Query-Heart-failure
... LVEF less than 40% or a narrative description of left ventricular systolic (LVS) function consistent with moderate or severe systolic dysfunction. (ACC/AHA 2005 Guideline Update for the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Heart Failure in the Adult) ...
... LVEF less than 40% or a narrative description of left ventricular systolic (LVS) function consistent with moderate or severe systolic dysfunction. (ACC/AHA 2005 Guideline Update for the Diagnosis and Management of Chronic Heart Failure in the Adult) ...
Heart Failure Whistle Stop Talks
... ‘Many of the symptoms of HF are non-discriminating and, therefore, of limited diagnostic value. Many of the signs of HF result from sodium and water retention and resolve quickly with diuretic therapy, i.e. may be absent in patients receiving such treatment. Demonstration of an underlying cardiac ca ...
... ‘Many of the symptoms of HF are non-discriminating and, therefore, of limited diagnostic value. Many of the signs of HF result from sodium and water retention and resolve quickly with diuretic therapy, i.e. may be absent in patients receiving such treatment. Demonstration of an underlying cardiac ca ...
Perioperative management of pulmonary atresia with intact
... pulmonary regurgitation,[3] leading to right ventricular dilatation, dysfunction and tricuspid annular dilatation with tricuspid regurgitation, carrying a high risk of developing significant hemodynamic instability. Maintaining sinus rhythm and atrioventricular synchrony is especially important in t ...
... pulmonary regurgitation,[3] leading to right ventricular dilatation, dysfunction and tricuspid annular dilatation with tricuspid regurgitation, carrying a high risk of developing significant hemodynamic instability. Maintaining sinus rhythm and atrioventricular synchrony is especially important in t ...
Chemotherapy Induced Cardiac Toxicity
... – Has been studied most extensively and has demonstrated the most significant reductions in heart problems – Has shown a similar anticancer effect to doxorubicin, but with less cardiac toxicity ...
... – Has been studied most extensively and has demonstrated the most significant reductions in heart problems – Has shown a similar anticancer effect to doxorubicin, but with less cardiac toxicity ...
invasive hemodynamic monitoring
... Measure the PCWP at end expiration PCWP should not be higher than PA diastolic PCWP is an indirect measurement of left ventricular end ...
... Measure the PCWP at end expiration PCWP should not be higher than PA diastolic PCWP is an indirect measurement of left ventricular end ...
Papillary fibroelastoma of the mitral valve: a rare cause of
... tumours of the endocardium that most commonly are found on the aortic or mitral valve.' They are a few millimetres to some centimetres in diameter and look like sea anemones (fig). Most are found coincidentally at necropsy but a few cause patients to present with systemic emboli derived from detache ...
... tumours of the endocardium that most commonly are found on the aortic or mitral valve.' They are a few millimetres to some centimetres in diameter and look like sea anemones (fig). Most are found coincidentally at necropsy but a few cause patients to present with systemic emboli derived from detache ...
Slide 1
... – Has been studied most extensively and has demonstrated the most significant reductions in heart problems – Has shown a similar anticancer effect to doxorubicin, but with less cardiac toxicity ...
... – Has been studied most extensively and has demonstrated the most significant reductions in heart problems – Has shown a similar anticancer effect to doxorubicin, but with less cardiac toxicity ...
File
... What is the valve that blood passes through from the left atrium into the left ventricle and prevents blood from flowing back into the left atrium from the ventricle? ...
... What is the valve that blood passes through from the left atrium into the left ventricle and prevents blood from flowing back into the left atrium from the ventricle? ...
parasympathomimetic stimulation provokes vagally
... We included three female patients with symptomatic PVC’s with left bundle branch block morphology and vertical axis (right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) origin). Previous ablation attempts failed because PVC’s were absent and could not be provoked by sympathetic stimulation (isoprenaline), atropi ...
... We included three female patients with symptomatic PVC’s with left bundle branch block morphology and vertical axis (right ventricular outflow tract (RVOT) origin). Previous ablation attempts failed because PVC’s were absent and could not be provoked by sympathetic stimulation (isoprenaline), atropi ...
File
... Cardiac output as the product of heart rate and stroke volume. Pressure and volume changes and associated valve movements during the cardiac cycle. Candidates should be able to analyse and interpret data relating to pressure and volume changes during the cardiac cycle. ...
... Cardiac output as the product of heart rate and stroke volume. Pressure and volume changes and associated valve movements during the cardiac cycle. Candidates should be able to analyse and interpret data relating to pressure and volume changes during the cardiac cycle. ...
CPR Facts and Statistics
... If bystander CPR is not provided, a sudden cardiac arrest victim’s chances of survival fall 7 percent to 10 percent for every minute of delay until defibrillation. Few attempts at resuscitation are successful if CPR and defibrillation are not provided within minutes of collapse. ...
