists studyi ...
... many scientists around the world trying to unearth our nervous system’s countless mysteries. Dr. Artur Kania, Director of the IRCM’s Neural Circuit Development research unit, and a postdoctoral fellow in his laboratory, Dr. Tzu-Jen Kao, recently uncovered a new piece of the puzzle. Scientists studyi ...
Here we can focus directly on the input neurons, the Schaffer
... Here we can focus directly on the input neurons, the Schaffer collaterals ending on the CA1 pyramidal cells. We now see on the right hand side this is the whole synaptic cell, notice we are now focusing on the post-synaptic cell. The early change for explicit memory storage is going to have a pul ...
... Here we can focus directly on the input neurons, the Schaffer collaterals ending on the CA1 pyramidal cells. We now see on the right hand side this is the whole synaptic cell, notice we are now focusing on the post-synaptic cell. The early change for explicit memory storage is going to have a pul ...
sample exam - McLoon Lab
... C. Commissural axons would grow towards the floor plate, would cross, and then would likely recross at random intervals as they grow rostrally in the spinal cord. D. Commissural axons would grow towards the floor plate, would cross, and then would fail to grow further. E. No abnormalities would be e ...
... C. Commissural axons would grow towards the floor plate, would cross, and then would likely recross at random intervals as they grow rostrally in the spinal cord. D. Commissural axons would grow towards the floor plate, would cross, and then would fail to grow further. E. No abnormalities would be e ...