... If bystander CPR is not provided, a sudden cardiac arrest victim’s chances of survival fall 7 percent to 10 percent for every minute of delay until defibrillation. Few attempts at resuscitation are successful if CPR and defibrillation are not provided within minutes of collapse. ...
Signal-Averaged Electrocardiography (SAECG)
... defibrillators (ICD) to promptly detect and terminate tachyarrhythmias when they occur. Because sudden cardiac death, whether from arrhythmias or pump failure, is one of the most common causes of death after a previous MI, there is intense interest in risk stratification to target therapy. The focus ...
... defibrillators (ICD) to promptly detect and terminate tachyarrhythmias when they occur. Because sudden cardiac death, whether from arrhythmias or pump failure, is one of the most common causes of death after a previous MI, there is intense interest in risk stratification to target therapy. The focus ...
Signature Assignment, Action Potential Graphing, Biology 232
... blood pressure); Spironolactone (a diuretic medication for fluid build-up related to heart failure): Lisinopril (look it up!) Physical examination: Martha's jugular veins were noticeably distended (JVD). Auscultation of the heart reveals a low-pitched, rumbling systolic murmur, heard best over the l ...
... blood pressure); Spironolactone (a diuretic medication for fluid build-up related to heart failure): Lisinopril (look it up!) Physical examination: Martha's jugular veins were noticeably distended (JVD). Auscultation of the heart reveals a low-pitched, rumbling systolic murmur, heard best over the l ...
Parent-Athlete Signature Form
... Information Sheet and Acknowledgement of Receipt and Review Form What is sudden cardiac arrest? Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is when the heart stops beating, suddenly and unexpectedly. When this happens, blood stops flowing to the brain and other vital organs. SCA doesn’t just happen to adults; it ta ...
... Information Sheet and Acknowledgement of Receipt and Review Form What is sudden cardiac arrest? Sudden cardiac arrest (SCA) is when the heart stops beating, suddenly and unexpectedly. When this happens, blood stops flowing to the brain and other vital organs. SCA doesn’t just happen to adults; it ta ...
Chapter 13
... all the way; this creates a clicking sound at the end of a contraction. •Heart Murmurs – valves do not close completely, causing an (often) harmless murmur sound. Sometimes holes can occur in the septum f the heart which can also cause a murmur ...
... all the way; this creates a clicking sound at the end of a contraction. •Heart Murmurs – valves do not close completely, causing an (often) harmless murmur sound. Sometimes holes can occur in the septum f the heart which can also cause a murmur ...
background - Medtronic
... ICDs are proven to be 98 percent effective in treating dangerous ventricular arrhythmias that can lead to sudden cardiac arrest.3, 4 Medtronic estimates more than 70,000 lives have been saved by implantable defibrillators over the past five years. 5 Implantation and Testing Implantation of an ...
... ICDs are proven to be 98 percent effective in treating dangerous ventricular arrhythmias that can lead to sudden cardiac arrest.3, 4 Medtronic estimates more than 70,000 lives have been saved by implantable defibrillators over the past five years. 5 Implantation and Testing Implantation of an ...
The most common cause of sudden cardiac death
... of sudden cardiac death in young athletes in America (4, 6). Inherited in an autosomal dominant, characterized by a high degree of penetrance genes, it is characterized by a distinct genetic heterogeneity, with more than 400 different mutations in any of the 11 different genes encoding protein synth ...
... of sudden cardiac death in young athletes in America (4, 6). Inherited in an autosomal dominant, characterized by a high degree of penetrance genes, it is characterized by a distinct genetic heterogeneity, with more than 400 different mutations in any of the 11 different genes encoding protein synth ...
Right Ventricular Arrhythmic Cardiomyopathy: an Update on
... familial disease in the boxer and appears to be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. Therefore, theoretically, there should not be any silent carriers. Unfortunately, the disease also appears to be a disease of variable genetic penetrance and affected dogs can have many different presentations ...
... familial disease in the boxer and appears to be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait. Therefore, theoretically, there should not be any silent carriers. Unfortunately, the disease also appears to be a disease of variable genetic penetrance and affected dogs can have many different presentations ...
Care of the Pediatric Patient with Cardiovascular Problems
... Figure 21–6 A young child with an uncorrected or partially corrected defect that reduces pulmonary blood flow may squat (assumes a knee–chest position) to reduce systemic blood flow return to the heart. ...
... Figure 21–6 A young child with an uncorrected or partially corrected defect that reduces pulmonary blood flow may squat (assumes a knee–chest position) to reduce systemic blood flow return to the heart. ...
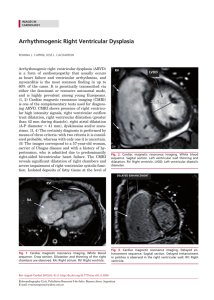
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
... is a form of cardiomyopathy that usually occurs as heart failure and ventricular arrhythmias, and myocarditis is the most common finding in up to 60% of the cases. It is genetically transmitted via either the dominant or recessive autosomal mode, and is highly prevalent among young Europeans. (1, 2) ...
... is a form of cardiomyopathy that usually occurs as heart failure and ventricular arrhythmias, and myocarditis is the most common finding in up to 60% of the cases. It is genetically transmitted via either the dominant or recessive autosomal mode, and is highly prevalent among young Europeans. (1, 2) ...
2013 - Dr. Dhiren Shah
... valve leaflets, the chordate tendineae, the papillary muscles, or the supporting left ventricular walls may lead to MR. The cause of MR in ischemic MR is due to (1) mitral annular dilatation, and/or (2) papillary muscle displacement. This process causes (1) leaflet malcoaptation, which is the failur ...
... valve leaflets, the chordate tendineae, the papillary muscles, or the supporting left ventricular walls may lead to MR. The cause of MR in ischemic MR is due to (1) mitral annular dilatation, and/or (2) papillary muscle displacement. This process causes (1) leaflet malcoaptation, which is the failur ...
Task 1. Baby of 2 months. Admitted to the hospital with presumptive
... kinase MB, troponin were normal. ECG: signs of left ventricular hypertrophy, and negative T waves in the left precordial leads, deep pathologic Q wave in II, III, V4-V6, frequent ventricular extrasystoles. Holter ECG: frequent ventricular extrasystoles, ventricular tachycardia. Echocardiography: the ...
... kinase MB, troponin were normal. ECG: signs of left ventricular hypertrophy, and negative T waves in the left precordial leads, deep pathologic Q wave in II, III, V4-V6, frequent ventricular extrasystoles. Holter ECG: frequent ventricular extrasystoles, ventricular tachycardia. Echocardiography: the ...
Tako-tsubo cardiomyopathy
... hemodynamic support is chosen, most patients only require it for a short time and typically demonstrate rapid clinical recovery. Prognosis In most patients, the left ventricular function returns to normal within two weeks. The ECG abnormalities usually disappear completely within six months [12]. Co ...
... hemodynamic support is chosen, most patients only require it for a short time and typically demonstrate rapid clinical recovery. Prognosis In most patients, the left ventricular function returns to normal within two weeks. The ECG abnormalities usually disappear completely within six months [12]. Co ...
081013.HEMODYNAMICS
... Normal Value 2-8 mm Hg Clinical Significance: Equivalent to central venous pressure. Abnormalities: Increased – Right ventricular failure, tricuspid valve abnormalities (stenosis or regurgitation), cardiac tamponade, right ventricular infarct, VSD with a left to right shunt. – Pulmonary stenosis, Po ...
... Normal Value 2-8 mm Hg Clinical Significance: Equivalent to central venous pressure. Abnormalities: Increased – Right ventricular failure, tricuspid valve abnormalities (stenosis or regurgitation), cardiac tamponade, right ventricular infarct, VSD with a left to right shunt. – Pulmonary stenosis, Po ...
hemodynamics - health120years.com
... Normal Value 2-8 mm Hg Clinical Significance: Equivalent to central venous pressure. Abnormalities: Increased – Right ventricular failure, tricuspid valve abnormalities (stenosis or regurgitation), cardiac tamponade, right ventricular infarct, VSD with a left to right shunt. – Pulmonary stenosis, Po ...
... Normal Value 2-8 mm Hg Clinical Significance: Equivalent to central venous pressure. Abnormalities: Increased – Right ventricular failure, tricuspid valve abnormalities (stenosis or regurgitation), cardiac tamponade, right ventricular infarct, VSD with a left to right shunt. – Pulmonary stenosis, Po ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) in which a portion of the myocardium is hypertrophied (thickened) without any obvious cause, creating functional impairment of the cardiac muscle. It is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.The occurrence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden unexpected cardiac death in any age group and as a cause of disabling cardiac symptoms. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.HCM is frequently asymptomatic until sudden cardiac death, and for this reason some suggest routinely screening certain populations for this disease.A cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the muscle of the heart. With HCM, the myocytes (cardiac contractile cells) in the heart increase in size, which results in the thickening of the heart muscle. In addition, the normal alignment of muscle cells is disrupted, a phenomenon known as myocardial disarray. HCM also causes disruptions of the electrical functions of the heart. HCM is most commonly due to a mutation in one of nine sarcomeric genes that results in a mutated protein in the sarcomere, the primary component of the myocyte (the muscle cell of the heart). These are predominantly single-point missense mutations in the genes for beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponinT, or tropomyosin. These mutations cause myofibril and myocyte structural abnormalities and possible deficiencies in force generation. Not to be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or any other cardiomyopathy.While most literature so far focuses on European, American, and Japanese populations, HCM appears in all ethnic groups. The prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population.